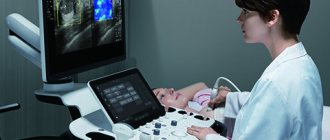
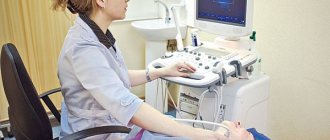
Frequent headaches and dizziness can be a consequence of vascular pathologies of the brain. In order to identify them, there are various diagnostic and research methods, one of which is duplex scanning of the vessels of the neck and head.
This method is non-invasive and therefore considered safe. What is especially attractive is that it does not require any special training and has no contraindications.
What is a diagnostic method
This method of vascular diagnostics provides complete information about the state of the human vascular system. Using ultrasound, you can evaluate and analyze the speed and nature of blood flow, as well as determine the presence of blood clots or other vascular pathologies.
The study usually proceeds in two stages: two-dimensional mode and duplex study.
Content:
- What is a diagnostic method
- Why is the procedure necessary?
- What is the difference between duplex and triplex scanning?
- Who needs the procedure
- Preparation for the procedure and contraindications
- How the procedure works
- Advantages and disadvantages of the technique
In two-dimensional mode, you can see the vessels and adjacent tissues, limited only by this information. It does not provide any information about blood supply.
With a duplex study, the doctor sees a complete picture of what is happening in the vessels, with a detailed description and a color two-dimensional picture.
Doppler ultrasound of the main arteries of the head: indications for performing
An ultrasound examination is prescribed by a neurologist for patients who have factors contributing to the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system, as well as during the treatment phase. Ultrasound scanning of the main arteries of the head, the price of which in the neurology clinic is available for patients with various financial capabilities, is performed in the following cases:
- for early diagnosis of thrombophlebitis;
- for thrombosis;
- for varicose veins, diagnosis is especially important in the severe stage of the disease;
- when preparing the patient for surgery to determine the location of the lesion;
- for pathologies of deep veins;
- when a patient is diagnosed with atherosclerosis of the main arteries of the head.
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital are attentive to the condition of each patient, therefore, before making a diagnosis, a comprehensive diagnosis and collection of information are carried out. When referring a patient for examination, the specialist explains what a triplex scan of the main arteries of the head shows and what results can be expected.
Why is the procedure necessary?
Unlike simple ultrasound, this diagnostic method provides the most complete information about hard-to-reach vessels of the neck and head. This is especially true of the brain, which is difficult to visualize.
Before the advent of the technique, examining the state of the brain was extremely difficult, if not almost impossible.
Diagnosis was carried out using Doppler ultrasound equipment. The sonographer applied the sensor to problem areas and recorded the sound using a special device.
But it became possible to see what was happening in the vessels of the cervical spine and brain only by using the duplex scanning technique.
Triplex scanning MAG in Moscow
A person who is scheduled for diagnosis seeks to find a clinic in close proximity to his home or place of work. If triplex scanning of the main arteries of the head is required, then the Nagornaya metro station is one of the most accessible and convenient for travel.
Near the Nagornaya metro station there is the Yusupov Hospital, which has several clinics, including a neurology clinic. Experienced doctors treat patients with various diseases of the nervous system. To diagnose violations, specialists use modern high-precision equipment. In the neurology clinic, the main arteries of the head are examined using ultrasound machines.
Patients of the clinic can undergo various tests at affordable prices. For the convenience of clients, various options for making an appointment are provided; in addition, you can visit a specialist at a convenient time without a long wait in line. In order to make an appointment with a neurologist and undergo an ultrasound scan of the main arteries of the head, please contact the clinic staff by phone.
What is the difference between duplex and triplex scanning?
These diagnostic methods are very similar to each other and have practically no differences, with the only difference being that with triplex scanning the vessels can be viewed in three-dimensional space. Duplex mode presents information in only two planes. In fact, triplex scanning is positioned as an additional procedure when conducting a duplex study.
And if we take into account the fact that the crystal transmitting and receiving the signal is the same, then the resolution of the triplex method is considered slightly worse than the duplex one. The quality of the work will depend entirely on the quality of the apparatus and the qualifications of the doctor conducting the research, and not on the diagnostic method.
Duplex scanning of head and neck vessels
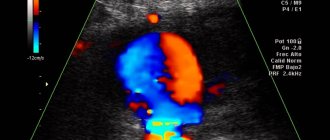
Duplex scanning (grayscale echography with color Doppler coding and spectral Doppler analysis, in relation to the intracranial part of the vascular system of the brain - transcranial duplex scanning) currently serves as the main method for diagnosing various types of pathology of the vascular system of the brain.
Duplex scanning combines the ability to visualize the lumen of the vessel and the tissues surrounding the vessel in B-mode (two-dimensional gray scale echography mode) and simultaneous analysis of the hemodynamic state using Doppler technologies. Based on the results of the study in B-mode, data can be obtained on the state of rigidity and elasticity of the vascular wall (elastic characteristics), the functional state of the endothelium (its vasomotor activity), the presence, nature and prevalence of changes in the structure and thickness of the vascular wall, violation of the integrity of the vascular wall (dissection), the presence of intraluminal formations, their localization, extent, echogenicity (an indirect characteristic of density), the degree of disturbance of the patency of the lumen of the vessel, changes in the diameter of the vessel, vascular geometry (presence of deformations, deviations of the course of the vessel from the usual anatomical trajectory), anomalies of origin, course and branching of blood vessels.
Indications for the study of extracranial sections of vessels supplying blood to the brain:
- clinical signs of acute or chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency, including headache syndrome;
- risk factors for the development of cerebrovascular diseases (smoking, hyperlipidemia, obesity, arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus);
- signs of damage to other arterial basins with the systemic nature of vascular processes;
- planning surgical interventions for various types of cardiac pathology, primarily coronary heart disease (coronary artery bypass grafting, coronary artery stenting);
- pathology of surrounding organs and tissues with the potential for extravasal effects;
- clinical signs of pathology of the jugular veins (usually thrombosis).
Indications for transcranial duplex scanning:
- detection of stenotic/occlusive pathology during duplex scanning (or Doppler ultrasound) of the extracranial sections of the brachiocephalic arteries - a potential source of cerebral blood flow disorders;
- the presence of indirect signs of damage to intracranial arteries;
- signs of acute or chronic cerebral ischemia without established specific causes of its development;
- headache syndrome;
- systemic vascular disease is a potential source of development of cerebral circulatory disorders (arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, systemic vasculitis, etc.).
- pathology of the brain substance (detected using other imaging techniques - CT, MRI, scintigraphy, etc.), accompanied by changes in its structure and cerebral vascular circulation, clinical signs of intracranial hypertension;
- the need for dynamic monitoring of cerebral blood flow indicators to assess the effectiveness of therapy in the acute period of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke and chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency, as well as to determine the condition of blood vessels at various stages of surgical revascularization, regardless of the type of the latter.
Currently, issues related to the use of imaging ultrasound methods in the clinic of urgent angioneurology are being actively developed. Based on the capabilities of duplex scanning, the research objectives for acute ischemic cerebrovascular accidents are as follows.
- Determination of possible causes of ischemic stroke.
- Study and assessment of background indicators of blood flow in extra- and intracranial arteries and veins and the state of reactivity of the cerebral circulatory bed.
- Establishment of sources of collateral redistribution of flows, their consistency and sufficiency.
- Monitoring the level of blood flow in one or more vessels to confirm the effectiveness of pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy.
CLINICAL CASE STUDY 1.
Patient T., 55 years old, was admitted to the therapeutic department due to dizziness, weakness, and decreased exercise tolerance. From the anamnesis: he has suffered from coronary artery disease for 8 years (AMI - 2009, PICS. In 2010 - CABG. In 2011 - surgery of carotid endarterectomy and stenting on the left.
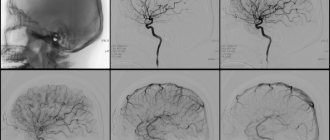
When performing duplex scanning of extra- and intracranial vessels, echographic signs of stenosis up to 90-95% along the ECA on the right and subocclusion-occlusion of the ICA on the right are determined (Fig. 1, 2)
Signs of stenosis in the V 2 segments of the vertebral arteries on both sides - according to spectral characteristics - 75-85% (right VA - in Fig. 3). In Fig. 4 – signs of subocclusion – occlusion of the CCA on the left (condition after stenting and endarterectomy – 2011).
During a transcranial study, there were signs of collateral blood flow (Fig. 6), with signs of an increase in LSV along the PCA on both sides, including against the background of stenosis of 50% (Fig. 5 - PCA on the right), with registration of retrograde blood flow in both eyes arteries (Fig. 7 - right HA).
Duplex scanning allows us to tentatively determine the possible causes of ischemic stroke.
When examining the extracranial sections of the brachiocephalic arteries, it is possible to identify differential signs characteristic of stenotic atherosclerosis, thrombosis, macroembolism, angiopathy, and vasculitis. In the absence of obvious causes of arterio-arterial embolism, and in some cases even if they are present, it is necessary to conduct an echocardiographic study to exclude the cardio-arterial origin of cerebrovascular accident.
The second possible cause of the development of acute ischemia is occlusion (or non-occlusive thrombosis) of cerebral arteries at the extra- and/or intracranial level.
CLINICAL CASE STUDY 2.
Patient N., 25 years old, was admitted to the study at the outpatient consultation department. From the anamnesis - pregnancy and childbirth 2 years ago. Over the past 3 months - discomfort in the throat. When examined by ENT specialists, there was no significant pathology.
When performing duplex scanning of the BCA, echographic signs of chemodectoma (paraganglioma, non-chromatoffin paraganglioma, carotid chemodectoma) are revealed - a benign neoplasm of the carotid glomus.
Carotid chemodectoma - (chemodectoma caroticum: synonym: carotid tumor, carotid paraganglioma, struma of the carotid gland) a tumor developing from the carotid glomus, located in the fork of the carotid arteries.
The tumor makes up about 60-70% of all paragangliomas of the head and neck: in most cases it is benign - malignancy is observed in 6-10% of cases. Criteria for malignancy are often the presence of relapses or metastases rather than morphological signs of the tumor. Carotid chemodectoma develops from the carotid glomus (carotid body, carotid paraganglion), which is often located in the area of branching of the common carotid artery . According to most researchers, the carotid glomus plays the role of a chemoreceptor - an informant to the central nervous system about chemical changes in the blood.
To date, more than 700 observations have been described. The tumor most often occurs in women 20 - 50 years old .
Malignant chemodectomas are observed in 15 - 20% of patients. The criterion for malignancy is the appearance of relapses and metastases; morphological signs are not always characteristic. Symptoms for chemodectomas are usually scant, and the only complaint of patients is most often the presence of a tumor; headache, dizziness or a brief fainting state when pressing on the tumor are less common. Chemodectomas are located under the sternocleidomastoid muscle of the neck at the site of division of the common carotid artery. The skin over the tumor is unchanged. The tumor is spherical or oblong, measuring from 2 to 6 cm or more, smooth or slightly lumpy. A characteristic feature of a chemodectoma is its displacement in the horizontal and lack of displacement in the vertical directions, the inability to divert the tumor from the pulsating vessel and transmission pulsation above the tumor. The criteria for malignant chemodectoma (15 - 20%) are rapid tumor growth, infiltration of surrounding tissues, the appearance of metastases and relapses after surgical treatment. The degree of spread of carotid chemodecoma in patients, according to the anatomical classification of the tumor according to Shamblin WR et al., 1971 - type I (“small” tumor) - the tumor is in close contact with the walls of both carotid arteries; was found in one patient. The size of the tumor (in diameter) reached 2.5 cm, its contours were in close contact with the medial walls of both carotid arteries. — type II (“large” tumor) — the tumor is in tight adhesion to the adventation of the carotid arteries (removal is considered difficult); was found in 2 patients. The tumor partially grew into the carotid arteries - in both cases its size was less than 5 cm. - type III (“large” tumor) - the tumor is in intimate adhesion with the adventitation of the carotid arteries (the degree of surgical risk is regarded as high); was found in the remaining 2 patients. The tumor completely enveloped the carotid arteries - its size was more than 5 cm. The rarity of the disease and the paucity of symptoms explain the difficulty of diagnosis. The correct diagnosis is established in 10 - 40% of patients. A puncture biopsy with cytological examination of the punctate and angiography are used. It is difficult to establish a cytological diagnosis of chemodectoma, however, in a number of patients, examination of tumor punctate allows one to reject this diagnosis (when obtaining elements of the thyroid gland, lymph node, etc.) It is to differentiate carotid chemodectoma with neuromas from the vagus, glossopharyngeal and hypoglossal nerves, lateral neck cysts , lymphadenitis (usually tuberculous etiology), lymphosarcoma and cancer metastases. Correct diagnosis will allow patients to be referred to specialized medical institutions involved in vascular surgery.
And fig. 1 – OSA on the right. In Figures 2, 3, you can see how the tumor covers the internal carotid artery on the right, tightly fused to the adventitia. The patient was urgently referred for consultation to a vascular surgeon at the VMA named after. S.M.Kirova.
Duplex scanning , like any other ultrasound technique, is operator-dependent and to a certain extent subjective. The success of using a complex of ultrasound imaging methods in clinical neurology, in addition to the experience and skills of the operator, largely depends on the technical characteristics of the equipment used. In this regard, in all controversial diagnostic cases, as well as when planning surgical treatment on cerebral vessels, the reference method in relation to ultrasound is X-ray contrast angiography and its varieties, recognized as the “gold standard” in angiology.
← Back
Who needs the procedure
Typically, a doctor prescribes such a procedure to a patient if he is diagnosed with: atherosclerosis or endarteritis, thrombophlebitis, thrombosis or vasculitis, aortic aneurysm, diabetic angiopathy, various vascular injuries, varicose veins, vascular anomalies of the head and neck, vertebral artery syndrome.
Such an examination is indicated as screening for asymptomatic diseases and as a control after surgical intervention in the vessels of the circulatory system.
Currently, transcranial duplex scanning of the vessels of the neck and head is considered mainly a technique for studying the vascular system. It is done using ultrasound with color Doppler mapping, as well as through spectral analysis.
The main indications for such an examination are:
- dizziness, severe headaches, migraines;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- deterioration of memory, attention;
- curvature of the spine in the cervical region, hernias in this area;
- hearing loss;
- chronic and acute cerebral ischemia;
- vasculitis and diabetes mellitus;
- vascular pathologies of the brain;
- various brain diseases with identified blood flow disorders after surgery.
What the study will show
Duplex scanning is based on the ability of an ultrasonic wave to be reflected from moving red blood cells. This is how a visual image of the vessels is formed. The objects of study are brachycephalic vessels: carotid, subclavian, vertebral arteries and intracranial vessels.
Duplex scanning of the great vessels of the head (MAG) allows you to see and evaluate in quite detail:
- The structure of the vascular network.
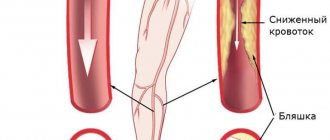
- The condition of large vessels and their walls - the size of the lumen in them, the presence of atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots, the elasticity of the walls, their thickening, stratification, stretching and other deformations.
- Type of pathology, place of its occurrence and other parameters.
This information will help identify symptoms of vascular pathologies, and with timely treatment, prevent cerebrovascular accidents and such acute and dangerous manifestations as stroke.
Preparation for the procedure and contraindications
This technique is especially popular precisely because it is absolutely harmless and has no contraindications. This procedure can be performed on patients regardless of age: both children and the elderly. You can repeat the manipulation as many times as necessary until the diagnosis is definitely established.
In addition, the diagnostic examination does not require any preliminary preparation. But there are some recommendations that will make this procedure much more effective.
On the day of the examination, stop nicotine and any other substances that to one degree or another affect vascular tone. This::
- coffee;
- energy;
- strong tea.
If you use any medications, such as adaptogens (schisandra chinensis, ginseng, etc.), magnesium, piracetam, vinpocetine, you should first notify the neurologist who prescribed this procedure. Before scanning, you need to get rid of jewelry from your neck and head: earrings, chains, hairpins and others. After the examination, you must wash your hair thoroughly.
Duplex MAG: service price
People diagnosed with stenosing atherosclerosis of the main arteries of the head and other vascular diseases strive to find a clinic that will provide medical care at an affordable price. At the Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, the price for diagnostic and therapeutic methods is optimal. In addition, the hospital provides rehabilitation programs for patients who have suffered strokes, suffer from dementia and other diseases.
A beneficial option for the rehabilitation of patients after Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, stroke, multiple sclerosis are comprehensive programs, including examination by experienced doctors, development of a rehabilitation program and other activities. If necessary, duplex scanning of the main arteries of the head and neck and other studies are performed.
When contacting the Yusupov Hospital, you can be confident in the accuracy of the diagnosis, the quality of treatment, and the friendly attitude of the staff. A personal quality manager helps patients resolve any issues. For the convenience of patients and their relatives, the clinic has created the necessary conditions: the ability to receive medical care 24 hours a day, healthy and tasty food, comfortable rooms with satellite TV and wireless Internet. If you need a triplex scan of the main arteries of the head or a consultation with a neurologist, please contact the clinic staff to make an appointment.
How the procedure works
This diagnostic method is absolutely painless and does not require general or local anesthesia. The patient is examined standing, lying or sitting, depending on which organ needs to be examined.
The surface of the skin is lubricated with a special gel, which facilitates signal transmission. The ultrasound technician then directs the probe to the desired area.
During duplex scanning of the brain, the sensor is placed in places called “ultrasonic windows” - parts of the skull where the bones are thinner or where there are physiological openings in them.
Through such zones, the ultrasound beam easily enters the cranial cavity.
During the procedure, the patient may be required to adopt a more comfortable position for the examination. The doctor may also ask you to hold your breath or do other similar actions. The manipulation lasts approximately half an hour and causes absolutely no discomfort.
Duplex scanning MAG in Moscow
At the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital you can undergo a MAG duplex scan. Diagnostics are carried out using highly informative ultrasound equipment that has sensitive sensors, due to which a specialist can objectively assess the parameters being studied and make a diagnosis based on the information received.
The experience and professionalism of the medical staff of the Yusupov Hospital allows us to successfully diagnose even minor problems and quickly choose tactics for eliminating them, using innovative techniques during therapy and recovery. Doctors at the Neurology Clinic, together with other specialists, provide detailed consultations to patients and their families in an accessible manner. Thus, the patient has information about the state of health, the course of the disease, and risk factors.
MAG duplex scanning in the neurology clinic is performed in accordance with current standards and legislation. The Yusupov Hospital offers affordable prices in the segment of highly informative ultrasound examinations. You can find out the details of the procedure, sign up for a consultation and diagnostics through a special form on the website, after which a clinic employee will contact you to clarify the details or by phone.
Make an appointment
Who is prescribed such a study?
The study is prescribed to identify the causes of headaches, with elevated cholesterol levels in tests, for early diagnosis of atherosclerosis, with pathologies of the spine, suspected tortuosity of the vessels supplying the brain, and frequent dizziness. To make a full diagnosis, an ultrasound examination of the vessels is performed both at the level of the neck and inside the skull.
Symptoms for which duplex scanning is indicated:
- pain in the head that appears with alarming and noticeable frequency;
- memory loss for a short period of time;
- dizziness;
- bleeding from the nose for no apparent reason;
- high cholesterol;
- mechanical damage in the neck area;
- noise in ears;
- the presence of certain diseases - stroke, heart attack, TIA, diseases caused by circulatory disorders, weakened blood flow, diabetes.
When assessing the results of a duplex study, a specialist considers a lot of characteristics and data, comparing them with normal indicators. What is important for the doctor is the thickness of the vessel wall (normally 0.12 cm), the location of the arteries relative to each other, surrounding tissues and organs, the speed of blood in different branches, the nature and presence of branches in certain areas, etc.
Duplex scanning not only reveals pathological processes when symptoms have already appeared, but also shows vascular pathologies at an early stage of their development. This allows you to prevent the disease in time and quickly begin treatment.
If the wall is thickened, it can be assumed that fat accumulates on it and connective tissue grows. If, with a thickened wall, the vascular layers are poorly distinguishable, this indicates vasculitis. When observing characteristic plaques in the vessels, we can talk about atherosclerosis (data on the location and size of plaques are of great importance for treatment).
Common advantages and disadvantages of the presented method
Duplex scanning has a number of obvious advantages:
- is highly informative;
- does not require the use of ionizing radiation;
- a cheaper and more accessible research method than alternative ones;
- carried out in real time, does not require waiting for a conclusion;
- helps to reflect the condition of soft tissues that are not sufficiently visualized on x-rays;
- non-invasive, performed without contrast (to which allergies are sometimes found), does not bring any unpleasant sensations;
- Suitable for children and pregnant women.
Any method, along with positive ones, also has negative sides, and in some cases it makes sense to choose other types of research. The decision is made by the doctor on an individual basis, after evaluating the results of other diagnostic procedures and tests, examination, and questioning of the patient.
The disadvantages of the method include:
- difficulty in examining small vessels;
- the possibility of diagnosis only during the research process, and not after it based on the results;
- narrow area to be examined because the bones of the adult skull impede the passage of ultrasound.
An important role in the quality of the diagnostics performed is played by the level of equipment and the professionalism of the doctor. This is one of the diagnostic methods to which increased demands are placed on the professionalism of doctors, so you should choose a clinic for duplex scanning especially carefully, because the result can differ significantly.
Technique for duplex brain scanning
The beginning of a duplex scan involves the doctor moving an ultrasound probe over the patient's head to examine intracerebral vessels or along the neck to examine the vertebral and carotid arteries. The sensor sends and picks up ultrasound signals from the walls of blood vessels, which the computer processes into an image. The information obtained makes it possible to detect impaired vascular patency and the causes of its formation, such as congenital pathologies and vascular loops, narrowing of the lumen and thickening of the walls of blood vessels, as well as the presence of blood clots and vascular junctions.
During duplex scanning, a specialist determines the speed and direction of blood flow, calculation of indices and distribution of blood circulation in the vessel, which allows obtaining complete and reliable information about the structure of the vessel being studied. To identify the mechanism of vascular regulation, blood flow is studied during stress tests and functional tests.