✅ Hawthorn is famous not only for its super-hard wood, but also for its active use of fruits, flowers, leaves and branches of the plant in folk medicine.
❎ Moreover, hawthorn tincture is generally a medicinal product certified by the Ministry of Health, acceptable for use for therapeutic purposes.
In this article we will discuss the general effect of hawthorn on the cardiovascular system, as well as for which diseases it will be most effective.
Features of using hawthorn for diseases
Hawthorn has a complex positive effect on the entire cardiovascular and nervous system of a person, but this effect is especially noticeable in the following diseases:
1️⃣ Arrhythmia
With this disease, the normal heart rhythm is disrupted. And since hawthorn improves the conduction of impulses through the heart muscle, it will help normalize the rhythm of contraction of the heart chambers and also alleviate atrial fibrillation.
2️⃣ Tachycardia
With this disease, the heart rate increases to 100 beats per minute or higher, which in most cases indicates a lack of oxygen in the blood. By “accelerating” the blood and the amount of oxygen consumed (which is why shortness of breath occurs), the body tries to compensate for the deficiency. And, in fact, it is necessary to normalize the balance of hemoglobin, which transports oxygen. Hawthorn contains iron and flavonoids - these are precisely what are needed for the production of hemoglobin molecules.
3️⃣ Extrasystole
Violation of the rhythm of heart contraction. This is when the chambers of the heart muscle contract at the wrong period, causing the nominal blood flow to be disrupted. Most often, ventricular extrasystole is a consequence of impaired conduction of impulses from the sinus node. Hawthorn normalizes sensitivity to such impulses.
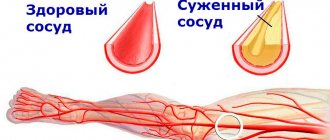
4️⃣ Vascular atherosclerosis
It develops against the background of the accumulation of low-density cholesterol (it is often called “harmful”), which leads to blockage of blood vessels and the formation of cholesterol plaques. Hawthorn helps lower cholesterol levels by stimulating its breakdown in the liver.
5️⃣ Heart failure
With this disease, the functionality of the myocardial wall is impaired with the accumulation of intercellular fluid. By normalizing blood pressure, the negative effect of the disease is minimized (but, unfortunately, not completely eliminated).
6️⃣ Prevention of heart attack
There are many reasons for the occurrence of this disease, but the most common provoking factor is high blood pressure combined with the active formation of cholesterol plaques. Hawthorn helps cleanse blood vessels, thereby reducing the likelihood of a heart attack. But is it possible to take hawthorn after a heart attack? This depends on many factors, so it is best to discuss this issue with your doctor.
7️⃣ Angina pectoris
One of the most common diseases among people of retirement age. Indicates a lack of blood in one or more chambers of the heart, which most often develops against the background of extrasystole (impaired conduction of impulses by the heart muscle). Carotene, iron, vitamin E help neutralize this negative effect, and they are found in large quantities in hawthorn.
Medicines based on hawthorn
There are drugs based on hawthorn, which are officially certified by the Ministry of Health for use in the treatment and prevention of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
These include:
1️⃣ Complex of hawthorn and red grape extracts
It is used specifically for the prevention of diseases of the cardiovascular system. Available in the form of capsules (300 mg of active ingredients each). Prescribe 2 capsules per day for 1 – 2 months (at the discretion of the attending physician). Contraindications include only pregnancy and breastfeeding.
2️⃣ Drops “Gerboton”
It is an alcohol infusion (the quantitative ethanol rate is 70%). Sold in bottles of 25 and 100 milliliters. Prescribed for functional failures in the cardiovascular system (including neurocirculatory dystonia). Take 20 drops 3 times a day. Prescription is also allowed for children, but only from 12 years of age (the dosage is determined individually by the doctor).
3️⃣ Kratal
It is a concentrated extract of hawthorn and motherwort fruits. Prescribed for neurocirculatory dystonia during an exacerbation, can be used for the prevention of cardiac disorders. Take 2 - 3 times a day, 1 - 2 tablets, course - up to 30 days.
There are many other medications that your pharmacist or doctor can recommend.
Although the above drugs are sold without a prescription, you should not take them without medical advice. For some diseases of the cardiovascular system, their use is strictly prohibited!
Hawthorn is a common plant that is actively used in the treatment of diseases of the cardiovascular system. There are minimal contraindications for its use: individual intolerance, age under 12 years, pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Tea, decoction and infusion based on it are an excellent option for the prevention of cardiac diseases. It was also previously widely used in cooking for making jam and compote.
The name of the plant comes from the Greek “strong”, which reflects either the property of the wood - strong and hard, or the ability of the plant to live long: the age of hawthorn can reach 300 years.
Hawthorns are tall shrubs, less often - trees up to 5-8 meters high with strong shoots, planted with thick, sparse thorns of stem origin. The flowers are white, fragrant, collected in corymbose inflorescences. The leaves and fruits vary from species to species. True to its name, the fruits of hawthorn are blood-red with 3–4 seeds. The leaves are dark green above, lighter below. It blooms in May–June, the fruits ripen in August–September. The plant bears fruit from the age of 10–15 years and can live up to 200–300 years.
The healing properties of hawthorn have been known since ancient times. For example, in surviving ancient manuscripts one can find references to the fact that hawthorn was widely popular and was used in the treatment of a number of ailments, especially in cases of cardiac dysfunction. In the East, hawthorn was called “wild apple tree”: the hawthorn tree really looks like an apple tree, especially with its leaves and roots. This was noted by Avicenna, who wrote that hawthorn “knits stronger than rowan, suppresses bile and blocks the flow more strongly than any other fruit.” Avicenna believed that hawthorn was harmful to the stomach, it “locks the stomach and does not retain urine.” The German doctor Jening noted back in 1896 that hawthorn has a positive effect on heart diseases, increases heart contractions and has a calming effect on the central nervous system (CNS). Some doctors achieved complete cessation of attacks of pain due to angina pectoris by giving patients hawthorn preparations. During the Great Patriotic War, hawthorn fruits were used as a substitute for heart medications that were in short supply at that time.
Many peoples call hawthorn a thorn: among the Germans it is a white thorn, among the British it is simply a thorn. Indeed, the thorn is the most noticeable part of the plant. By origin, hawthorn thorns are former twigs. If you look closely, you can see that at the very beginning of development, the soft and green spines have small leaves that quickly fall off. The grown thorns become incredibly strong, sometimes they are even used instead of nails. A large thorn pierces the foot through almost any sole, so you need to walk very carefully near hawthorns. The length of the spines is a species characteristic.
The blood-red hawthorn has a European-Siberian type of habitat, the length of which from west to east exceeds 5 thousand km. It grows in forest, forest-steppe and steppe zones in sparse dry forests, on forest edges and clearings, along river floodplains.
Hawthorn flowers and fruits are harvested as medicinal plant raw materials. The flowers are collected at the beginning of flowering, when some of them have not yet opened, by cutting off the thyroid inflorescences and individual flowers. Dry in dryers at a temperature of 40 ° C in attics, under canopies or in rooms with good ventilation. Hawthorn fruits are harvested during the ripening period from the end of September until frost, tearing off entire scutes with fruits or individual fruits. Dry in dryers at a temperature of 70 ° C. The shelf life of fruits and flowers is 2 years.
The State Pharmacopoeia of the XI edition includes 12 species of hawthorn permitted for procurement as medicinal raw materials. Hawthorn fruits and flowers are included in the State Pharmacopoeia as medicinal raw materials (two separate articles).
Unlike other medicinal plants, almost all parts of hawthorn, with the exception of the roots, contain a lot of useful substances. However, only fruits and flowers are used in medicine.
The flowers contain flavone glycosides hyperoside and quercitrin, which have the aglycone quercetin, but contain different sugars: hyperoside is quercetin-3-galactoside, quercitrin is quercetin-3-rhamnoside. Other phenolic compounds in hawthorn flowers include caffeic and chlorogenic acids. Acetylcholine, choline and trimethylamine were also found. The smell is caused by essential oil and some volatile compounds.
Hawthorn fruits contain hyperoside. Caffeic and chlorogenic acids, tannins (which are dimers of L-epicatechin and leucoanthocyanidin), triterpene compounds (ursolic and oleanolic acids), essential oil, β-sitosterol (the latter two substances in the seeds), sorbitol, choline and acetylcholine. Fresh ripe fruits are soft, mealy and tasty; their medicinal value is not much inferior to rose hips; they contain from 4 to 11% sugar, mainly fructose, so they can be eaten even if you have diabetes. Quite a lot of pectin, which not only forms jelly during processing, but also removes heavy metal salts and other harmful substances from the body.
Hawthorn is used as a cardiotonic and blood circulation regulating agent for palpitations, insomnia, and high blood pressure.
As a result of the use of hawthorn preparations in patients, their general well-being improves, blood pressure decreases, headaches, dizziness, noise in the head or ears decrease or disappear, the cholesterol content decreases (effective in the event of atherosclerotic plaques) in the blood and the concentration of lecithin increases, there is a tendency to normalization of blood clotting parameters. Hawthorn preparations are successfully used for symptoms of circulatory failure in elderly and senile people; they have a particularly beneficial effect on the blood supply to the brain; used for diseases of the menopausal period (both in women and men), thyrotoxicosis, atherosclerosis, angiotrophoneurosis, arterial hypertension, angina pectoris, atrial fibrillation and paroxysmal tachycardia, extrasystaly, insomnia, pneumonia, influenza-like diseases. Hawthorn has a slight sedative effect, regulating the functioning of the central nervous system, improves blood flow in the coronary vessels, and reduces body tension. Hawthorn helps improve memory and concentration. It is beneficial for patients with diabetes. The best effect is achieved with regular long-term use of hawthorn.
Hawthorn fruits are used for tachycardia, arterial hypertension, chronic heart failure (grades I–IIa), atherosclerosis, cardialgia, atrial fibrillation, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, extrasystole, digitalis intoxication; insomnia, thyrotoxicosis, menopausal and asthenoneurotic syndrome. Fruits are contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity, in childhood (up to 12 years) and during pregnancy (first trimester). Use internally in the form of tincture and extract, 20–30 drops 3–4 times a day. In the form of an infusion - 15-30 ml 2-3 times a day. Side effects may include allergic reactions (urticaria, itching), bradycardia (with prolonged use); when used in large doses – decreased blood pressure, drowsiness. When administered together with cardiac glycosides, the cardiotonic effect is enhanced; with β-blockers – hypotensive effect.
Hawthorn tincture is used as part of complex therapy for functional disorders of the heart, cardialgia, menopausal syndrome, and asthenoneurotic conditions. Prescribed orally: for adults – 20–30 drops 3–4 times a day before meals (course of treatment is 20–30 days); children over 12 years old - 10-15 drops, diluted in 1/4 glass of water 3-4 times a day before meals (course of treatment is 20-30 days). The tincture should be used with caution in case of liver diseases, alcoholism, traumatic brain injury, and brain diseases. The absolute alcohol content in the maximum single dose of the drug for adults is 0.45 g, for children – 0.23 g; in the maximum daily dose of the drug for adults - 1.8 g, for children - 0.9 g. During the treatment period, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Hawthorn flowers have antiarrhythmic and hypotensive effects, improve coronary and cerebral circulation, and reduce heart rate. Reduce the excitability of the central nervous system, reduce cholesterol in the blood and increase the amount of lecithin; normalize blood clotting indicators. With hypogalactia, lactation is increased and dyspeptic symptoms in infants are eliminated. The hypotensive effect is more pronounced than that of hawthorn fruits. Use internally as an infusion of 15–30 ml 2–3 times a day. To prepare the infusion, 5 g (1 tablespoon) of raw material is placed in a glass or enamel container, poured with 200 ml of water, covered with a lid and heated in a boiling water bath for 15 minutes. Cool at room temperature for 45 minutes, filter, and squeeze out the remaining raw materials. The volume of the resulting infusion is adjusted to 200 ml with boiled water. Allergic reactions are possible as side effects; bradycardia (with prolonged use); nausea, vomiting, intestinal colic (when taken on an empty stomach).
The liquid extract of the fruit is part of the complex preparation Cardiovalen (adoniside + hawthorn fruit extract + valerian officinalis rhizomes with roots tincture + gray jaundice juice + camphor + sodium bromide). It has a cardiotonic and sedative effect and is indicated for the initial stage of chronic heart failure and cardiopathy. Apply 15–20 drops orally 1–2 times a day.
For insomnia and heart neuroses, a mixture of hawthorn and valerian preparations works well.
It must be remembered that prolonged and uncontrolled use of hawthorn preparations can cause depression of heart rate.
The fruits of large-fruited hawthorn species are quite tasty; they can be eaten fresh, processed into jam, wine, compote, and brewed as tea. However, hawthorn should not be overused. It is not recommended to eat more than a glass of berries at one time, as this can cause a sharp drop in blood pressure and heart rhythm disturbances. One rosette of hawthorn jam replaces a double dose of such a strong heart remedy as adonizide. Hard hawthorn wood is used to make wooden products. The bark is used to dye fabrics red. The fruits are used to make jam, jelly, substitute coffee and tea. Dried berry flour is added to dough to create bread with a fruity flavor.
Information about the authors: Samylina Irina Aleksandrovna - Doctor of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Professor, Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Director of the Research Institute of Pharmacy; Head of the Department of Pharmacognosy MMA named after. THEM. Sechenov. Tel.; Sorokina Alla Anatolyevna - Doctor of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Pharmacognosy of the MMA named after. THEM. Sechenov. Tel.; Pyatigorskaya Natalya Valerievna - candidate of pharmaceutical sciences, associate professor, deputy director of the Research Institute of Pharmacy for scientific work. Tel.