Impaired glucose tolerance is a real problem in the modern world. Cases of detection of such violations have become significantly more frequent and the reason for this is the change in the rhythm of modern life.
The main provoking factor is physical inactivity. After a hard day's work, a person does not have the strength to walk or visit a fitness center and it is much more convenient for him to relax on a comfortable sofa in front of his own TV screen.
The next factor, literally creeping on the previous one, is poor nutrition. A hearty and certainly fatty, high-calorie dinner allows you to instantly cope with hunger that is not satisfied during the day.
A person believes that he hasn’t eaten all day, but only burned calories, so he can afford it. But the body will not agree with him.
Impaired glucose tolerance is a pathological change, the manifestation of which can be prevented, how to do this and, most importantly, how to detect the change in time? Answers to the main questions are presented to the reader.
A harbinger of SD.
What does NTG mean?
Everyone knows that diabetes is an incurable disease. But its danger is often underestimated. People do not understand that diabetes is the need for regular monitoring of blood sugar throughout life, and overall well-being largely depends on the number on the glucometer.
Many people do not think about the dangerous complications of the disease that arise when the basic recommendations provided for diabetics are not followed. DM cannot be cured, but its development can be prevented.
In this matter, the optimal means of prevention is the timely detection of impaired glucose tolerance. With early detection and taking the necessary measures, you can prevent the development of a dangerous disease or delay the manifestation of the disease for many years.
Carbohydrates consumed in food are broken down into glucose and fructose during the digestion process. glucose immediately enters the bloodstream. An increase in blood sugar concentration increases the activity of the pancreas; it produces the hormone insulin, which helps sugar get from the blood to the body's cells. Glucose in cells is a source of energy and ensures adequate metabolic processes.
What does such a diagnosis mean?
For a healthy person, the time limit given to absorb a portion of glucose is no more than 2 hours. After this period, sugar levels return to normal. If the marks remain marginal, a violation of tolerance is diagnosed.
Attention! Diabetes mellitus can be diagnosed if, after 2 hours after the test, the sugar level has not stabilized, but remains within the limit of about 11 mmol/l.
Prediabetes is a disorder of glucose tolerance. Such a violation implies the manifestation of a complex of changes:
- against the background of disruption of the process of insulin production by pancreatic cells, the concentration of the hormone in the body decreases,
- the sensitivity of membrane proteins to insulin is significantly reduced.
It is worth remembering that a blood sugar test for IGT taken on an empty stomach in most cases shows the norm.
This is due to the fact that overnight, the human body is still able to efficiently process the glucose that enters the blood. Based on this information, we can conclude that such a study is not enough to detect prediabetes.
Poor nutrition.
Impaired fasting glucose is diagnosed when blood sugar levels exceed acceptable limits, but do not reach levels that allow diagnosing the development of diabetes mellitus.
Treatment of IGT
What to do if NTG is confirmed?
Typically clinical recommendations are as follows:
- regularly monitor blood sugar levels;
- monitor blood pressure readings;
- increase physical activity;
- follow a diet to achieve weight loss.
Additionally, medications may be prescribed to help reduce appetite and accelerate the breakdown of fat cells.
The importance of proper nutrition
Adhering to the principles of proper nutrition is useful even for a completely healthy person, but in a patient with a disorder of carbohydrate metabolism, changing the diet is the main point of the treatment process and following a diet should become a way of life.
The dietary rules are as follows:
- Fractional meals. You need to eat more often, at least 5 times a day and in small portions. The last snack should be a couple of hours before bedtime.
- Drink 1.5 to 2 liters of clean water daily. This helps thin the blood, reduce swelling and speed up metabolism.
- Bread products made from wheat flour, as well as desserts with cream, sweets and candies are excluded from consumption.
- Limit consumption of starchy vegetables and alcoholic beverages to a minimum.
- Increase the amount of fiber-rich vegetables. Legumes, greens and unsweetened fruits are also allowed.
- Reduce the consumption of salt and spices in your diet.
- Replace sugar with natural sweeteners; honey is allowed in limited quantities.
- Avoid dishes and foods with a high percentage of fat in the menu.
- Low-fat dairy and fermented milk products, fish and lean meat are allowed.
- Bread products must be made from whole grain or rye flour, or with the addition of bran.
- For cereals, give preference to pearl barley, buckwheat, and brown rice.
- Significantly reduce high-carbohydrate pasta, semolina, oatmeal, and refined rice.
Avoid fasting, overeating, and low-calorie diets. The daily calorie intake should be in the range of 1600-2000 kcal, where complex carbohydrates account for 50%, fats approximately 30% and protein foods 20%. If you have kidney disease, the amount of protein decreases.
Physical exercise
Another important point of therapy is physical activity. To lose weight, you need to provoke intense energy expenditure, in addition, this will help reduce sugar levels.
Regular physical exercise accelerates metabolic processes, improves blood circulation, strengthens vascular walls and heart muscle. This prevents the development of atherosclerosis and heart disease.
Aerobic exercise should be the main focus of physical activity. They lead to an increase in heart rate, which accelerates the breakdown of fat cells.
For people suffering from hypertension and pathologies of the cardiovascular system, low-intensity exercises are more suitable. Slow walks, swimming, simple exercises, that is, anything that does not lead to increased blood pressure and shortness of breath or heart pain.
For healthy people, classes should be more intense. Running, jumping rope, cycling, skating or skiing, dancing, and team sports are suitable. A set of physical exercises should be designed in such a way that the majority of the workout is aerobic exercise.
It is good to alternate the intensity of the loads, starting with a slow pace, then speeding up and again reducing the pace of movements.
The main condition is regularity of classes. It is better to devote 30-60 minutes daily to sports activities than to exercise for two to three hours once a week.
It is important to monitor your well-being. The appearance of dizziness, nausea, pain, and signs of hypertension should be a signal to reduce the intensity of the exercise.
Reasons for the manifestation of the disorder
The cause of IGT may be due to the influence of certain factors:
| What factors can provoke impaired glucose tolerance? | ||
| Factor | Description | Characteristic photo |
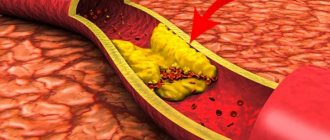
| Excess weight | Patients whose BMI (body mass index) exceeds 27 are at particular risk. This is due to the fact that it takes a lot of energy to support a “large” body and, as a result, organs such as the heart, kidneys and pancreas suffer first of all, that is wear out quickly. |
|
| Physical inactivity | The patient's consumption of high-calorie, carbohydrate-rich foods leads to the body working in an overly active rhythm. The pancreas produces insulin spasmodically, in significant doses. A significant amount of excess glucose entering the blood is converted into fat. |
|
| Genetics | Having diabetes in one or both parents increases the likelihood that the child will develop the disease. However, the statistics are quite adequate - if all recommendations are followed, the risk of developing the disease does not exceed 5%. The most unfavorable prognosis for identifying type 2 diabetes in a twin is 90%. |
|
| Gender | IGT is more often encountered by females over the age of 45 years. |
|
| Pancreatic lesions | The list of predisposing factors includes pancreatitis, the presence of tumors, cysts and all kinds of injuries to the pancreas. |
|
| ES pathologies | Pathologies of the endocrine system often lead to imbalance of hormones, which in turn causes metabolic failures. |
|
| Gynecological diseases | Impaired glucose tolerance is often detected in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. |
|
The video in this article will introduce readers to the reasons for the manifestation of NTG in more detail.
How does impaired glucose tolerance manifest?
There are no characteristic symptoms.
There are no intense disturbances that could indicate the development of IGT. When glucose tolerance is impaired, blood sugar increases slightly and for a short period of time, therefore any characteristic changes indicating the development of pathology may in this case appear only after several years.
In this case, IGT is detected in conjunction with the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the patient.
Symptoms of IGT can be presented as follows, but the patient must remember that they do not always appear:
- large amounts of fluid intake, due to the constant presence of dryness in the mouth - thus, the body tries to reduce the concentration of sugar in the blood,
- frequent urination due to active fluid intake,
- the patient complains of a feeling of heat, nausea and dizziness after eating,
- periodic headaches.
The listed symptoms are not specific, therefore their manifestation cannot indicate the development of IGT in the patient. Data obtained from the use of a home glucometer are also not always informative and their reliability must be confirmed by a laboratory test.
Blood collection process.
Attention! Diagnosis of impaired glucose tolerance involves a special test to determine whether the patient suffers from metabolic disorders.
Present danger
The main danger of impaired glucose tolerance is the development of type 2 diabetes in the patient. Statistics indicate that in approximately 30% of cases the human body copes with disorders on its own and no outside intervention is required.
In 70% of cases, people unaware of a TG disorder live with a similar change, which gradually turns into acquired diabetes. In order to reduce the likelihood of developing a disease that has many complications, it is worth conducting an annual examination to identify indicators of glucose tolerance.
The main danger.
Attention! Patients at risk of developing the disease should regularly visit an endocrinologist.
Principles of therapy
A glucose tolerance test may indicate the development of carbohydrate metabolism disorders in the human body. Patients who receive such results should treat their health with great attention. It is imperative to register with an endocrinologist. The doctor will monitor the progress of the recovery process.
How to prevent diabetes.
Attention! Treating IGT is hard work. The patient will have to carefully reconsider his own lifestyle and change his attitude towards bad habits, completely abandoning them.
Proper nutrition
The main cause of impaired glucose tolerance is excess insulin in the blood, produced by pancreatic cells as a response to eating carbohydrates. To restore the sensitivity of cells and restore their ability to absorb the hormone, its concentration should be reduced. This is extremely simple to do - the patient must limit the consumption of foods containing sugar.
Normalization of diet.
Attention! The instructions drawn up by a nutritionist require the patient to sharply reduce the amount of carbohydrates consumed. It is worth eliminating foods with a high glycemic index from the menu. The cost of not following these rules is high.
The list of basic recommendations can be presented in the format of the following rules:
- The patient should eat often, but in small portions.
- It is worth paying attention to the need to count calories. The permissible food intake is divided into 4-5 approaches.
- The patient should consume enough water.
- The basis of the diet can be vegetables and fruits - that is, foods with zero calorie content.
The patient's menu should be balanced, but carbohydrates should make up a smaller proportion of the diet. If this rule is not followed, therapy will be ineffective.
Sport
In order to reduce the likelihood of diabetes, the patient must completely change his own rhythm of life for the better. Change also requires daily exercise.
Running and morning exercises will benefit the patient's body. If possible, Nordic walking and pool swimming are acceptable sports.
Light physical activity.
After exercise, the patient should not feel excessive fatigue. All exercises performed should bring pleasure and satisfaction.
The attention of patients with impaired glucose tolerance should be focused on the fact that resorting to the use of medications to stabilize well-being is possible only in an emergency. In some cases, such drugs cause harm to the patient’s body and can cause the development of diabetes, that is, accelerate the course of an already running process.
Diagnostic methods
If IGT is suspected, the patient is sent for a consultation with an endocrinologist. The specialist collects information about the patient’s lifestyle and habits, clarifies complaints, the presence of concomitant diseases, as well as cases of endocrine disorders among relatives.
The next step is to order tests:
- blood biochemistry;
- general clinical blood test;
- urine test for uric acid, sugar and cholesterol.
The main diagnostic test is a tolerance test.
Before conducting the test, a number of conditions must be met:
- the last meal before donating blood should be 8-10 hours before the test;
- Nervous and physical stress should be avoided;
- do not drink alcohol for three days before the test;
- do not smoke on the day of the study;
- You cannot donate blood if you have viral or colds or after a recent surgery.
The test is carried out as follows:
- Blood sampling for the test is taken on an empty stomach;
- the patient is given a glucose solution to drink or the solution is administered intravenously;
- After 1-1.5 hours, the blood test is repeated.
The violation is confirmed by the following glucose levels:
- blood taken on an empty stomach – more than 5.5 and less than 6 mmol/l;
- blood taken 1.5 hours after a carbohydrate load - more than 7.5 and less than 11.2 mmol/l.