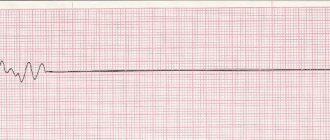
Adrenaline is a stress hormone produced in the adrenal medulla. During a stressful situation, its production increases significantly and can reach a critical level. The body sends certain impulses to create a certain reaction. The hormone plays an important role for humans and affects the normal functioning of organs and systems.
When faced with a stressful situation, stress hormones guide actions and prompt certain reactions. For example, if it is necessary to carry out an action that is unpleasant for a person, the stomach may begin to ache, and when speaking in public, the voice may suddenly disappear.
How to trigger an adrenaline rush?
The production of adrenaline is associated with a person’s emotional state. Its release can be provoked artificially. For this it is enough:
- watch a scary movie;
- jump with a parachute;
- play dangerous games;
- see something scary, etc.
For some people, it is enough to “wind up” themselves in order for the hormone to begin its independent production. It is impossible to regulate it with products. These are exclusively emotions and the work of the nervous system.
A mind full of anxiety and various obsessive thoughts can trigger the production of the hormone. This is especially true at night, when there is silence in the apartment and various thoughts creep into your head. The receptive brain is able to draw various pictures, which is accompanied not only by fear, but also by an active loss of energy.
To control the stress hormone, it is enough to organize your thoughts. Minimize TV viewing, remove sources of bright light before bed, remove mobile phones and music.
Stress hormones
A number of studies have shown that in athletes during training and competitive loads, the activity of the sympathetic-adrenal and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal systems increases. In this case, activation of general adaptation mechanisms by physical activity is observed, which leads to changes in the hormonal spectrum, ensuring the mobilization of both the energy and plastic reserves of the body, as well as its restoration.
One group of stress hormones is produced by the adrenal medulla and is called catecholamines. This group includes the hormones adrenaline and norepinephrine. Both hormones are synthesized from the amino acid tyrosine under the influence of nerve impulses. The main hormone of this group is adrenaline. When the medulla is stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system, approximately 80% adrenaline and 20% norepinephrine are released. Catecholamines have potent effects similar to those of the sympathetic nervous system.
Another group of stress hormones is produced by the adrenal cortex and is called glucocorticoids (corticosteroids). One of the main representatives of this group is the hormone cortisol.
You can read about the relationship between hormones and muscle mass in my book “Hormones and Hypertrophy of Human Skeletal Muscles”
The effect of adrenaline on the body
Experiencing stress is a normal state of the body, which is very useful for survival. But a person needs to know methods of counteracting stress, because regular release of adrenaline has a negative impact on the condition of blood vessels, increased blood pressure and the risk of developing diseases of the cardiovascular system.
To control stress hormones in women, it is necessary to learn to activate the parasympathetic nervous system. Rest and digest the situation counteract the classic fight-and-flight pattern of adrenaline. The hormone affects the entire body:
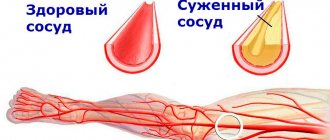
- heart and blood pressure. The reaction caused by adrenaline provokes the expansion of the bronchi and other air passages. This is a classic reaction aimed at providing the muscles with additional oxygen. Adrenaline causes blood vessels to contract, sending blood to major muscle groups, as well as the heart and lungs. This process leads to an increase in heart rate and stroke volume, promotes dilation of the pupils and constriction of arterioles;
- metabolic processes. The stress hormone in men and women causes an increase in blood sugar levels, this is due to increased catalysis of glycogen to glucose in the liver. By a similar principle, glycogen breakdown is activated;
- central nervous system. Adrenaline is produced under the control of the central nervous system. The hypothalamus, located in the brain, receives a signal of danger. This signal communicates with the body through the sympathetic nervous system. It is noteworthy that adrenaline helps to increase brain activity and physical strength. This is why some people easily cope with stressful situations and find effective solutions;
- smooth and skeletal muscles. Under the influence of adrenaline, most muscles relax. This leads to the fact that during a stressful situation people experience discomfort in the internal organs, including the stomach and heart;
- blood clotting. Blood clotting increases in critical situations, and this is a proven fact. The body responds to stress by increasing the number of platelets and the rate of blood clotting. It is noteworthy that adrenaline inhibits erection and affects male potency.
Under adrenaline stress, anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory properties are enhanced. It is noteworthy that the hormone is used to treat anaphylactic shock, as well as sepsis. It is widely used for asthma.
Sympathoadrenergic activity and fat metabolism[edit | edit code]
Intravenous administration of epinephrine at rest causes an increase in lipolytic activity, assessed by microdialysis of subcutaneous adipose tissue samples, and this effect is gradually weakened by repeated injections of epinephrine (Stallknecht, 2003). In patients with spinal cord injury, while performing exercise on an arm ergometer using microdialysis, the level of lipolysis was determined in samples of subcutaneous adipose tissue taken in areas above and below the border separating the area of the body with sympathetic innervation (within the clavicle) from the area of the sepsis. deprived (above the buttocks) (Stallknecht et al., 2001). In both areas, an increase in the intensity of lipolysis was observed during physical exercise, which suggests that direct sympathetic innervation is not particularly important for lipolysis processes during muscle work. However, adrenaline circulating in the circulatory system may be the most likely candidate for the role of activator of lillolytic processes. Exercise training leads to a decrease in adipose tissue volume and adipocyte size, and it appears that the sympathoadrenergic system is very important in mediating this adaptation.
Adrenaline is able to stimulate the breakdown of fats not only in adipose tissue, but also in muscles, and lipoprotein lipase (LPL) and hormone dependent lipase (HSL) play an important role in this regulation. Activation of HSL can occur both under the influence of muscle contractile activity and increased levels of adrenaline (Donsmark, 2002), and it has recently been shown that in individuals with removed adrenal glands, there is a parallel activation of HSL and glycogen phosphorylase after adrenaline injections during exercise (Kjaer et al., 2000). This may mean that adrenergic activity leads to the simultaneous mobilization of intramuscular stores of glycogen and triglycerides, and further selection of the substrate for energy supply processes is carried out at a different level.
What are the dangers of excess adrenaline?
When stress hormones are elevated, the body may react negatively. It is noteworthy that in some cases, excessive adrenaline production may not be caused by stress. An increased amount of the hormone is accompanied by dizziness, weakness, and also:
- rapid heartbeat;
- tachycardia;
- general anxiety;
- headache;
- tremor of the limbs;
- hypertension.
In severe situations, acute pulmonary edema cannot be ruled out. With a constant overabundance of the hormone, constant anxiety and irritability are observed. If these symptoms appear, it is advisable to seek help from specialists. Altimed Medical Center specializes in the treatment of abnormalities in the body using innovative equipment. Modern devices accurately determine the weak point. Based on the diagnosis, the optimal treatment regimen is determined.
When is adrenaline released?
Adrenaline is produced in cases of stress, trauma, burns, shock, physical exertion, and emotional shocks. Its development is an adaptation process to the current situation. For example, during painful shock, thanks to adrenaline, a person does not fully feel pain. Otherwise, death would have occurred from the pain reaction.
Adrenaline is produced in order to make the body faster and stronger. In other words, this hormone mobilizes all the forces of the body.
Any living organism in nature has protective functions, one of which is called “fight or flight”. That is, the animal protective instinct is triggered during times of stress, when it is necessary to either defend or run away. This is a physiological process that occurs regardless of our desires.
Thanks to adrenaline, your mood and desire to carry out your plans increase.
Interesting fact!
For each person, the level of adrenaline is purely individual. There are people for whom this bar is quite high, and in order to keep it, they need to go to the mountains, play in casinos, and engage in extreme sports. The effect of adrenaline after the release lasts no more than five minutes, because the processes of its inactivation are activated. When the hormone level drops, apathy and depression occur. Therefore, active people need to replenish it again and again. For others, the level of this hormone is quite low, and they are satisfied with absolutely passive types of relaxation: sofa, TV, reading books. It depends on the individual characteristics of a person’s character, his temperament, hereditary factors, etc. We are all individual.
How to normalize adrenaline levels
You can normalize the level of adrenaline in the body yourself, but if the condition is not critical. Simple rules will help control the hormone.
How to lower stress hormones without medications? Follow the established rules:
- restore mode;
- eat a balanced diet;
- exercise regularly;
- learn to control emotions;
- find a relaxing activity;
- receive positive emotions;
- interact more with animals.
But these are just recommendations. If the hormone content is high, which negatively affects the general condition and poses a clear threat, it is necessary to seek professional help.
The effect of physical activity on the concentration of adrenaline and norepinephrine in the blood
The level of adrenaline and norepinephrine in the blood increases with increasing intensity of exercise. During dynamic exercises, the concentration of adrenaline in the blood plasma increases 5-10 times. It has been proven that the level of norepinephrine in the blood plasma increases significantly with an intensity of physical activity of more than 50% of MOC (J. Wilmore, D.L. Costill, 1977). At the same time, the concentration of adrenaline increases slightly until the intensity of physical activity exceeds 60-70% of the MOC. After cessation of physical activity, the concentration of adrenaline in the blood returns to its original level within a few minutes, while the concentration of norepinephrine in the blood remains elevated for several hours.
Catecholamines do not have a direct effect on increasing skeletal muscle mass. However, they are responsible for increasing the level of other hormones, and primarily testosterone.
Literature
- Samsonova A.V. Hormones and hypertrophy of human skeletal muscles: textbook. allowance. – St. Petersburg: Kinetics, 2021. – 204 p.
- Wilmore JH, Costill DL. Physiology of sports and physical activity. – Kyiv: Olympic Literature, 1997. – 504 p.
- Endocrine system, sports and physical activity. – Kyiv: Olympic Literature, 2008. – 600 p.
Best regards, A.V. Samsonova
[1] Hypercapnia is a condition caused by excess CO2 in the blood, such as carbon dioxide poisoning. It is a special case of hypoxia.
Negative effects of excess adrenaline
With constant or frequent release of adrenaline by the adrenal glands, they become depleted and the adrenal system as a whole is depleted. A person becomes lethargic, apathetic, weak, lacking initiative, and depressed.
An excess amount of adrenaline in the blood is observed with constant stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system: during chronic stress, during constant anxiety, fear. With excessive and frequent production of adrenaline, so-called panic attacks can occur. This is a functional state of the body in which the level of adaptive capabilities is significantly less than the level of adrenaline.
Symptoms of panic attacks:
- irrational fear of death;
- tachycardia, arrhythmia;
- pain in the heart area;
- a sharp increase in blood pressure;
- cold clammy sweat;
- dizziness;
- fainting state;
- tremor of limbs, convulsions;
- increasing shortness of breath, suffocation;
- sudden changes in body temperature;
- dry mouth.
In another way, this condition is called sympathoadrenal or vegetative crisis, vegetative storm, vegetative neurosis with a crisis course, etc. This condition is not organic. Although it is very unpleasant and painful for patients, it is absolutely functional. If the adrenaline rush continues, panic attacks will recur. This condition is treated and monitored by psychotherapists and psychiatrists together with specialized specialists. And the treatment of such patients is aimed precisely at eliminating the cause, that is, at stopping or reducing the release and effect of adrenaline on the body.
Such conditions are also observed in athletes. This may be due to excessive physical and psychological stress. This is especially true before serious competitions, when the athlete bears great responsibility. A person feels constant tension, and the body can respond to such stress with vegetative storms.
The use of adrenaline in modern medicine
In modern medicine, adrenaline is used as a medicine. It is produced in ampoules of 1 ml/1 mg. This is a fairly serious drug. Very often it is used in emergency conditions.
Main indications for use:
- heart failure;
- myocardial infarction;
- attack of bronchial asthma;
- respiratory arrest;
- acute bleeding;
- acute inflammatory reactions.
Main contraindications:
- atrial fibrillation;
- myocardial hypertrophy;
- thrombosis;
- oncological pathology;
- intestinal atony;
- bronchodilation.