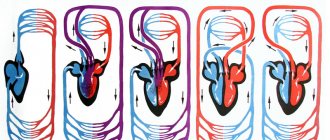
In the conditions of modern workload, the need to process the information flow, people are increasingly choosing a sedentary lifestyle, preferring to travel by transport, and as a result, diseases associated with physical inactivity are being discovered. In such conditions, every system suffers: neurology, gynecology, cardiology.
One of the serious consequences is stagnation of blood in the pelvis.
The very definition of “blood stagnation” means a violation of the natural outflow of blood from any area. Due to the location of a large number of organs in the pelvis, this disorder causes significant damage to the quality of life.
Pelvic organs:
- lower gastrointestinal tract, including the rectum;
- bladder;
- in women, reproductive organs: uterus, ovaries and vagina;
- in men: prostate gland and seminal vesicle.
All pelvic organs are secured by ligaments in their anatomical places and influence each other. The inflammatory process in one of them leads to inflammation in the others.
Causes of blood stagnation in the pelvis
The blood supply to the pelvic organs is carried out through the large abdominal aorta, the outflow occurs through the venous network, which has a special structure - without valves. Arterial vessels for guaranteed blood supply to each organ have redundant branches.
The main reasons that lead to stagnation of blood in the pelvis:
- Physical inactivity. With a sedentary lifestyle, the amount of adipose tissue increases, flabby muscles compress the blood vessels;
- Tight or tight underwear that compresses blood vessels also impairs blood flow;
- Varicose veins are a violation of the elasticity of blood vessels, their deformation;
- Bad habits: alcohol, smoking lead to vasospasm, and this undoubtedly affects blood circulation;
- Unbalanced diet. The vascular tissues are constantly renewed and, obviously, for a healthy state you need proper replenishment of nutrients that will maintain the elasticity of the walls;
- Problems with the nervous system. Prolonged stress leads to vasospasm, and, accordingly, blood flow worsens;
- Prolapse of internal organs. This may be due to childbirth, heavy pregnancy, or heavy lifting. Displaced organs compress the vessels and impede outflow;
- In women, stagnation can be caused by structural features of the uterus, for example, a bend, a side effect of taking oral contraceptives, or abortion.
Diet for phlebolitis
Nutrition for vascular diseases is aimed at strengthening the venous walls, normalizing blood flow and diluting it. Eating vegetables and fruits containing vitamins and quercetin, the routine helps thin the blood and improves the overall health of the immune and cardiovascular systems. Vegetables contain vitamins and microelements, fiber, which are beneficial for blood vessels, and can be consumed in any form. You should avoid vegetables that contain starchy substances and increase blood sugar levels. Fruits and berries, such as apples, cherries, cherries, rose hips, containing vitamin C and K, are very useful for poor blood clotting and as antioxidants. Frequent consumption of melons and watermelons, which contain very large amounts of liquid and sugars, should be avoided. Vegetable oils containing omega acids have a venotonic effect and contain vitamin E. The drinking regimen should consist of water and natural diluted juices.
It is not recommended to consume baked goods, confectionery products, fatty and fried foods, smoked foods, pickles and alcohol.
Symptoms
With stagnation, the negative effect accumulates. At the first stage, a person does not feel anything, but subsequently the condition worsens and the following symptoms appear:
- At the beginning, there are sensations of slight tingling and aching pain, which can worsen, for example, under stress;
- Feelings of heaviness in the abdomen, pressure;
- Pain in the lower abdomen, many go for a pelvic ultrasound to find out where the inflammation is. The pain often radiates to the lower extremities, lower back, thigh, and genitals;
- Numbness of the lower extremities. Impaired blood supply to the pelvic organs leads to a deficiency of blood in the legs, and swelling may develop;
- Frequent urination and urinary incontinence.
Symptoms can occur individually or together. As a rule, deterioration of the condition is observed after physical activity and sexual intercourse.
Our doctors
Drozdov Sergey Alexandrovich
Cardiovascular surgeon, phlebologist, Doctor of Medical Sciences
47 years of experience
Make an appointment
Malakhov Yuri Stanislavovich
Doctor - cardiovascular surgeon, phlebologist, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Doctor of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 36 years
Make an appointment
Diseases that develop against the background of blood stagnation
As a result of prolonged stagnation, diseases develop that have to be treated with medication and, in some cases, surgery.
The following pathologies are observed in women:
- Adnexitis, inflammation of the appendages;
- Menstrual irregularities;
- Miscarriage;
- Infertility.
In men, the diseases are as follows:
- Prostatitis;
- Varicocele;
- Impotence.
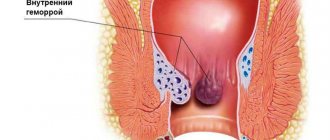
One of the most common ailments is hemorrhoids, and almost everyone notices a deterioration in their emotional state.
Treatment of inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs in women
Pelvic inflammatory diseases (PID) are characterized by various manifestations depending on the level of damage and the strength of the inflammatory response. The disease develops when a pathogen (enterococci, bacteroides, chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, trichomonas) penetrates into the genital tract and in the presence of favorable conditions for its development and reproduction. These conditions occur during the postpartum or post-abortion period, during menstruation, during various intrauterine manipulations (insertion of an IUD, hysteroscopy, hysterosalpingography, diagnostic curettage) [1, 5].
Existing natural protective mechanisms, such as anatomical features, local immunity, the acidic environment of the vaginal contents, the absence of endocrine disorders or serious extragenital diseases, can in the vast majority of cases prevent the development of genital infection. In response to the invasion of a particular microorganism, an inflammatory response occurs, which, based on the latest concepts of the development of the septic process, is usually called a “systemic inflammatory response” [16, 17, 18].
Acute endometritis always requires antibacterial therapy. The basal layer of the endometrium is affected by the inflammatory process due to the invasion of specific or nonspecific pathogens. Endometrial protective mechanisms, congenital or acquired, such as T-lymphocyte aggregates and other elements of cellular immunity, are directly related to the action of sex hormones, especially estradiol, act in conjunction with the macrophage population and protect the body from damaging factors. With the onset of menstruation, this barrier on a large surface of the mucous membrane disappears, which makes it possible to become infected. Another source of protection in the uterus is the infiltration of the underlying tissues with polymorphonuclear leukocytes and the rich blood supply of the uterus, which promotes adequate perfusion of the organ with blood and nonspecific humoral protective elements contained in its serum: transferrin, lysozyme, opsonins [16].
The inflammatory process can spread to the muscle layer: then metroendometritis and metrothrombophlebitis occur with a severe clinical course. The inflammatory reaction is characterized by a disorder of microcirculation in the affected tissues, expressed by exudation; with the addition of anaerobic flora, necrotic destruction of the myometrium can occur [12].
Clinical manifestations of acute endometritis are characterized already on the 3rd–4th day after infection by an increase in body temperature, tachycardia, leukocytosis and an increase in ESR. Moderate enlargement of the uterus is accompanied by pain, especially along its ribs (along the blood and lymphatic vessels). Purulent-bloody discharge appears. The acute stage of endometritis lasts 8–10 days and requires quite serious treatment. With proper treatment, the process is completed, less often it turns into subacute and chronic forms, and even less often, with independent and indiscriminate antibiotic therapy, endometritis can take a milder abortive course [5, 12].
Treatment of acute endometritis, regardless of the severity of its manifestations, begins with antibacterial infusion, desensitizing and restorative therapy.
Antibiotics are best prescribed taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen to them. The dosage and duration of antibiotic use are determined by the severity of the disease. Due to the frequency of anaerobic infections, additional use of metronidazole is recommended. Considering the very rapid course of endometritis, cephalosporins with aminoglycosides and metronidazole are preferable among antibiotics. For example, cefamandole (or cefuroxime, cefotaxime) 1.0–2.0 g 3–4 times a day IM or IV drip + gentamicin 80 mg 3 times a day IM + Metrogyl 100 ml IV /in drip.
Instead of cephalosporins, you can use semi-synthetic penicillins (for abortive cases), for example, ampicillin 1.0 g 6 times a day. The duration of such combination antibacterial therapy depends on the clinic and laboratory response, but should not be less than 7–10 days. To prevent dysbacteriosis from the first days of antibiotic treatment, use nystatin 250,000 units 4 times a day or Diflucan 50 mg/day for 1–2 weeks orally or intravenously [5].
Detoxification infusion therapy may include a number of infusion agents, for example, Ringer-Locke solution - 500 ml, polyionic solution - 400 ml, hemodez (or polydesis) - 400 ml, 5% glucose solution - 500 ml, 1% calcium chloride solution - 200 ml, Unithiol with a 5% solution of ascorbic acid, 5 ml 3 times a day. In the presence of hypoproteinemia, it is advisable to carry out infusions of protein solutions (albumin, protein), blood replacement solutions, plasma, red blood cells or whole blood, and amino acid preparations [12].
Physiotherapeutic treatment occupies one of the leading places in the treatment of acute endometritis. It not only reduces the inflammatory process in the endometrium, but also stimulates ovarian function. When normalizing the temperature reaction, it is advisable to prescribe low-intensity ultrasound, inductothermy with an HF or UHF electromagnetic field, magnetic therapy, and laser therapy.
Every fifth woman who has suffered salpingo-oophoritis is at risk of infertility. Adnexitis can cause a high risk of ectopic pregnancy and pathological course of pregnancy and childbirth. The fallopian tubes are the first to be affected, and the inflammatory process can involve all layers of the mucous membrane of one or both tubes, but more often only the mucous membrane of the tube is affected, and catarrhal inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tube occurs - endosalpingitis. Inflammatory exudate, accumulating in the tube, often flows through the ampullary opening into the abdominal cavity, adhesions form around the tube and the abdominal opening of the tube closes. A saccular tumor develops in the form of a hydrosalpinx with transparent serous contents or in the form of a pyosalpinx with purulent contents. Subsequently, the serous exudate of the hydrosalpinx resolves as a result of treatment, and the purulent pyosalpinx can perforate into the abdominal cavity. The purulent process can capture and melt increasingly large areas of the pelvis, spreading to all internal genitalia and nearby organs [9, 10, 13].
Inflammation of the ovaries (oophoritis) as a primary disease is rare; infection occurs in the area of the ruptured follicle, since the rest of the ovarian tissue is well protected by the covering germinal epithelium. In the acute stage, swelling and small cell infiltration are observed. Sometimes, in the cavity of the follicle of the corpus luteum or small follicular cysts, ulcers and microabscesses form, which, merging, form an ovarian abscess or pyovarium. In practice, it is impossible to diagnose an isolated inflammatory process in the ovary, and this is not necessary. Currently, only 25–30% of patients with acute adnexitis have a pronounced picture of inflammation; the remaining patients experience a transition to a chronic form, when therapy is stopped after a rapid subsidence of the clinic.
Acute salpingoophoritis is also treated with antibiotics (preferably third generation fluoroquinolones - Ciprofloxacin, Tarivid, Abaktal), since it is often accompanied by pelvioperitonitis - inflammation of the pelvic peritoneum.
Inflammation of the pelvic peritoneum most often occurs secondary to the penetration of infection into the abdominal cavity from an infected uterus (with endometritis, infected abortion, ascending gonorrhea), from the fallopian tubes, ovaries, from the intestines, with appendicitis, especially with its pelvic location. In this case, an inflammatory reaction of the peritoneum is observed with the formation of serous, serous-purulent or purulent effusion. The condition of patients with pelvioperitonitis remains either satisfactory or moderate. The temperature rises, the pulse quickens, but the function of the cardiovascular system is slightly impaired. With pelvioperitonitis, or local peritonitis, the intestine remains unbloated, palpation of the upper half of the abdominal organs is painless, and symptoms of peritoneal irritation are determined only above the pubis and in the iliac regions. However, patients note severe pain in the lower abdomen, there may be retention of stool and gas, and sometimes vomiting. The level of leukocytes is increased, the formula shifts to the left, the ESR is accelerated. Gradually increasing intoxication worsens the condition of patients [14, 15].
Treatment of salpingoophoritis with or without pelvioperitonitis begins with a mandatory examination of the patient for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics. The most important thing is to determine the etiology of inflammation. Today, benzylpenicillin is widely used for the treatment of specific gonorrheal process, although drugs such as Rocephin, Cephobid, Fortum are preferable.
The “gold standard” in the treatment of salpingoophoritis from antibacterial therapy is the prescription of Claforan (cefotaxime) at a dose of 1.0–2.0 g 2–4 times a day intramuscularly or one dose of 2.0 g intravenous in combination with gentamicin 80 mg 3 times/day (gentamicin can be administered once at a dose of 160 mg IM). It is imperative to combine these drugs with the administration of Metrogyl IV 100 ml 1-3 times a day. A course of antibiotic treatment should be carried out for at least 5–7 days, prescribing cephalosporins of the second and third generations (Mandol, Zinacef, Rocephin, Cephobid, Fortum and others at a dose of 2–4 g/day) [14].
In case of acute inflammation of the uterine appendages, complicated by pelvioperitonitis, oral administration of antibiotics is possible only after the main course, and only if the need arises. As a rule, there is no such need, and the persistence of previous clinical symptoms may indicate the progression of inflammation and a possible suppurative process.
Detoxification therapy is mainly carried out with crystalloid and detoxification solutions in an amount of 2–2.5 liters with the inclusion of solutions of hemodez, Reopoliglyukin, Ringer-Locke, polyionic solutions - acessol, etc. Antioxidant therapy is carried out with a solution of Unithiol 5.0 ml with a 5% solution of ascorbic acid 3 times/day i.v. [14].
In order to normalize the rheological and coagulation properties of blood and improve microcirculation, acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin) 0.25 g/day is used for 7–10 days, as well as intravenous administration of Reopoliglucin 200 ml (2–3 times per course). Subsequently, a whole complex of resorption therapy and physiotherapeutic treatment is used (calcium gluconate, autohemotherapy, sodium thiosulfate, Humisol, Plazmol, Aloe, FiBS) [3, 15]. Among the physiotherapeutic procedures for acute processes, ultrasound is appropriate, providing analgesic, desensitizing, fibrolytic effects, enhancing metabolic processes and tissue trophism, inductothermy, UHF therapy, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, and later - sanatorium-resort treatment.
Among 20–25% of inpatients with inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages, 5–9% develop purulent complications requiring surgical interventions [9, 13].
The following provisions regarding the formation of purulent tubo-ovarian abscesses can be highlighted:
- chronic salpingitis in patients with tubo-ovarian abscesses is observed in 100% of cases and precedes them;
- the spread of infection occurs predominantly through the intracanalicular route from endometritis (with IUD, abortion, intrauterine interventions) to purulent salpingitis and oophoritis;
- frequent combination of cystic transformations in the ovaries with chronic salpingitis;
- there is a mandatory combination of ovarian abscesses with exacerbation of purulent salpingitis;
- Ovarian abscesses (pyovarium) are formed mainly from cystic formations, often microabscesses merge with each other.
Morphological forms of purulent tubo-ovarian formations:
- pyosalpinx - predominant lesion of the fallopian tube;
- pyovarium - predominant damage to the ovary;
- tubo-ovarian tumor.
All other combinations are complications of these processes and can occur:
- without perforation;
- with perforation of ulcers;
- with pelvioperitonitis;
- with peritonitis (limited, diffuse, serous, purulent);
- with pelvic abscess;
- with parametritis (posterior, anterior, lateral);
- with secondary lesions of adjacent organs (sigmoiditis, secondary appendicitis, omentitis, interintestinal abscesses with the formation of fistulas).
Clinically differentiating each of these localizations is almost impossible and impractical, since the treatment is fundamentally the same; antibacterial therapy takes a leading place both in the use of the most active antibiotics and in the duration of their use. The basis of purulent processes is the irreversible nature of the inflammatory process. Irreversibility is due to morphological changes, their depth and severity, often accompanying severe renal dysfunction [3, 9].
Conservative treatment of irreversible changes in the uterine appendages is unpromising, since if it is carried out, it creates the preconditions for the occurrence of new relapses and aggravation of impaired metabolic processes in patients, increases the risk of upcoming surgery in terms of damage to adjacent organs and the inability to perform the required volume of surgery [9].
Purulent tubo-ovarian formations represent a difficult diagnostic and clinical process. Nevertheless, a number of characteristic syndromes can be identified:
- intoxication;
- painful;
- infectious;
- early renal;
- hemodynamic disorders;
- inflammation of adjacent organs;
- metabolic disorders.
Clinically, intoxication syndrome manifests itself in intoxication encephalopathy, headaches, heaviness in the head and severity of the general condition. Dyspeptic disorders (dry mouth, nausea, vomiting), tachycardia, and sometimes hypertension (or hypotension in the onset of septic shock, which is one of its early symptoms along with cyanosis and facial hyperemia against the background of severe pallor) are noted [4].
Pain syndrome is present in almost all patients and is of an increasing nature, accompanied by a deterioration in general condition and well-being, there is pain during a special examination, displacement behind the cervix and symptoms of irritation of the peritoneum around the palpable formation. Pulsating increasing pain, persistent fever with a body temperature above 38°C, tenesmus, loose stools, lack of clear contours of the tumor, lack of effect from treatment - all this indicates the threat of perforation or its presence, which is an absolute indication for urgent surgical treatment. The infectious syndrome is present in all patients, manifested in the majority by high body temperature (38°C and above), tachycardia corresponds to fever, as well as an increase in leukocytosis, ESR and leukocyte index of intoxication increase, the number of lymphocytes decreases, the shift of white blood to the left and the number of molecules of average mass, reflecting increasing intoxication. Often there is a change in kidney function due to impaired urine passage. Metabolic disorders manifest themselves in dysproteinemia, acidosis, electrolyte imbalance, etc.
The treatment strategy for this group of patients is based on organ-preserving principles of surgery, but with radical removal of the main source of infection. Therefore, for each specific patient, the volume of the operation and the time of its implementation should be optimal. Clarifying the diagnosis sometimes takes several days - especially in cases where there is a borderline variant between suppuration and an acute inflammatory process or in differential diagnosis from an oncological process. Antibacterial therapy is required at each stage of treatment [1, 2].
Preoperative therapy and preparation for surgery include:
- antibiotics (use Cefobid 2.0 g/day, Fortum 2.0–4.0 g/day, Reflin 2.0 g/day, Augmentin 1.2 g IV drip 1 time/day, Clindamycin 2.0– 4.0 g/day, etc.). They must be combined with gentamicin 80 mg IM 3 times a day and Metrogyl infusion 100 ml IV 3 times;
- detoxification therapy with infusion correction of volemic and metabolic disorders;
- mandatory assessment of the effectiveness of treatment based on the dynamics of body temperature, peritoneal symptoms, general condition and blood counts.
The surgical stage also includes ongoing antibacterial therapy. It is especially valuable to administer one daily dose of antibiotics on the operating table immediately after the end of the operation. This concentration is necessary as a barrier to further spread of infection, since penetration into the area of inflammation is no longer prevented by dense purulent capsules of tubo-ovarian abscesses. Betalactam antibiotics (Cephobid, Rocephin, Fortum, Claforan, Tienam, Augmentin) pass these barriers well.
Postoperative therapy includes the continuation of antibacterial therapy with the same antibiotics in combination with antiprotozoal, antimycotic drugs and uroseptics in the future (according to sensitivity). The course of treatment is based on the clinical picture and laboratory data, but should not be less than 7–10 days. Antibiotics are discontinued based on their toxic properties, so gentamicin is often discontinued first, after 5–7 days, or replaced with amikacin.
Infusion therapy should be aimed at combating hypovolemia, intoxication and metabolic disorders. Normalization of gastrointestinal motility is very important (intestinal stimulation, HBOT, hemosorption or plasmapheresis, enzymes, epidural blockade, gastric lavage, etc.). Hepatotropic, restorative, antianemic therapy is combined with immunostimulating therapy (UVR, laser blood irradiation, immunocorrectors) [2, 9, 11].
All patients who have undergone surgery for purulent tubo-ovarian abscesses require post-hospital rehabilitation in order to prevent relapses and restore specific body functions.
Literature
- Abramchenko V.V., Kostyuchek D.F., Perfileva G.N. Purulent-septic infection in obstetric and gynecological practice. St. Petersburg, 1994. 137 p.
- Bashmakova M. A., Korkhov V. V. Antibiotics in obstetrics and perinatology. M., 1996. No. 9. P. 6.
- Bondarev N. E. Optimization of diagnosis and treatment of mixed sexually transmitted diseases in gynecological practice: abstract. dis. ...cand. honey. Sci. St. Petersburg, 1997. 20 p.
- Ventsela R.P. Nosocomial infections // M., 1990. 656 p.
- Gurtovoy B. L., Serov V. N., Makatsaria A. D. Purulent-septic diseases in obstetrics. M., 1981. 256 p.
- Keith L. G., Berger G. S., Edelman D. A. Reproductive health: Vol. 2 // Rare infections. M., 1988. 416 p.
- Krasnopolsky V.I., Kulakov V.I. Surgical treatment of inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages. M., 1984. 234 p.
- Korkhov V.V., Safronova M.M. Modern approaches to the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the vulva and vagina. M., 1995. No. 12. P. 7–8.
- Kumerle X. P., Brendel K. Clinical pharmacology during pregnancy / ed. X. P. Kumerle, K. Brendel: trans. from English T. 2. M., 1987. 352 p.
- Serov V.N., Strizhakov A.N., Markin S.A. Practical obstetrics: a guide for doctors. M., 1989. 512 p.
- Serov V.N., Zharov E.V., Makatsaria A.D. Obstetric peritonitis: diagnosis, clinic, treatment. M., 1997. 250 p.
- Strizhakov A. N., Podzolkova N. M. Purulent inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages. M., 1996. 245 p.
- Khadzhieva E. D. Peritonitis after cesarean section: a textbook. St. Petersburg, 1997. 28 p.
- Sahm DE The role of automation and molecular technology in antimicrobial susceptibility testing // Clin. Microb. And Inf. 1997; 3: 2(37–56).
- Snuth CB, Noble V., Bensch R. et al. Bacterial flora of the vagina during the mensternal cycle // Ann. Intern. Med. 1982; p. 948–951.
- Tenover FC Norel and emerging mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in nosocomial pathogens // Am. J. Med. 1991; 91, p. 76–81.
V. N. Kuzmin, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor MGMSU, Moscow
Treatment
Treatment of diseases caused by blood stagnation is only a temporary measure. In any case, if there is a reason why the outflow is disrupted, then it must be eliminated; in order to receive recommendations, you need to schedule a visit to a therapist. It is very important to deal with the root problem; in most cases, diet and increased physical activity help, but this will have to be approached under the supervision of a doctor so as not to stimulate deterioration.
At the Heratsi Medical Center you can visit a therapist for free. It is also possible to invite a doctor to your home.
The cost of all services of the medical center can be viewed in the “Price” section or by calling the 24-hour hotline.
Watch a video with a simple exercise that will help get rid of blood stagnation in the pelvis:
Discovery and description of phleboliths
Phleboliths in the pelvis - what is it? These are vein stones, which are calcifications of dried blood clots and look like beads of different diameters.
Phleboliths were first described and discovered by Albers-Schoenberg in 1905. The nature of their origin was described by pathologists Frenkel and Forsel. Phleboliths have a homogeneous and layered shadow with a dense center. Homogeneous phleboliths are formed during the sequential calcification of a blood clot. And layered - when fibrin threads join the calcification process.
Potential health hazard
Pelvic congestion is a health problem that is often mistakenly taken insufficiently seriously by both doctors and patients. In fact, difficulties with blood circulation in this area can cause real illnesses that significantly reduce the quality and length of life. Aesthetic defects associated with the manifestation of dilated veins are only a harmless symptom. The main negative impact of this pathology is on reproductive function. Difficult onset of pregnancy and its difficult course, problems with the cycle, its regularity and abundance of discharge, excessive ovarian function, lack of orgasms - women face this. Men suffer from decreased libido and erectile dysfunction, accelerated ejaculation, hemorrhoids, painful urination and ejaculation. In addition, stagnation in the pelvis entails venous insufficiency of the lower extremities - this already applies to representatives of both sexes.
Risk group
As practice shows, the likelihood of tumors appearing in the genitourinary system increases in men:
- Those who abuse tobacco products. According to statistics, kidney cancer is diagnosed in smokers 2 times more often.
- Middle aged (after 45 years). This is due to a decrease in the level of male sex hormones along with an increase in female ones.
- People who work in hazardous industries (for example, when a person often comes into contact with hazardous chemicals).
- Those who have been on dialysis for a long time. This often leads to kidney cancer.
What are blockades
Therapeutic blockades are the relief of acute or chronic pain and spasms. It is performed by injection into the area where the nerve trunks and plexuses pass. Severe pain causes physical and psychological suffering, incapacitates the patient and can cause disability. Depression that occurs against this background often leads to suicide attempts.
Therapeutic blockades quickly relieve acute pain. After some time, swelling, inflammation, spasm of muscles and blood vessels decrease. This leads to a lasting improvement in the condition. At the 100med medical center, blockades are performed by neurologists and anesthesiologists. Several groups of drugs are used for the procedure:
- local anesthetics;
- corticosteroid hormones;
- chondroprotectors.
The effect of drug administration lasts from several days to several weeks. After the medicine stops working, the pain may return. However, its severity will be less by about 50%.
During the procedure, the patient may feel some discomfort associated with the injection. However, the discomfort quickly passes. There is no need to be afraid of blockades, as this method is one of the safest. Our specialists strictly follow all the rules for performing the procedure, as well as asepsis and antiseptics. This guarantees the effectiveness and safety of blockades in our clinic.
Joint blockade
Joint blockade is a method of introducing a drug into the joint cavity or adjacent soft tissues (articular capsule). The method not only relieves pain, but eliminates inflammation, relieves muscle and vascular spasm, and restores range of motion in the joint. The procedure is indicated for the following diseases:
- arthritis of joints of various sizes;
- arthrosis;
- arthralgia;
- synovitis;
- bursitis;
- tendovaginitis;
- periarthritis;
- facet syndrome;
- Reiter's disease;
- Bekhterev's disease.
The injection is performed without additional preparation after a thorough examination. The patient is seated or laid on a couch and the skin over the joint is treated. The injection is made into the cavity of the joint capsule, into the area of the periarticular ligaments or bursa. The effect occurs within a few minutes and lasts up to 3 weeks. The duration of the course depends on the severity of the lesion and can be up to 15 procedures.
How to prevent phlebolithiasis
The risk of developing venous stones increases when patients have a tendency to develop blood clots. Taking this into account, prevention of the formation of phleboliths and calcifications includes the following measures:
- increased tone of venous vessels;
- elimination of stagnation;
- timely treatment of diseases of the pelvic organs;
- normalization of blood viscosity;
- regulation of metabolic processes.
It is necessary to pay due attention to sports, swimming and cycling are especially useful.
At the first signs of varicose veins, you should consult a phlebologist and undergo an examination. The prognosis for phlebolithiasis is favorable. Small vein stones do not require treatment. People with this pathology are advised to monitor the condition of the coagulation system, as well as monitor blood viscosity, calcium and hormone levels.
Celiac plexus block
With this type of blockade, the medicine is injected into the solar plexus area. The injection is done under the control of an X-ray machine or ultrasound.
The procedure is effective for:
- chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic necrosis;
- abdominal adhesions;
- Crohn's disease;
- tumors of the abdominal organs;
- ineffectiveness of painkillers.
You should prepare for the blockade in advance. A few days before the procedure, the doctor at our clinic recommends stopping taking anticoagulants and diuretics and adjusting the dose of glucose-lowering medications. The patient is placed on his stomach with a bolster or pillow. First, the doctor anesthetizes the soft tissue at the injection site. Then, under X-ray control, a special long needle is inserted. Through it, a local anesthetic or a drug that destroys nerve cells is supplied to the solar plexus. The patient feels warmth in the abdomen and a decrease in pain. After the procedure, observation is required in our hospital for 24 hours.
Paravertebral blockade
Paravertebral blockade is performed to reduce pain in the spine. The effect is achieved by blocking the ganglia or spinal nerves on one or both sides. Indications for this are:
- osteochondrosis;
- radiculitis, lumbago;
- neuralgia;
- myositis;
- hernias and protrusions of intervertebral discs;
- spinal injuries.
To carry out the manipulation, the patient is placed on a flat couch. Local soft tissue anesthesia is first performed. The medicine is injected into the segment of the spine where the pain is felt the most. The injection is given on one or both sides depending on the patient’s condition.
Diagnostics
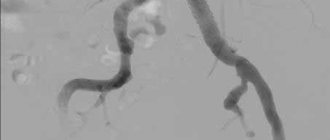
Making a diagnosis requires collecting a complete patient history, as well as studying the results of functional diagnostics. The doctor takes into account factors such as the patient’s age, lifestyle, the presence of chronic diseases, the number of pregnancies and births in women, and the presence of diagnosed vascular problems.
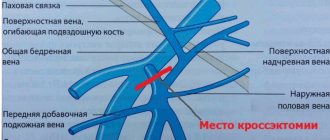
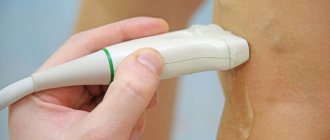
During the examination of the patient, the doctor assesses the visibility of dilated veins in the groin area and examines the genitals for nodules. A gynecological examination in a chair in women can reveal by palpation the soreness of the vaginal walls and detect hidden internal nodes. Men are examined in the abdomen, groin, and anus. The condition of the veins is visualized using ultrasound and x-ray examination. Through venography, it is possible to assess the presence of reflux in the veins; Doppler ultrasound allows one to assess the parameters of the veins. For advanced cases, when it is difficult to carry out a differential diagnosis using the listed methods, abdominal ultrasound, MRI, and even laparoscopy may be recommended.