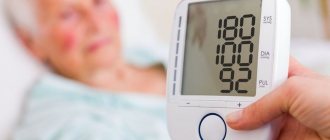
What is the blood pressure of a hypertensive patient?
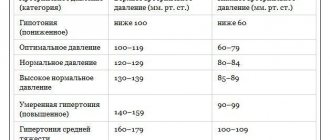
Doctors recognize normal blood pressure levels as 120 to 80 mmHg.
If it is higher than normal, a diagnosis of hypertension is made, and if it is lower, hypotension is diagnosed. Blood pressure in hypertensive patients can change throughout the day, and short-term increases are caused by physical activity and poor lifestyle. Blood pressure can also rise sharply due to nervousness. Hypertension is a pathology in which elevated blood pressure levels depend on physiological and pathological factors:
- Emotional stress
- Mental fatigue
- Genetic predisposition,
- Age,
- Hormonal changes
- Overweight,
- Concussion and other brain injuries
- Pathologies of the endocrine system,
- Chronic, infectious diseases,
- Exceeding the permissible cholesterol level.
The normal blood pressure of hypertensive patients depends on the degree of the disease:
- 1st degree or mild: systolic blood pressure from 140 to 160 mmHg, diastolic from 90 to 99 mmHg,
- Grade 2 or moderate: systolic blood pressure from 160 to 180 mm. Hg, diastolic - from 100 to 110 mmHg,
- Grade 3 or severe: blood pressure remains stable above 180 to 110 mmHg.
Apilak
This low blood pressure medicine comes in the form of sublingual tablets and ointment. "Apilak" belongs to the group of natural stimulants for the complex treatment of asthenia, neurotic disorders, and hypotension. Apilak contains a complex of biologically active substances, minerals and vitamins. The active substance is royal jelly. "Apilak" improves vascular tone, tones the nervous system and stimulates the body as a whole.
Contraindications include: allergies to bee products, age under 18 years, Addison's disease, hypertension.
What is the danger?
The cardiovascular system of a hypertensive patient is constantly tense. A sharp drop in blood pressure in such a situation threatens the health and functionality of the entire cardiac mechanism and the body as a whole. Therefore, it is prohibited to sharply reduce high blood pressure in hypertensive patients, otherwise the following dangerous processes will develop:
This condition in the patient provokes a narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain.
- The rapid expansion of blood vessels leads to a lack of blood flow, since it cannot increase in a short period of time.
- As a result of the current difficult situation, a narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain occurs.
- The blood supply to the brain is disrupted, as a result of which it gives the command to reduce the pressure. Oxygen starvation occurs, which leads to the death of its damaged areas. The occurrence of hemorrhage ends in instant death.
Return to contents
Symptoms
A sign of a decrease in indicators may be cold hands of the patient. High blood pressure causes a characteristic state of the body, to which a person gradually gets used. When blood pressure levels decrease, a hypertensive patient does not immediately pay attention to this, attributing all the signs to his underlying disease. Therefore, every person with high blood pressure should know the signs of a hypotensive crisis:
- pale skin;
- bluishness of the lips or skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle;
- sticky sweat;
- cold extremities (upper and lower);
- veins collapse;
- There is a tingling sensation in the arms and legs;
- noise in ears;
- hearing loss;
- darkens and swims in the eyes;
- orientation in space is disturbed;
- speech is confused.
The norm for pathologically low blood pressure is different for each hypertensive patient. But if characteristic symptoms are present, and the pressure has dropped to 100 to 60 or lower, you should urgently call an ambulance.
Return to contents
Dangerous consequences
The most unpleasant complication of hypotension is hypoxia - oxygen starvation of tissues. The patient’s condition and the reversibility of pathological changes depend on its degree. If hypoxia leads to prolonged cerebral ischemia, coma develops and the cerebral cortex ceases to function. Without immediate medical attention, death can occur.
In addition, the consequences of hypotension can be memory disorders, dementia, and depressive syndromes. The most harmless thing against this background looks like chronic fatigue syndrome, which is the scourge of the 21st century.
General recommendations for nutrition for hypotensive patients
With hypotension, it is important to adjust both the diet and diet. There are several eating habits that contribute to high blood pressure:
- Eat more often, but in small portions. This will ensure a constant supply of energy and high tone.
- Drink more water. When dehydrated, the volume of circulating blood decreases and blood pressure drops. If a person drinks enough water, the blood volume will be larger and the blood pressure will be higher. You need to additionally increase the volume of fluid you drink in hot weather and during physical activity.
- Don't skip meals. Such omissions can provoke overeating, which will cause blood pressure to drop.
- Reduce alcohol consumption. It causes dehydration and may worsen hypotension.
To improve your health with hypotension, you need to change your diet as follows:
- Get enough salt from food. Hypotonic people can eat dishes with added sea or table salt, as well as canned vegetables, cheeses, and salted fish. This will help retain fluid in the body and increase blood volume to increase blood pressure. In this case, total salt consumption should not exceed 5 g per day.
- Drink caffeinated drinks. It is better if it is natural coffee, black or green tea. The caffeine they contain causes heart rate to increase and blood pressure to rise. This effect is temporary. It should not be overused: if a person drinks a lot of coffee or tea, it can have a bad effect on heart health. In addition, over time, tolerance to caffeine may develop, and it will no longer provide a tonic effect.
- Get more vitamin B9 and B12 from foods. Hypotension may be associated with anemia caused by a deficiency of B vitamins. Hypotonic people need to eat more foods containing vitamin B12 (fish, chicken, eggs, low-fat dairy products) and B9 (broccoli, asparagus, lentils and chickpeas, liver).
- Control your carbohydrate intake. If your diet contains a lot of foods containing carbohydrates, this can have a bad effect on your heart condition and cause anemia. In addition, such foods are quickly digested, after which the pressure drops sharply. To reduce the symptoms of anemia, you need a balanced diet. It should not be overloaded with foods containing easily digestible carbohydrates (sweets, starchy foods, sweet vegetables, fruits and dried fruits, foods and drinks with added sugar).
In addition to nutrition, healthy habits such as good sleep and exercise are important (Figure 2).
Figure 2. General recommendations for hypotensive patients. Source: MedPortal
List of foods you can eat for hypotension
Hypotonic people can eat almost any food, but it is important that the diet remains balanced. The menu can include:
- fresh vegetables and salads made from them with added salt (but it is better to limit the overall use of salt and control it so that it does not provoke swelling);
- boiled or baked vegetables;
- cereals;
- fruits, dried fruits in limited quantities;
- meat, poultry, fish (preferably low-fat so that the level of cholesterol in the blood does not increase);
- cheeses, dairy, fermented milk products;
- bread, pastries, sweets (in limited quantities);
- chocolate;
- coffee and other caffeinated drinks;
- eggs;
- spices, hot seasonings (including ginger, pepper).
Additional dietary restrictions may apply that are not related to high or low blood pressure. To take them all into account, it is better to create a menu together with your therapist or nutritionist.
Reasons for decreased blood pressure
The main reason for low blood pressure in hypertensive patients is considered to be drug overdose. Most often this occurs due to a lack of knowledge and taking medications without a doctor’s prescription.
Among the secondary reasons are:
- Low blood pressure - what to do, first aid. Causes of low blood pressure and treatment at home
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system (coronary heart disease, heart failure, endo- and myocarditis, pulmonary edema).
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Infectious diseases.
- Diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands.
- Reduced blood sugar levels.
- Mental illnesses – depression, severe and prolonged stress.
- Taking antidepressants, analgesics.
- External and internal bleeding (perforated ulcer, hemorrhoids).
- Anaphylactic shock.
- Severe pain syndrome (attack of pancreatitis, renal colic, peptic ulcer, periodic pain in women).
Provoking factors
Not only the above conditions, but also a number of other provoking factors can lead to a decrease in blood pressure.
Common risk factors include:
- Prolonged bed rest.
- Pregnancy.
- Fever.
- Elderly age.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Orthostatic collapse when abruptly getting out of bed (especially in old age).
- Exposure to elevated temperatures that cause vasodilation (thermal springs, baths, saunas).
- Errors in nutrition.
- Prolonged exposure to the sun and tanning can cause blood pressure to drop. When tanning, adrenaline turns into the tanning hormone melanin and very little of it remains to maintain blood vessels in tone. Hence - weakness and hypotension after prolonged exposure to the sun.
A decrease in blood pressure due to hypertension always manifests itself with characteristic symptoms.
The most notable ones include:
- General weakness, lethargy, asthenia.
- State of depression.
- Headache.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Darkening in the eyes.
- Dizziness.
- Possibly frequent loose stools.
Some symptoms are characteristic of both hypertensive and hypotensive crises. Therefore, you should pay attention to the totality of other manifestations.
| Hypotonic crisis | Hypertensive crisis |
| Skin | |
| The skin is pale, cold. Often - cold sticky sweat. Cold hands and feet. | The skin is pink and warm. The face is hyperemic. Extremities are warm. |
| Headache | |
| The pain is aching in nature, often diffuse. | The pain is pulsating in nature, often localized in the back of the head. |
| Heartbeat | |
| Weak, pulse is poorly defined. | Strong, often rapid. The pulse is frequent and well filled. |
| State of mind | |
| Depressed, increased sleepiness is noted. | Excited. |
| Other manifestations | |
| Nausea, single vomiting. Unsteady gait. Darkening in the eyes. Possible loss of consciousness. | Nausea, repeated vomiting, which does not bring relief. Flashing of flies before the eyes. |
A sharp decrease in blood pressure in a hypertensive patient is much more severe than in an ordinary person. And prolonged hypotension leads to negative changes in organs and tissues.
Caffeamine
This drug for increasing low blood pressure is available in tablets and is sold by prescription. Belongs to the group of combined psychostimulants, the active substances are caffeine and ergotamine. “Caffetamine” tones the nervous system and constricts blood vessels.
This medicine is prescribed for migraines, hypotension and intracranial hypertension.
Among the contraindications: allergic reactions to the components of the drug, age under 18 years, atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, pregnancy and breastfeeding, insomnia, glaucoma, psychosis, serious heart disease, advanced age of the patient. Side effects: nausea, increased sweating, agitation, tachycardia.
Caffeamine
KRKA-RUS, Russia
The drug is used for: Vasoparalytic form of migraine;
arterial hypotension; as a means of lowering intracranial pressure in vascular, traumatic and infectious lesions of the central nervous system. from 151
5.0 1 review
517
- Like
- Write a review
Read also How to treat migraine: the best drugs Top 5 best drugs against migraine
Diagnostics
There can be many reasons why blood pressure drops. To find out which of them influenced a person’s condition in a particular situation, you need to contact a neurologist and cardiologist. The main attention is paid to complaints and examination of the patient, blood pressure indicators are determined. If it is not possible to determine why the indicator drops sharply, they resort to consultation with highly specialized specialists.
Return to contents
- Low intracranial pressure: main symptoms, development and effective treatment
Preventive measures
Signs of primary hypotension are easily eliminated, so there is no need to panic if your blood pressure drops. It is important to know how to increase blood pressure when it drops sharply and follow the rules of prevention, which boil down to the following:
- do exercises in the morning;
- spend more time in the fresh air;
- take vitamins;
- ensure yourself healthy sleep;
- eat rationally;
- drink enough liquid, especially in the hot season;
- try not to be nervous;
- control your weight;
- do acupressure.