Local therapist
Ablyazov
Irshat Ravilevich
21 years of experience
Local therapist of the highest category. Member of the Russian Scientific Medical Society of Therapists.
Make an appointment
Thrombocytopenia is a separate disease or a symptom of another disease that is characterized by a low platelet count (less than 150,000 units per microliter). The condition is accompanied by high bleeding, as well as slow stopping of bleeding from small vessels.
Symptoms
Symptoms of thrombocytopenia include:
- Purpura. This is the name for hemorrhages in mucous tissues or skin. In fact, it looks like red spots - most often they can be seen in places of strong contact with clothing. The spots do not hurt, they can be pinpoint or quite extensive - including bruises of different colors (depending on the time of formation).
- Regular nosebleeds. Since small vessels are weakened, bleeding can begin due to a cold, sneezing, or minor injury. Bright red blood may flow for ten minutes or more, putting the patient at risk of losing a lot of blood.
- Bleeding gums, prolonged bleeding after tooth extraction. The mechanism is the same: due to weak blood vessels, the blood cannot stop quickly in case of small or large injuries.
- Bleeding of internal organs. For example, blood is found in the gastrointestinal tract, when the stool becomes colored, or in the genitourinary system - then the urine becomes colored. Both symptoms are very alarming and require immediate contact with specialists.
- Too heavy and long menstruation. Moreover, bleeding can be observed on other days of the cycle.
All of these symptoms may indicate other diseases - both concomitant with thrombocytopenia and independent. What complicates the situation is that there are a lot of reasons and mechanisms for the development of this condition. In medicine, there are several types of this disease.
Reasons for the increase
Primary thrombocytosis, when the number of blood platelets increases due to an increase in the number of megakaryocytes, includes myeloproliferative diseases, including:
- polycythemia;
- chronic myelosclerosis;
- thrombocythemia;
- myelofibrosis.
Elevated platelets in myeloproliferative diseases are found in the blood at the onset of the disease. In the advanced stage of the disease, the platelet count drops below normal.
The deviation in the number of blood platelets in primary thrombocytosis is manifested by both a slight excess of the norm and a sharp increase in indicators to an extreme degree of thrombocytosis, amounting to more than 1000 * 109/l.
Most often, an increase in platelets is secondary in nature, and develops against the background of an illness, or as a manifestation of a compensatory mechanism in response to physiological changes in the body.
Causes of secondary thrombocytosis
A secondary increase in platelets, which is a concomitant sign of diseases, is found in diseases:
- inflammatory in nature - tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, osteomyelitis, ulcerative colitis, enterocolitis, liver cirrhosis;
- chronic infectious diseases;
- autoimmune processes – rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis,
- amyloidosis – disorders of protein metabolism;
- acute anemia – iron deficiency, hemolytic;
- malignant tumors - kidney adenocarcinoma, stomach, pancreas, lung cancer, lymphogranulomatosis, lymphoma;
- blood loss, including operating;
- giving up alcohol;
- Randu-Osler - hereditary inferiority of the endothelium (inner lining) of blood vessels;
- after splenectomy – partial removal of the spleen;
- tetanus;
- sepsis.
The cause of an increased number of platelets in women's blood can be menstruation, toxicosis during pregnancy, or the last weeks before childbirth, when the body is preparing for significant blood loss.
An increased level of platelets in the blood of women during pregnancy can be caused by insufficient daily fluid intake, intestinal or respiratory infection, or hepatitis.
Treatment of deficiency conditions caused by a lack of vitamins B12 and B9, the use of vincristine and adrenaline can cause an increase in analysis results. Common causes of increased platelet levels in the blood in women include iron deficiency anemia and chronic inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
Large platelets
For diagnosis, not only quantitative changes in blood platelets are important, but also qualitative disturbances in the composition of the population. The P-LCR and P-LCC values on the test form reflect how many large (large) platelets are present, with a mean volume (MPV) greater than 12 fL.
- There are few platelets in a blood test - what does this mean and what to do?
For comparison, the average volume of a normal mature cell form is 7.2 - 10.8 fL; you can read about the value of this platelet index on another page of the site.
- P-LCR is a relative value that shows the ratio (%) of large platelets or the ratio of the number of platelets larger than 12 fL to the total number of platelets.
- P-LCC is an absolute measure of large platelets, indicating the number of these cells, measured at *109/L.
Normally, the platelet coefficient P- LCR should be in the range of 13 – 43%, and the platelet count should not go beyond the range of 30 – 90*109/l.
Exceeding these indicators may be caused by an increased content of young forms in the blood, which are larger than old ones, since normally, over 9–11 days of life, the size of the platelet gradually decreases.
In addition, an increase in the P-LCR coefficient can be caused by the appearance of activated forms that have a flattened, asymmetrical shape with bizarre processes. And if the content of large activated platelets in the blood is increased, this most often means that the endothelium of the blood vessel is damaged.
An increase in the number of activated PLT cells means an increased need for this cell population. Activated blood platelets have an increased ability to aggregate with each other and adhere (adhesion) to the endothelium of blood vessels at the site of damage. These properties are needed primarily to maintain the integrity of blood vessels.
Large platelets are increased in conditions such as:
- cardiac ischemia;
- myocardial infarction;
- diabetes;
- atherosclerosis;
- thrombocytopenic purpura.
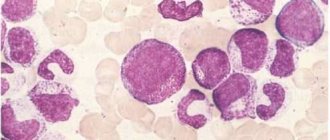
Large PLT plates appear in myeloproliferative diseases. The blood smear reveals morphologically altered cells, large (giant) PLT cells.
However, if the size of platelets is increased, and large PLT cells with a volume greater than 12 fl are detected in a blood test in an adult, then this does not always indicate a myeloproliferative disease. This pathology, in addition to an increase in giant platelets, is also characterized by disturbances in their internal structure.
Classification of thrombocytopenia
Let's talk about the causes of thrombocytopenia that underlie the different types of this disease.
Hereditary thrombocytopenias
These conditions are based on diseases of genetic origin. These may be May-Hegglin anomaly, Bernard-Soulier syndrome, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, TAR syndrome, as well as congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia.
Each of these diseases has many characteristics. For example, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome occurs exclusively in boys and occurs in four to ten cases per million. Bernard-Soulier syndrome can only develop in a baby who has received the altered gene from both parents, and May-Hegglin anomaly can develop in 50% of cases, provided that only one parent has the prerequisites for this. As a rule, all of these diseases have among their symptoms not only a low level of platelets, but also a number of other pathological conditions, and therefore require special treatment.
How to avoid bleeding
Cancer and cancer treatments can cause low platelet counts. When your platelet count is low, you are at risk of bleeding. If your doctor has told you that you have a low platelet count, it is important to try to avoid injury.
We will list some general tips that can help you prevent bleeding. It is also very important to discuss your lifestyle with your healthcare professional. They may suggest other ways to prevent bleeding if your platelet count is low.
Personal care
- Do not use sharp objects such as straight razors, scissors or nail clippers. You can use an electric razor.
- Do not: manicure or pedicure;
- waxing;
- electrolysis;
- tattoos
- rectal suppositories (medicines that are inserted into the anus);
Dental care
- Use a brush with soft bristles.
- Consult your doctor before starting dental treatment.
Daily Activities
- Wear gloves when doing gardening, cooking, or making repairs at home.
- Avoid activities that could cause injury. These include: contact sports;
- climbing a stepladder;
- intense physical exercise;
- Biking;
- lifting weights.
- use lubricants if necessary;
Medicines
- Do not take: aspirin or medications containing aspirin;
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen (Advil®, Motrin®) and naproxen (Aleve®);
- vitamin E
to come back to the beginning
Productive thrombocytopenia
They are also caused by a huge list of reasons and factors of various origins. All of them are associated with the fact that platelet formation processes in the red bone marrow are disrupted.
For example, this includes some types of anemia, cancer metastases, acute leukemia, and taking cytostatic medications. There are even factors such as radiation or alcohol abuse.
For example, in acute leukemia, a disease of the circulatory system causes a mutation in the bone marrow stem cell. Because of this, it divides and begins to displace hematopoietic cells. As a result, the number of not only platelets, but also leukocytes, erythrocytes, and lymphocytes decreases. This condition has its own name - pancytopenia. That is, immune thrombocytopenia in this case is part of it.
If we are talking about the effect of medications, then most often a decrease in platelet levels is caused by drugs from the following groups:
- antidiabetic,
- anti-inflammatory,
- antipsychotics,
- antithyroid,
- antibiotics,
- diuretics,
- anticonvulsants.
Of course, not all medications and not in all cases are capable of causing such a reaction, but this is another reason to think about the fact that you should not prescribe any medications yourself or take them without the supervision of your doctor.
Moreover, there is also such a factor as increased sensitivity to certain medications. Usually it is initially determined by a peculiar genetic predisposition, but this is quite rare.
When we talk about radiation, we are talking not only about a person’s presence in dangerous areas, but also about treatment with radiation therapy. When tumors are destroyed, the blood-forming cells of the red brain can be affected, so a condition where platelet levels drop can become a side effect of cancer treatment.
The development of symptoms of thrombocytopenia due to alcohol abuse most often occurs against the background of binge drinking and is associated with a high level of ethyl alcohol in the blood. It has negative and long-lasting effects on the bone marrow and usually causes a temporary decrease in platelets. If binge drinking becomes frequent and too long, there is a risk that the changes will be irreversible.
What does this mean during pregnancy?
Among the physiological causes of low platelets in women, pregnancy is named, and for the early stages this is indeed a normal situation, if we are talking about acceptable low values. In the early stages, pregnant women experience an increase in the volume of circulating blood due to plasma, while the mass of red blood cells and platelets is produced at a less rapid pace. As a result, the effect of hemodilution is observed - blood thinning, accompanied by a reduced content of red blood cells and platelets.
Typically, this transient phenomenon does not have any significant impact on hemostasis. If platelets are reduced to a level of 50 units per microliter or lower, emergency measures may be required to stabilize the indicators. Especially if there are few platelets a couple of weeks before giving birth, this means that the body is not preparing for the upcoming blood loss and can suffer greatly during childbirth.
- Thrombocytopenia - symptoms and treatment
This is when the value of a general blood test becomes obvious - thanks to it, it is possible to promptly detect a low platelet count, suggest the reasons for the deviation and take action.
The range of conservative methods for increasing low platelets during pregnancy is limited, but the expectant mother will not be left without help, since the arsenal of medicine includes drugs with minimal effects on the fetus.
Thrombocytopenia destruction
Here we are talking about the active destruction of platelets, which is usually observed in the spleen. Such processes are also caused by a large number of factors. These include taking certain medications, some viruses, Fisher-Evans syndrome, etc.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenia deserves special consideration. This is the case when it is not possible to establish the cause even with a huge number of possible options. At the same time, doctors note that even in such a situation, the action of provoking factors is observed. For example, the problem appears after bacterial and viral infections, preventive vaccinations, use of a number of medications, hypothermia or prolonged exposure to the sun.
This condition also occurs in newborns. It begins to form in the womb, when antibodies in her body cause the destruction of platelets in the child.
Fisher-Evans syndrome is also not an independent cause, since it itself is a consequence of various systemic diseases. This syndrome occurs in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis, but in some cases it can be an independent deviation. As for viruses, rubella, chicken pox, measles, and influenza can lead to a decrease in platelet levels. Sometimes this is a reaction to vaccination, although such a mechanism is described quite rarely and almost never occurs.
Thrombocytopenia consumption
Here the mechanism is as follows: platelets, for some reason, begin to be activated in the vascular bed. In response to this, the red bone marrow begins to actively produce them - and as a result, its capabilities are slowly depleted. After this, the level of red cells begins to fall.
One of the causes of consumption thrombocytopenia is disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome. It stands for disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome. And it can develop against the background of severe tissue destruction during operations, burns, injuries, due to severe infections, chemotherapy, organ transplants, etc. That is, there are many underlying reasons that can cause a decrease in the level of platelets in the blood.
What does a low level of thrombotic cells indicate in an adult?
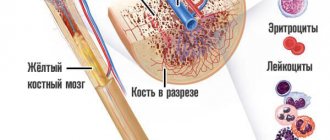
Unlike red blood cells, whose life cycle is approximately 120 days, thrombotic plates are destroyed on days 9-12 of their existence. Their quantity is continuously renewed by the bone marrow to maintain the physiologically necessary amount in the blood.
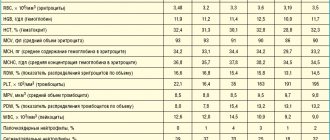
As with other blood cells, platelets have values called normal; they are defined in the range 180-320*10 9 units per liter, or 180-320 thousand units per microliter. If, according to the results of the analysis, it turns out that the number of thrombotic cells does not reach the normal level, this indicates the development of thrombocytopenia in an adult or child.
Thrombocytopenia (platelets significantly lower than normal) occurs due to the accelerated destruction of thrombotic cells or disruption of their production, which occurs in a number of diseases.
Thrombocytopenia redistribution
If we explain this mechanism very simply, it looks like this: due to some reasons, the patient’s spleen enlarges. And if under normal conditions it stores up to 30% of platelets, then in an enlarged state it retains up to 90% of these cells. At the same time, the system does not see that there are not enough platelets and does not trigger a compensatory mechanism.
The mechanism is also based on various causes: cirrhosis of the liver, some infections such as tuberculosis, autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus), tumors of the circulatory system, alcoholism.
What to do in case of bleeding
If you start bleeding at home, take the following measures:
- Apply direct pressure to the bleeding area. If you have a nosebleed, pinch the bridge of your nose and apply ice to it.
- After applying pressure to the bleeding area, call your Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) doctor. If you cannot reach your doctor and are unable to stop the bleeding, go to your nearest emergency room.
When should you call your doctor?
Call your doctor right away if you have any of the following:
- black stools, blood in the stool, or bleeding from the rectum;
- blood in urine;
- persistent headache;
- blurred vision;
- dizziness;
- any persistent bleeding, including coughing up blood, vomiting blood, or bleeding from the nose.
to come back to the beginning
Thrombocytopenia dilution
This condition is usually observed in people who receive a large number of transfusions of various liquids: for example, plasma, plasma substitutes, etc. As a result, the level of platelets decreases due to the banal dilution of the blood.
Considering the huge number of reasons that can cause immune thrombocytopenia (and we have not named all the options), a patient with its symptoms should immediately consult a doctor who will find the essence of the problem and prescribe effective treatment.
Diagnostics
Since there are so many reasons, it is not possible to name diagnostic measures in detail - everything will depend on the specific situation. But we can highlight the main components of diagnosis:
- General blood analysis.
- Checking bleeding time (Duke test).
- Determining the time it takes for blood to clot.
- Red bone marrow puncture. The method allows you to identify quantitative and qualitative changes in cells.
- Determination of antibodies in blood.
- Research for genetic diseases.
- Ultrasound of internal organs. Most often, the liver and spleen are studied immediately, but this list can be very large.
- MRI. Used to study internal organs and blood vessels.
Diagnosis of the disease begins with a visit to a general practitioner, who, based on a survey, initial examinations and tests, prescribes visits to other specialists.
Treatment and severity
Treatment of thrombocytopenia most often comes down to identifying the primary disease and its treatment, as well as eliminating various unpleasant symptoms. In the process, it is also important to take into account that the severity of thrombocytopenia varies:
Mild degree. It assumes that the platelet concentration is from 50 to 150 thousand units per microliter. The condition of the capillaries is usually normal, bleeding does not develop. Usually, treatment is not necessary at this stage - doctors recommend waiting and monitoring the development of the patient’s condition.
Average degree. In this case, the concentration is 20-50 thousand platelet units per microliter. Under this condition, bleeding gums and nosebleeds are observed. If injuries and bruises occur, serious hemorrhages form in the skin. At this stage, drug therapy may be prescribed.
Severe degree. The platelet concentration is below 20 thousand, hemorrhages are spontaneous and severe. At the same time, the patient himself may feel quite comfortable, does not complain of feeling unwell, but tests show that he needs help.
Since the treatment of thrombocytopenia requires the most thorough and detailed diagnosis, it is important to choose a modern clinic that will help you. JSC "Medicine" in Moscow is just the place where you can get qualified help from the best specialists. The clinic has everything necessary for both examination and treatment of each patient.
Prognosis and prevention
Thrombocytopenia is a dangerous disease that poses a huge threat to the life and health of the patient. Anemia often develops, and vision loss can occur due to hemorrhages in the retina. Advanced forms can provoke hemorrhages in the internal organs and in the brain. In most cases this leads to death.
Thrombocytopenia has no specific prevention. Experts give the following recommendations:
- Take a general blood test every year and undergo a general medical examination;
- Eat properly and nutritiously: eat as much meat and fresh vegetables as possible;
- Play sports and lead an active lifestyle;
- Avoid self-medication: taking aspirin and steroid drugs should be under the strict supervision of a doctor;
- Try to avoid any procedures where there is a risk of cutting (shaving, manicure);
- Treat any infectious processes in a timely manner;
- Take precautions when working with chemicals;
- Give up bad habits: drinking alcohol slows down platelet production.
Thrombocytopenia is a disease that requires constant medical supervision. If you suspect you have it or know about the pathology and want to get rid of it, contact the Medscan medical center. Experienced doctors will perform the necessary diagnostics and develop an individual treatment plan.