Causes and mechanism of action
Hereditary predisposition is considered one of the main causes of vegetative-vascular dystonia (especially in childhood). In combination with unfavorable external factors, it affects the state of the brain (in particular the hypothalamus), increasing the manifestations of the syndrome. The development of psychoneurological disorders leads to excessive activation of some processes and inhibition of others. This state of the body has a negative impact on various systems and organs. In adolescence, this is especially evident at the neurophysiological level. The causes and symptoms of VSD in adults are particularly influenced by hormonal changes.
Among the risk factors for vegetative-vascular dystonia, the following are usually distinguished, having the most powerful effect:
- disruptions in the functioning of the body (endocrine disorders, pregnancy, menopause, etc.);
- consequences of past infections, injuries, as well as the presence of chronic diseases;
- bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol, etc.);
- emotional overload, stress, etc.
Pregnancy in women suffering from VSD
For women suffering from VSD, pregnancy raises many questions that cannot but worry them. Eg:
- Is pregnancy compatible with the disease?
- Are there any peculiarities of its course?
- Is there a chance that VSD will be inherited by the baby?
- Will pregnancy provoke an exacerbation of the disease due to hormonal changes?
- What to do with therapy with psychotropic drugs if they are prescribed: cancel or continue treatment.
To eliminate doubts it is necessary to dispel them.
The course of pregnancy with a diagnosis of VSD
Here we can say unequivocally - the course of pregnancy will not differ from the standard one. VSD does not in any way affect the pregnancy of the baby. Toxicosis and gestosis are likely, but this will not depend on the diagnosis of “vegetative-vascular dystonia”, but on the individual characteristics of the expectant mother and her general health indicators. It is worth saying that a woman, at the level of instincts, tries to protect her unborn baby, so the symptoms of VSD usually become less noticeable or disappear altogether.
If a woman has no contraindications to pregnancy, then VSD is not a reason to refuse the opportunity to become a happy mother.
Is VSD inherited?
VSD is not a hereditary disease. A child may have a predisposition to disturbances in the nervous system, but it is reliably known that the children of women suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia, in 70 percent of cases, before reaching adulthood, never experienced a single symptom characteristic of VSD.
Of course, the baby, while in the womb, is exposed to all its conditions. Therefore, a pregnant woman needs to take maximum care, eat healthy foods, not take medications unless absolutely necessary, not experience stress, not be nervous, and lead a healthy lifestyle that excludes bad habits. It is necessary to carefully monitor compliance with all these conditions before reaching 13 weeks of pregnancy.
Any exposure to harmful factors can cause a malfunction in the baby’s central nervous system, which, in turn, can provoke VSD in the future.
Will the condition of a patient diagnosed with VSD worsen during pregnancy?
Usually, women diagnosed with vegetative-vascular dystonia feel better during pregnancy, childbirth and after it. The general condition improves, panic attacks practically disappear. This is a consequence of the fact that the body protects the baby by mobilizing the entire woman’s body. In addition, hormonal changes have a beneficial effect on the health of the expectant mother.
It is unlikely that you will be able to avoid headaches, attacks of heartburn, or increased blood pressure, but these signs are also typical for the pregnancy of healthy women, so this can hardly be considered a deviation from the norm.
The main thing is to immediately, at the very beginning, get rid of bad thoughts and tune in to the positive. You should try to let go of the situation and the body will cope on its own.
treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia during pregnancy
It is better to avoid using antidepressants and psychotropic drugs while expecting a baby. But it is permissible to use them occasionally if there is a threat to the life of the expectant mother.
By using antidepressants during pregnancy, a woman threatens to provoke withdrawal syndrome in her baby after birth, which will definitely lead to depression of the central nervous system and increase the risk of developing defects and miscarriage.
As soon as you start planning a pregnancy, you should remember that during pregnancy and breastfeeding you will have to give up antidepressants, since their benefits for the mother cannot be compared with the harm that will be caused to the child. That is, bearing a child, childbirth and feeding presuppose a complete refusal to treat VSD.
Childbirth with VSD
Childbirth with a diagnosis of VSD takes place as usual, as in any healthy woman, if the general health of the woman in labor allows natural labor.
There's definitely nothing to be afraid of here. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Types and symptoms of VSD
In most cases, it is quite difficult to identify clearly distinguishable symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia. Many signs of this complex of syndromes may be indicators of the presence of diseases that are not directly related to VSD. Only a comparison of all indicators of the autonomic nervous system and/or brain in combination with cardiac or cardiovascular manifestations provides the basis for a definite medical conclusion. Before making a diagnosis of VSD, the doctor must understand the characteristics of the patient’s individual symptoms. Vegetative-vascular dystonia is usually divided into three types (based on blood pressure level):
- the hypertensive type is characterized by increased pressure (periodic surges), symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia of the hypertensive form may include increased sweating, anxiety, chills of the extremities, rapid heartbeat and visualized pulsation of large blood vessels (for example, carpal or popliteal);
- the hypotonic type is characterized by a decrease in blood pressure, in this case the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia include shortness of breath, nausea, headache, general weakness, a tendency to faint, coldness of the toes and hands;
- the mixed type is characterized by periodic fluctuations in blood pressure (sometimes also called VSD of the cardiac form), here the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia are usually considered to be general signs of fatigue, a feeling of lack of air, as well as interruptions in the functioning of the heart.
If you find yourself with the signs listed above, first of all, you should reconsider your work and rest schedule. Of course, consulting a doctor is also necessary.
Symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia
The syndrome is characterized by many different manifestations. Every pregnant woman needs to listen to her body. This will help distinguish the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia from those that may indicate other disorders in the body. With an exacerbation of VSD, a pregnant woman complains of heart problems and dizziness, which will be discussed in detail below, and the following phenomena:
- feeling of constant overwork;
- bloating and other disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- numbness of the limbs and tingling in them;
- nausea;
- sleep problems;
- trembling in hands;
- labored breathing;
- frequent urination;
- weather dependence;
- regular changes in body temperature;
- irritability, tearfulness;
- disorders in the sphere of intimate life;
- attacks of causeless anxiety, panic;
- anemia and fainting in thin girls;
- sweating and swelling in overweight women.
- Do they take into the army with VSD (diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia)
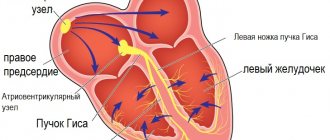
Heart problems
The disease always causes disruption of the cardiovascular system. A pregnant woman exhibits one or more of the following syndromes:
- Cardiological. This condition is sometimes mistaken for coronary heart disease. Accompanied by a feeling of pain in the chest.
- Tachycardic. Vegetative-vascular dystonia is sometimes accompanied by rapid heartbeat.
- Bradycardic. Low heart rate with VSD. Provokes a feeling of weakness.
- Arrhythmic. Violation of the rhythm of heart contractions.
- Hypertonic or hypotonic.
Dizziness
The most common symptom of the syndrome. Dizziness indicates a disruption of the nervous and vascular system. As a rule, it is accompanied by a feeling of lack of air and is especially intensified during moments of panic attacks. If a fragile, thin girl is dizzy, this can even cause fainting. If dizziness occurs, you should immediately sit down, relax, and rest a little. If it does not go away, then it is better to consult a doctor.
Consequences and complications
Along with the classic symptoms and diseases accompanying vegetative-vascular dystonia, the patient’s condition can be worsened by frequently occurring (approximately 50%) vegetative crises - sympathoadrenal, vagoinsular and mixed (depending on the predominance of disorders of a particular part of the system).
Sympathoadrenal crisis. The development of a so-called panic attack is associated with a sharp release of adrenaline. The crisis begins with a sudden headache, rapid heartbeat, and paleness/redness of the face. Arterial hypertension, chills, tremors, numbness of the extremities, and anxiety are usually observed. The attack also ends suddenly and is accompanied by asthenia and polyuria (increased urine production).
Vagoinsular crisis. Its symptoms are almost the opposite of sympathetic manifestations. The crisis begins with the release of insulin into the blood and a sharp decrease in glucose levels. The activity of the digestive system increases, intestinal motility increases, and rumbling appears in the stomach. A vagoinsular attack is characterized by a feeling of cardiac arrest, dizziness, arrhythmia, and difficulty breathing. Blood pressure decreases, the pulse becomes rare, sweating, skin flushing, and darkening of the eyes appear. The patient feels weak throughout the body. The attack ends with a state of severe asthenia.
Mixed crises are characterized by activation of both parts of the autonomic nervous system and, consequently, all of the listed complications. As a rule, in the absence of timely treatment of VSD, rather unpleasant consequences arise. This is especially true for childhood, since psychosomatic pathologies often appear during this period of development. These consequences are quite difficult to correct. VSD is not a life-threatening disease, but over time its quality can significantly decrease. If such severe symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia persist in adulthood, poor adaptation is observed, and it becomes impossible to fully work and study.
Diagnostics
If vegetative-vascular dystonia is suspected, the doctor usually prescribes a comprehensive examination due to the variety of symptoms. Only this approach helps to understand in detail the causes of the disease and methods of its treatment. What is important here is differential diagnosis, which allows one to exclude organic pathology. If VSD is suspected, the patient undergoes consultation with a neurologist, endocrinologist and cardiologist.
Identifying risk factors
Finding out the patient's medical history, the doctor establishes a family history of autonomic dysfunction. It is important if one of your close relatives has a stomach ulcer, bronchial asthma, hypertension, coronary heart disease, hyperthyroidism, or diabetes mellitus. In childhood, vegetative-vascular dystonia can be aggravated by recurrent focal infections - both acute and chronic.
Assessment of the state of the autonomic system
To prescribe effective treatment for vegetative-vascular dystonia, it is necessary to assess the initial autonomic tone (at rest) and determine indicators of autonomic reactivity. For this purpose, the patient’s complaints are analyzed, and an EEG (electroencephalography) of the brain is also performed. Autonomic reactions are verified through various functional tests.
Cardiovascular research
Since the causes of the disease are directly related to the condition of the blood vessels, in order to prescribe the correct treatment for vegetative-vascular dystonia, it may be necessary to undergo Doppler ultrasound of the vessels (neck, brain). It is also possible that your doctor will order an ECG (electrocardiogram).
It is highly recommended not to refuse treatment for vegetative-vascular dystonia, no matter how insignificant the chosen method may seem to you. If the doctor considers it necessary to prescribe therapy, complete the entire course - do not neglect your own health.
Treatment and prognosis
In patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia, treatment is carried out under the supervision of doctors of the following specializations: therapist, neurologist, endocrinologist, psychiatrist. Certain prescriptions will depend on the predominant symptoms of VSD. Usually, taking into account the nature and etiology of the disease, complex long-term individual therapy is carried out.
Physical therapy classes
Special physical education is most useful in the treatment of VSD in both adults and children. Such exercises have a general strengthening effect and are an excellent way to train the whole body and improve performance. Designed for the treatment of VSD and thought out taking into account age and health status, physical therapy should also exclude jumping. In general, an active lifestyle can be an integral component of the prevention of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Undergoing physical therapy
Therapeutic massage, water treatments, and reflexology also have a positive effect in the treatment of VSD. The physiotherapeutic effect is selected depending on the type of disease: it can be electrophoresis with calcium or caffeine (in the case of vagotonia) or with magnesium, papaverine or bromine (for the treatment of sympathicotonia).
Use of drug treatment
If general strengthening and physiotherapeutic measures are insufficient for the effective treatment of VSD, the specialist individually selects drug therapy, which may include the following drugs:
- sedatives that reduce the activity of autonomic reactions, antidepressants, nootropics;
- beta-blockers and herbal psychostimulants that help reduce vegetative-vascular manifestations;
- Vitamin-mineral complexes usually have a beneficial general strengthening effect.
If necessary, to treat various forms of VSD, a course of therapy is also carried out aimed at eliminating chronic foci of infection, concomitant endocrine or somatic pathology. The doctor regularly monitors a patient with vegetative-vascular dystonia. Clinical examination may be prescribed (every 3-6 months), especially in the autumn-spring period.
Prevention
Timely detection, treatment and consistent prevention lead to the disappearance or significant reduction of the main manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia (in 80-90% of cases). A full range of measures allows you to restore the body’s adaptive capabilities. A significant role in this is played by lifestyle correction, which includes normalizing the work regime, eliminating physical inactivity, providing daily dosed physical activity, limiting excessive emotional influences, and proper nutrition. An integral component of the prevention of vegetative-vascular dystonia is rest. It is extremely important to travel outside the city regularly. The best option would be to undergo treatment in a sanatorium, a stay in which not only allows you to fully relax from constant physical and psycho-emotional stress, but also provides the opportunity to undergo special procedures in one place.
If you are looking for a way to effectively treat and prevent VSD or want to undergo a comprehensive examination, contact the ABC-Medicine clinic. To contact specialists, dial our Moscow number +7.
Miracles of Pregnancy
There are cases where expectant mothers were not afraid to get pregnant with an existing diagnosis of VSD, and after giving birth they felt significantly better. This is due to the fact that under the influence of hormones that are released during pregnancy, the body changes its functioning. After the birth of the baby, the symptoms of the disease may either weaken or disappear forever. This natural treatment occurs in 10% of cases.
If you don’t want to give up and are ready to really, and not in words, fight for your full and happy life, you may be interested in this article .