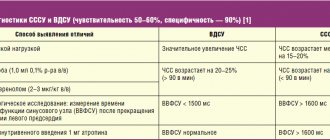
The condition when the heart beats slowly is called bradycardia. This term describes a slow or irregular heart rate (HR) that can cause dizziness or shortness of breath during normal daily activities or light exercise. The condition is defined as a heart rate less than 60 beats per minute. At this frequency, a sufficient amount of oxygenated blood cannot be distributed throughout the body.
Characteristics of the symptom
Typically the heart beats 60-90 times per minute. A person feels these contractions as a pulse when palpating the arteries. Under certain circumstances, heart activity may slow to below 60 beats per minute - in this case we are talking about bradycardia. Some people with slow heartbeats have serious problems with this condition, while others don't even know they have it.
Group 1 includes people whose slow heart rate is caused by other diseases, mainly dysfunction of the cardiac conduction system, disorders of the thyroid gland, and increased intracranial pressure. Group 2 includes athletes whose bradycardia is caused by training and is practically harmless.
Bradycardia
- home
- Articles
- Arrhythmias
- Types of arrhythmias
- Bradycardia
Bradycardia is a heart rate that is too slow.
It is important to distinguish pathology from the norm, because a low pulse does not always indicate problems with your heart. If since childhood you have had a pulse of 50-60 beats per minute and no pathology has been detected, and you feel great, most likely everything is fine with you. This is especially typical for people who are actively involved in sports: a trained heart pushes blood through the vessels much more efficiently - because of this, the heart of athletes beats quite rarely at rest (up to 40 beats per minute). When should you be wary? Firstly, if your heart has always beat at a frequency of 70-90 beats per minute, and then suddenly it began to beat at a frequency of 40-50 or lower. Secondly, if symptoms such as darkening of the eyes, unsteadiness of gait or loss of consciousness appear - i.e. signs that the heart cannot cope with its work and blood flows to the brain with a delay. The most common reason why the heart suddenly begins to beat rarely is a pathology of the sinus node, the place where the electrical impulse is born and where it comes from, exciting the entire heart. This is called sick sinus node syndrome (SSNS) and there are many reasons for it (from atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels to infectious heart disease - myocarditis). This syndrome is diagnosed simply - just do an ECG. Treatment: implantation under the skin of an electrical pacemaker (ECS) - a device that will artificially generate an impulse and work for the sinus node. Its dimensions are more than modest, its weight does not exceed 45 grams, its service life is from 5 to 10 years. Once a year, preventive examination and reprogramming (if required). It should be noted that one of the leading Russian specialists on the problem of SSSU is the scientific consultant of our Center, Professor V.A. Shulman. The second main reason is damage to the conduction pathways of the heart, when the impulse from the atria does not reach the ventricles. This is called AV block. It arises for the same reasons as SSSU. AV block has 3 degrees, which differ in the depth of damage: 1st degree - the impulse passes, but with a delay, 2nd degree - the impulse does not always pass and 3rd - the impulse does not pass at all. The worst thing is the 3rd degree, because the atria and ventricles begin to contract independently of each other (each in its own rhythm), which ultimately leads to ineffective blood circulation and increases the risk of sudden cardiac arrest. In terms of symptoms, diagnosis and treatment, AV block is very similar to SSSS: rare pulse, weakness, loss of consciousness; Taking an ECG is usually sufficient for diagnosis; it is treated by implantation of an pacemaker. And finally, the third main cause of bradycardia is hypothyroidism or decreased functioning of the thyroid gland. The fact is that an excess of thyroid hormones causes the heart to contract at an increased speed, and their deficiency leads to bradycardia. For diagnosis, you just need to donate blood for TSH (usually, when a person is diagnosed with bradycardia, an ECG and a blood test for TSH are prescribed to him immediately) and everything will fall into place. Treatment is replacement therapy. Typically, a lack of thyroid hormones is the result of a disease called autoimmune thyroiditis, which gradually affects the thyroid gland. Fortunately, in the 21st century, thyroid hormones have been synthesized a long time ago and it will be enough for a person to take them in the form of tablets, which is very convenient (unlike insulin, which can only be injected) Total:
— Bradycardia may be normal, especially in athletes. — If your pulse becomes less than 60 (although before that it was 70-80), and/or you have complaints of weakness, lethargy, darkening of the eyes or even loss of consciousness, this may indicate serious problems in the heart (for example, damage to the conduction systems heart) or hormonal dysfunction (thyroid problems). — For diagnosis, you need to do an ECG, take blood tests for TSH and consult a doctor.
For adults, a pulse of less than 60 beats is considered bradycardia. Bradycardia usually results from a whole range of concomitant diseases. With pronounced manifestations of bradycardia, the patient experiences: weakness, pain in the heart area, cold sweat, dizziness, fainting or complete loss of consciousness.
Basically, bradycardia can be caused by two reasons: the inability of the sinus node to generate impulses (the so-called sick sinus syndrome SSS) and poor conduction of these impulses. Bradycardia is often a consequence of coronary heart disease, arterial hypertension, myocarditis, taking certain medications, endocrine diseases, increased potassium levels in the blood, increased intracranial pressure, etc.
Methods for diagnosing bradycardia:
— Electrocardiography — Holter monitoring — Electrophysiological study — ECG by phone
IMPORTANT!
Heart rhythm disturbances are perfectly diagnosed and treated by all cardiologists at our Center.
Complex cases of cardiac arrhythmia requiring surgical correction are advised by cardiologists-arrhythmologists at the TERVE Medical Center on Partizana Zheleznyaka, 21A.
Particularly complex clinical cases (referred by cardiologists of our Center) are dealt with by cardiologist-arrhythmologist Professor G.V. Matyushin
Causes and diseases
Bradycardia is considered more of a physical disease. On the contrary, the human psyche increases heart rate. There are many reasons for the slowdown, so let’s look at the most common ones.
Sport
Professional athletes are usually well trained, and their cardiovascular system works effectively at rest, even at low frequencies. Therefore, it is not surprising that athletes often have a heart rate of about 50 beats per minute without accompanying symptoms. This bradycardia is discovered by chance, it is natural, does not limit a person, and does not jeopardize his health. For these reasons, she is not being treated.
Medicines
Bradycardia can be caused by medications that slow the heart rate. Most often, an overdose of β-blockers occurs. These drugs are prescribed primarily for heart disease. They have a wide range of effects - lowering blood pressure, reducing the risk of dangerous arrhythmias and, among other things, slowing heart rate, thereby reducing the impact of stress on the heart.
Overdosing on these drugs may slow your heart rate too much. The situation can be resolved relatively simply - by reducing the dose or discontinuing β-blockers. The risk of side effects from β-blockers is worsened when combined with certain calcium channel blockers (eg, Verapamil, Isoptin, Veragexal, Diacordin). Often the heart pumps slowly due to digoxin poisoning (severe bradycardia).
Decreased thyroid function
When the concentration of thyroid hormones decreases, cardiac activity slows down.
Sick sinus syndrome
This is a disease (English: Sick Sinus Syndrome - SSS), more common in old age. We are talking about a violation of the SA node, which is part of the cardiac conduction system. This is the area where electrical stimulation usually occurs. Excitement in the SA node propagates through the transmission system from the atrium to the ventricles, causing coordinated contractions of the myocardium. With sick sinus syndrome, the sinus node does not work properly, and the heart rate may be too slow and alternate with rapid atrial fibrillation. The cause of SA node failure is most likely due to age-related degeneration.
Disorder of the cardiac conduction system
When the SA node and atrial transport system are disrupted, the heart adapts and begins to generate electrical signals in the ventricular junction or ventricular region. But these areas cannot generate excitations with sufficient frequency, and the heart rate can drop to 40 beats per minute. A similar situation occurs with certain types of atrioventricular blockages, characterized by disturbances in the transmission of impulses from the atria to the ventricles.
Ion vibrations
Bradycardia often occurs as a concomitant sign of increased potassium concentrations.
What slows down the heart?
When examining a patient, a cardiologist may diagnose bradycardia. What is it? Bradycardia is a type of heartbeat disorder or arrhythmia in which the number of heart beats is less than 60 per minute. This term is used in medicine to describe a patient's symptoms during examination and during the diagnosis process. This disorder can be detected by counting the pulse. It leads to a lack of blood supply, as well as oxygen starvation of tissues and organs, which disrupts their full functioning. Bradycardia is of physiological and pathological types. Physiological appears in people involved in sports. In athletes, during sleep, the heartbeat slows down, since the body’s need for oxygen decreases in a calm state. Pathological bradycardia is observed in heart diseases and congenital defects. The heart rate can slow down after taking certain medications, with high ICP, in the presence of certain diseases, and even in a state of shock as a result of severe fright.
Associated symptoms
Slow heart action may not occur at all or may be accompanied by a variety of signs of heart failure. This is logical - a slow-working heart muscle ceases to sufficiently supply blood to tissues, including the brain.
Symptoms accompanying a slow pulse:
- dizziness;
- fainting;
- extreme fatigue;
- dyspnea;
- chest pain;
- problems with concentration;
- decrease in blood pressure.
Some people have no symptoms, or their symptoms are so mild that a slow heart rate is perceived as just a normal sign of aging.
Anemia
A disease that develops due to insufficient hemoglobin in the body. It is provoked by problems with the intestines, various infectious diseases, deficiency of vitamins and microelements.
Classification of anemia
Thus, vitamin deficiency anemia can cause shortness of breath and a number of other unfavorable symptoms, including:
- increased heart rate;
- impaired coordination and reflexes;
- general weakness;
- temperature increase.
Anemia - symptoms
Problems such as an increase in liver size and various types of mental disorders may occur.
Treatment
Bradycardia can occur as an independent condition or accompany other diseases. Therefore, it is important to determine its cause, and treat it accordingly. It is important to find out what medications the patient is taking. If beta-blockers are used, they should be stopped and replaced if necessary. If the cause of bradycardia is a thyroid disease, the disease must be controlled with medications (eg appropriate hormone tablets).
But, if the cause of a slow heartbeat is a dysfunction of the transport system, treatment is more complex. If the patient's condition is acute, medications that accelerate cardiac activity (Atropine, adrenaline) are prescribed, but their effect is short-term, and they cannot be used for a long time.
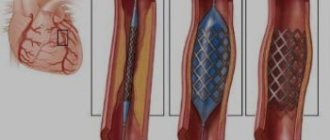
In the case of a disorder of the transfer system, the only long-term treatment option is the implantation of a pacemaker. A pacemaker is a small device implanted under the skin, most often under the collarbone on the left or right side of the chest. The pacemaker consists of a battery and computer circuits housed in a small metal case. The device constantly monitors heart rate.
When it detects a problem in the form of a slow rhythm, it sends a small electrical impulse aimed at correcting the problem.
FacebookvKontakteTwitterWhatsApp
Symptoms and treatment of bradycardia
In a person suffering from bradycardia , the brain and other important organs cannot receive enough oxygen.
As a result, symptoms such as:
- fainting;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- fatigue;
- breathing problems;
- chest pain;
- sleep disorders;
- memory problems.
Secrets of bradycardia prevention
Prevention of bradycardia is associated with the prevention of cardiovascular disease. People who have already developed heart disease should monitor it and follow the doctor's recommendations.
It is also important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, which includes: physical activity, a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, controlling cholesterol and blood pressure, stopping smoking and limiting alcohol consumption.
You should also avoid stress, which has a negative effect on the heart. Untreated bradycardia can be very dangerous to our health and life. Because of this, individuals at risk of bradycardia should remember to get regular checkups, as well as seek medical attention if alarming symptoms occur.
Heart rate stimulator
Electrical stimulation of the heart involves initiating its contractions using external electronic devices. The stimulator contains an electrical pulse generator, electrodes that transmit pulses and a microcomputer, which can be freely programmed, selecting individual settings for each specific patient. You can choose the heart rate, the strength and duration of the impulse, sensitivity and other parameters of its operation.
pacemaker implantation procedure is performed under local anesthesia. The electrode is inserted through a vein under the control of an X-ray machine, into the right ventricle, and sometimes into the right atrium.
During the implantation operation, measurements of heart parameters are taken to allow the device to be programmed correctly. The stimulator itself is implanted subcutaneously under the collarbone.
A patient with an implanted pacemaker should undergo routine annual examinations. Unfortunately, having an implanted system carries a certain risk of complications.
The most common are:
- movement of the electrode into the heart, causing disruption of pacing (in such a situation, another procedure is necessary);
- increasing the stimulation threshold (reprogramming the pacemaker is required);
- tachycardia (results from improper programming of the pacemaker);
- local infections: with weakened immunity, it can even lead to sepsis.