Anemia
or
“anemia”
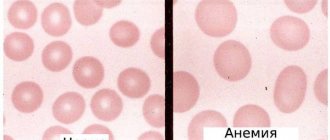
- a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood below established standards, most often, with a simultaneous decrease in the total volume of red blood cells (red blood cells that carry oxygen). Anemia, as a secondary symptom, can accompany various diseases, causing the development of oxygen starvation of tissues. The patient experiences chronic fatigue and weakness, constant drowsiness and loss of strength, dizziness and shortness of breath.
Anemia in men and women
Anemia is one of the most common diseases among the adult population of the Earth today. Risk groups for developing anemia include:
- lovers of vegetarian cuisine.
- patients suffering from large blood losses due to the physiological characteristics of the body or a number of chronic diseases.
- pregnant women.
- professional athletes.
Anemia in men is diagnosed in the presence of malignant neoplasms or hidden bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract, peptic ulcer, hemorrhoids and other pathologies. A decrease in the level of hemoglobin in a woman’s blood can be associated with heavy menstruation, pregnancy and lactation, and a period of hormonal changes during menopause. Varying degrees of anemia also appear in children due to lack of adequate nutrition, impaired absorption of iron in the gastrointestinal tract, gastritis or parasitic diseases, limited exposure to fresh air and physical inactivity.
Hypochromia in a child: why is it dangerous?
Anemic syndrome is very common in pediatric practice. The absorption of iron can be impaired as a result of a lack of it in food or from the state of the gastrointestinal tract, where it is absorbed. Since a child under three years of age has a much higher need for iron-containing products than adults, one can understand why hypochromia is more common in pediatrics.
Every day, children at an early age are depleted of iron reserves, as the growing body requires a lot of useful substances. If they have iron deficiency anemia, then such a long-term condition can lead to complications:
- Respiratory tract infections;
- Gastrointestinal diseases;
- Neuropsychic disorders;
- Decreased vision and hearing due to poor conduction of nerve impulses.
A low color index in an infant can occur for various reasons. First of all, in newborns, iron deficiency is associated with a lack of the element in the mother during pregnancy. This condition is also observed with difficult gestation, hypoxia, bleeding, abnormal development of the umbilical cord and placenta. Children who are fed formula or animal milk products rather than breast milk do not get enough iron.
If the drop in CPP is not caused by intrauterine disorders, then it is worth looking for pathologies in the child’s body. Bleeding leads to iron deficiency hypochromia:
- Esophageal hernia;
- Gastrointestinal ulcers, hemorrhoids;
- Diverticula, tumors, polyps of the intestinal tract;
- Internal bleeding in the respiratory system.
Taking hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs also contributes to the loss of hemoglobin. If iron absorption is impaired, it is important to differentiate between helminthic infestations, Crohn's disease, and dysbacteriosis.
You can recognize anemia in a child by external signs. All patients experience pale skin, moodiness, sweating, lethargy, decreased appetite, vomiting after feeding, regurgitation, insomnia, and loss of muscle tone. Up to a year, regression of motor skills may be observed. In the second half of the year, roughness of the skin, cracks on the lips, stomatitis, caries, and physical developmental delay appear.
Principles of classification of anemia
There are several types of classifications of anemia, based on a number of signs - the cause of the disease, the mechanism of its development, stages, symptoms and other parameters. The following groups are distinguished:
Sign up for an anemia screening
Make an appointment
What to do if the blood color indicator decreases
Treatment for low blood color index is prescribed taking into account the cause. First, the underlying disease is treated. Additionally, it is recommended to adhere to proper nutrition and abandon a vegetarian diet. Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol.
The blood color index is low in a small child - his nutrition needs to be adjusted. During periods of intensive tissue growth, tissues consume a lot of iron. The diet should include meat dishes, fresh vegetables and fruits.
If the blood color index is low in an adult, it is also recommended to start with regulating nutrition. If signs of anemia persist, iron supplements are prescribed.
Nutrition
A diet aimed at restoring CP should contain foods rich in iron and vitamins. In mild cases of deficiency anemia, proper nutrition allows you to restore hemoglobin levels and CP without the use of medications.
Iron-rich foods:
- meat by-products;
- red meat;
- green apples;
- buckwheat grain;
- grenades.
The absorption of iron improves with the simultaneous use of ascorbic acid. You should eat fresh vegetables and fruits, berries every day. Microelements and vitamins are destroyed during heat treatment. Vegetables, fruits and berries are best consumed raw.
Medications
If the color index is reduced to 0.6 or less, the nutrition will not be effective enough. Prescribed iron supplements:
- Sorbifer;
- Ferrum Lek;
- Maltofer;
- Ferro foil.
Medicines are available in the form of syrups for small children, tablets for older children and adults. There are combination preparations with additional content of ascorbic and folic acid. To improve absorption, ascorbic acid is prescribed additionally - if it is not in the drug.
The dosage and course of treatment are determined by the doctor, taking into account the tests. The minimum course of treatment is a month after restoration of hemoglobin and CP levels - a total of 1.5-2 months.
Classification of anemia by severity
The severity of anemia, determined by blood parameters depending on the age and gender of the patient, is conventionally divided into mild, moderate and severe. The mild form is characterized by a decrease in hemoglobin concentration to 90 g/l (the patient may experience general weakness and increased fatigue). The average degree is determined by the range from 70 to 90 g/l (patients complain of shortness of breath, tachycardia, headache, sleep disturbance, tinnitus, loss of appetite), and severe - below the limit of 70 g/l (the main danger of this condition is the development heart failure).
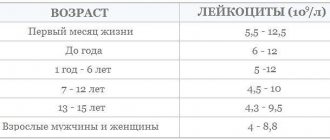
Normal blood color index among adults and children
The blood color index is normally higher in children, lower in adults:
- men and women - 0.8-1.1;
- newborns - 0.9-1.3;
- children under 15 years old - 0.85-1.
The color index of a child's blood is higher because fetal hemoglobin is present in his blood. This is a protein that is only present in the fetus during intrauterine development. A week after the birth of the child, it is destroyed, the CPU becomes lower.
There is no separate blood test for color indicator; it is looked at in a general clinical examination. An examination is prescribed if there are symptoms of anemia.
Classification of anemia by color index
The color index determines the level of saturation of red blood cells with hemoglobin. It is calculated during a laboratory blood test using a special formula. Depending on the results obtained, there are:
How the examination is carried out: blood test
The indication for laboratory diagnostics of red blood cells is to identify anemia. In order to correctly identify any abnormalities in the tests, it is important for the patient to adhere to the following rules before collecting biological fluid:
- Donate blood on an empty stomach in the morning;
- Do not eat food 8 hours before coming to the clinic;
- Do not drink alcohol-containing drinks and avoid fatty foods on the eve of the general analysis.
If the diagnosis is carried out correctly, reliable data will be obtained without false indicators. Based on them, the doctor will be able to understand whether it is necessary to refer the patient for additional examination or whether his health condition is normal.
A low color index indicates the presence of hypochromic anemia. As a rule, it is caused by iron deficiency in the body and is easily treated by adjusting the diet or prescribing medications. But there are also more serious pathological changes that reduce CPC.
Does it happen that hypochromia is detected with normal hemoglobin? Usually in such situations they do not talk about anemia, since all other indicators are normal. Most likely, the test result is not reliable and it is better to take another blood test to determine the exact data.
Classification of anemia according to the mechanism of development of the pathological process
The following states are distinguished:
Iron-deficiency anemia
– the name indicates the cause of the pathology. Due to a deficiency of an important microelement, hemoglobin synthesis in the body is disrupted. The supply of oxygen to tissue cells, the stability of redox processes, and the functioning of the immune, nervous and cardiovascular systems depend on the level of iron. Clinical manifestations of iron deficiency anemia are dizziness, fainting, weakness and lethargy, shortness of breath with any exertion, palpitations. Pallor of the skin, brittle nails, thinning hair, and cracks in the corners of the lips are also typical for this disease.
Hemolytic anemia
occurs as a result of the accelerated destruction of erythrocytes (red blood cells) and the rapid accumulation of their breakdown products in the body. The main manifestations are an increased amount of indirect bilirubin in the blood. The patient experiences the development of anemic and icteric syndromes with an enlarged spleen and liver, as well as characteristic staining of feces and urine.
Posthemorrhagic anemia
– hematological changes that appear after acute or prolonged chronic blood loss as a result of external or internal bleeding (trauma, heavy menstruation, hemorrhagic diseases, gastrointestinal and pulmonary bleeding). The main manifestations of posthemorrhagic anemia are palpitations, shortness of breath, severe dizziness, darkening of the eyes, and lethargy. In severe cases - loss of consciousness.
Sideroblastic (sideroachrestic) anemia
occurs as a result of a violation of iron synthesis, causing its deficiency in red blood cells. Due to a failure in the processes of getting this microelement into the hemoglobin molecule, iron in the cells is replaced by sideroblasts (red blood cell precursor cells interspersed with iron in the form of a ring). This condition can be congenital or acquired. Experts believe that the main reason for the development of such anemia is a lack of the substance protoporphyrin. This organic component, combining with iron, turns into heme - part of the hemoglobin molecule. The main symptoms of the disease are disturbances in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, indigestion, pale skin, dizziness, and memory loss. There is a danger of iron accumulation in various organs, which contributes to the occurrence of serious complications (liver cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus).
B12 deficiency anemia
– a disorder of hematopoiesis as a result of a lack of vitamin B12 in the human body. The main reasons for the development of such anemia are lack of adequate nutrition, impaired absorption of B12 due to inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract, alcoholism, and hereditary predisposition. The pathology develops gradually, causing damage to the digestive organs and disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system.
Reduced color index in an adult: how is it determined?
To calculate the CPC, it is necessary to consider only two quantities - red blood cells (Er) and hemoglobin (Hb). If a patient undergoes a general blood test, he will be able to see all these values in the results.
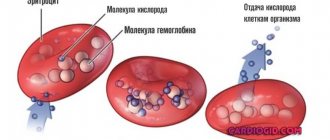
The color indicator is analyzed in order to understand how much oxygen the body needs. As you know, red blood cells perform several functions of the circulatory system:
- Transfer oxygen from the lungs to each cell of organs/tissues;
- Participate in the body’s metabolic processes, replacing processed substances with useful elements;
- Remove carbon dioxide.
If the CP is reduced, then doctors understand that the blood flow is not able to perform its functions 100% and the patient needs to restore the balance of the formed elements.
The color index in an adult is calculated by a simple formula:
CPC = hemoglobin*3 / first three digits of red blood cells
The result obtained is measured as a percentage. If a person has a CP below 0.86%, then the value is called hypochromia, that is, insufficient hemoglobin content in red blood cells. Figures in the range of 0.86-1.15% are considered normal or normochromia. Anything above this number will be hyperchromia.
CPC in adults and children under three years of age should normally be the same. In infants, the permissible level is slightly lower.
Cost of consultation for anemia?
| Name of service | Price, rub.) |
| Initial appointment with a cardiologist | 2000 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a cardiologist | 1500 rub. |
| Primary appointment with a general practitioner | 2000 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a general practitioner | 1500 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment (drawing up an individual treatment regimen) | 1500 - 3000 rub. |
All our services and prices
Diagnostic measures
To treat anemia, it is necessary to determine its type and cause of development. The main diagnostic method for this disease is laboratory blood tests (general and biochemical).
Changes that are observed in the general blood test:
small red blood cells (microcytosis).
Changes that are observed in the biochemical blood test:
In addition, a visual examination of the patient and a detailed history is required. Among the most common symptoms are pale skin and mucous membranes, cracks in the corners of the mouth, a “glossy” tongue, and an enlarged spleen.
To effectively correct the condition, instrumental examination methods may also be required:
computed tomography of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum. colonoscopy. Ultrasound of the liver, spleen, kidneys, genitals. X-rays of light.
Treatment of anemia
The course of medical therapy is carried out on the basis of the diagnosis and includes the prescription of a special diet and medications, as well as, if necessary, surgical intervention to eliminate the causes of blood loss.
A balanced diet is of great importance for anemia. It compensates for the lack of iron and microelements involved in hematopoiesis. Nutritionists recommend eating foods rich in vitamin B12, folic acid and iron. The diet must contain meat, offal (liver, heart, tongue), fish, egg yolks, mushrooms, buckwheat, legumes, black currants, pomegranate, strawberries, nuts, apples, rose hip decoction, dried fruits. Vitamin C accelerates the absorption of iron by the body, while strong tea, coffee, and calcium hinder it. Strong alcoholic drinks are harmful to a patient with anemia.
Iron supplements are considered the most effective for combating anemia. They are better absorbed, increase hemoglobin levels faster, restore its reserves in the body, and eliminate weakness and fatigue. Based on blood test data for each patient, depending on a number of indicators (type of anemia, severity of the disease and the cause of its development, age of the patient), an individual daily dose, course duration, and preventive measures are calculated. In severe cases, intramuscular and intravenous administration of ampoule iron preparations in a hospital setting is possible to avoid adverse reactions and allergies.
It is advisable to take iron supplements one hour before meals or two hours after meals. Medicines should not be taken with tea or coffee. These drinks reduce iron absorption. You must use water or juice.
The prognosis for iron deficiency anemia is favorable in most cases. The patients' condition improves significantly, the body's resistance increases, sleep and appetite normalize. The basis for preventing anemia is a balanced diet. Do not get carried away with protein foods and sweets. There should be vegetables, herbs and fruits on the table all year round. Another rule is to maintain a healthy lifestyle, exercise, walks in the fresh air, proper rest and good sleep.
Sign up for an anemia screening
Make an appointment
Fall in color index: reasons
Hypochromia occurs when there are disturbances in the synthesis process or poor absorption of iron elements in the bone marrow. This means that the patient has iron deficiency. There are not many factors that influence the decrease in value. For some people, the root cause is simple malnutrition, for others it is the development of serious disorders in the body.
Let's look at the main reasons for CPU decline:
- Cirrhosis of the liver;
- Tuberculosis, purulent infections;
- Malignant tumors;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- Thalassemia;
- Microcytosis (hemoglobin deficiency is observed with lead poisoning, iron deficiency, pregnancy);
- Iron-saturated hypochromia.
In 95% of cases, iron deficiency disorders occur. Most patients are women 15-50 years old. This phenomenon is due to the fact that less iron enters the body than the tissue consumes. Hypochromia is often caused by menstrual bleeding, hormonal disorders, pregnancy, lactation, and unbalanced diet. After taking iron supplements, the anemia goes away and CP is restored to normal.
And iron-saturated hypochromia is a condition that occurs when iron is normal in the body, but poor absorption by the bone marrow and hemoglobin formation. It is detected in cases of poisoning with chemicals or drugs that cause intoxication. It is impossible to cure the pathology with iron-containing drugs.
There is also iron redistribution anemia. In this case, we are talking about excess iron in the body, since the red cells are destroyed prematurely. It occurs in serious purulent processes - tuberculosis, infectious organ damage, endocarditis, etc. The decrease in indicators will be restored to normal after treatment of the underlying disease.