Colds, the most common group of infectious pathologies, affect people of all ages and social groups. However, ARVI and influenza pose the greatest threat to patients with impaired functioning of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems. It is they who, according to medical statistics, experience the greatest number of complications, including the occurrence of critical dysfunctions and death.
Diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular failure are systemic diseases; they negatively affect the condition of all organs and significantly reduce the body’s resistance to any infection. Due to the weak reactivity of the immune system, respiratory infections often last a long time and complications arise: sinusitis, bronchitis, pneumonia. The high activity of the infectious process, in turn, leads to even greater decompensation of the underlying disease, closing a vicious circle. Diabetes mellitus is often observed together with hypertension and atherosclerosis as part of the metabolic syndrome. Such patients with a cold require especially careful monitoring, both from a therapist and from a cardiologist and endocrinologist.
ARVI in diabetes mellitus
During the infectious process, a cascade of biochemical reactions is triggered, promoting, among other things, the active synthesis of corticosteroids that have a counter-insular effect: the hormone blocks the work of insulin at the cellular level and inhibits its formation in the pancreas. The total effect of corticosteroids and other biologically active substances significantly exceeds the effect of insulin in the patient’s usual dosage. In the absence of proper control of glycemic levels, which in acute respiratory viral infections is preferably carried out every 2-3 hours, the risk of ketoacidosis or hyperosmolar coma increases significantly. There are often cases when the deterioration of the patient’s condition is mistaken for signs of viral intoxication and an immediate threat to life is diagnosed late.
The patient no longer fears a heart attack
“It is very important that the doctor conveys to the patient what myocardial infarction is and why we are so afraid of it,” says senior researcher at the cardiology laboratory of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center for Physicochemical Medicine of the FMBA, head of the intensive care unit at State Clinical Hospital No. 29 Moscow, Doctor of Medical Sciences Alexey Erlikh . “Myocardial infarction is now treated so skillfully that for many patients it goes unnoticed. Something hurt, they brought you to the hospital, to the linear operating room, they inserted wires in the vessel, five days later you were discharged, and soon you were already at work, forgot about your heart attack.”
Article on the topic
Help yourself. What do you need to know to save yourself from a heart attack?
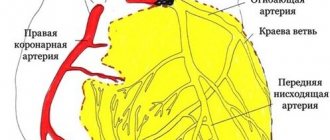
It is important to understand that myocardial infarction is a disease associated with two large processes that occur in the heart - atherosclerosis and thrombosis: the growth of atherosclerotic plaques and the formation of blood clots on these plaques, says Alexey Erlikh. “After a myocardial infarction, this process, unfortunately, does not stop,” he explains. “We doctors can slow it down with medication, but every patient who has had a myocardial infarction or any coronary event, or has risk factors for it, is very likely to have another attack. Moreover, this does not depend on what kind of heart attack it was. After unstable angina or after a small myocardial infarction, the likelihood of recurrent heart attacks is even higher than after a large heart attack.”
ARVI with ischemic heart disease
Recent analytical data reliably show a critical increase in the number of heart attacks in patients with coronary heart disease due to ARVI and influenza, especially in age groups after 50-60 years. Mortality in patients with cardiovascular disorders increases during periods of influenza epidemics by 18-20%, and the relative risk of death with coronary artery disease at this time increases by 3.5-4 times.
Western publications indicate that influenza virus RNA is found in atherosclerotic plaques2. Thus, the viral agent probably persists in the body, causing persistent infection and, at the same time, progressive plaque growth due to the activation of autoimmune mechanisms.
During a cold, the concentration of C-reactive protein, total cholesterol, triglycerides, and adhesion molecules to the endothelium in the blood increases significantly. Monocytes infected with the influenza virus have procoagulant properties, and some cytokines (interleukins 6 can initiate rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque due to local inflammation5. Thus, with ARVI there is a high risk of plaque instability, its growth and/or rupture with occlusion of the coronary artery.
Monocytes infected with the influenza virus have procoagulant properties, and some cytokines (interleukins 6 can initiate rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque due to local inflammation5. Thus, with ARVI there is a high risk of plaque instability, its growth and/or rupture with occlusion of the coronary artery.
First aid
The most dangerous stage of the disease is the first 5-10 minutes of an attack. It is important to properly help the person before the medical team arrives. First of all, you need to calm the sick person, sit him down or lay him down in a comfortable place. Your upper body should be slightly higher than your lower body and your knees should be slightly bent. It is necessary to ensure good air ventilation and free the person from constrictive clothing. It is important to understand that pain during a heart attack can be so intense that it can cause death. A person can die from painful shock. If a person has had heart problems for a long time, then most likely he will have a drug such as nitroglycerin with him. You need to put a tablet under your tongue to relieve the condition.
In some cases, the patient’s severe panic during an attack can seriously threaten his health. In this case, the person should be given some kind of sedative: valocordin or corvalol.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
If a person has lost consciousness and breathing is barely palpable, you need to start cardiopulmonary resuscitation. There is no more than five minutes to save a person.
To start a stopped heart, a precordial blow is applied (a strong blow to the chest with the edge of the palm). After this, the pulse is felt; if it is absent, you need to start chest compressions and perform artificial respiration. You need to place a cushion from any available items under the victim’s neck. The patient's head should be thrown back as much as possible. If necessary, the oral cavity can be cleaned with wipes.
Rescue measures can continue until the sick person comes to his senses, but this should take 5-7 minutes. If the heart cannot be started during this time, then the person cannot be saved.
The problem of treatment of ARVI and influenza in comorbid patients
ARVI and influenza complicate the course of cardiovascular pathology and diabetes mellitus and sharply increase the likelihood of decompensation of the disease. That is why the search for drugs to protect such patients, to treat ARVI as quickly and safely as possible, is a very pressing issue.
Most existing antiviral drugs only work against the influenza virus, which makes them difficult to prescribe. The drugs themselves are quite aggressive and have a long list of contraindications and side effects. Thus, their use should be avoided in cases of kidney and liver disorders, which often accompany coronary artery disease and diabetes.
It is also necessary to take into account the problem of drug interactions: antiviral and symptomatic drugs often do not combine well with continuous treatment of underlying diseases.
UZ "Mogilev City Emergency Hospital"
Prevention of myocardial infarction is divided into primary and secondary.
Since a heart attack provokes the gradual death of cardiac muscle cells, the main requirement of primary measures comes down to a radical change in lifestyle to maintain the performance of the myocardium and slow down the development of the pathological process.
Secondary measures are necessary to prevent recurrent attacks and are based on drug therapy with the possible use of traditional methods of treatment.
The basic principles of preventing myocardial infarction are:
- quitting smoking and alcohol abuse;
- gradual increase in physical activity;
- correction of diet;
- monitoring health status and its indicators;
- positive attitude;
- taking medications prescribed by the doctor;
- use of folk recipes.
Primary prevention
The main preventive measure to prevent primary myocardial infarction is a healthy lifestyle and constant monitoring of health indicators. It is important to remember that after secondary and tertiary cases of attack, the rules of primary prevention should be observed to a greater extent.
The goal of primary preventive methods is the treatment of chronic ischemic heart disease and the elimination of factors that can cause acute forms of heart disease and other severe consequences. - source:
Nutrition
To prevent a heart attack, it is important to adjust your daily diet. The recommendations are as follows:
- include in the diet or increase the amount of consumption of greens, green vegetables, root vegetables;
- regularly consume low-fat fish dishes, poultry and seafood dishes, but avoid frequent consumption of animal meat;
- eat fruits raw (only fresh);
- limit the amount of salt and fatty foods in the diet;
- think over a menu, the dishes of which should contain a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals to replenish their norm (in particular, calcium and magnesium).
- Such a diet will help reduce blood cholesterol levels and restore vitamin balance to maintain immunity.
Physical exercise
To keep your body in good shape, you need to be physically active whenever possible.
It is not recommended to start engaging in strenuous sports without prior preparation and with an unprepared body.
A set of exercises and sports must be discussed with your doctor in advance. Activities such as walking, swimming, running, and skiing are allowed in the absence of contraindications. It is important not to overload the body; it is enough to spend about half an hour on physical activity three times a week.
This activity reduces the risk of a heart attack by 30%, helps maintain weight within normal limits and distributes the load on the heart muscle.
Rejection of bad habits
An important requirement for a healthy lifestyle is giving up bad habits - active smoking and alcohol abuse. These factors provoke the risk of heart attack, ischemia and complications after them due to the negative impact on the cardiovascular system.
Smoking should be completely avoided, and the consumption of a minimum amount of alcohol is acceptable in the absence of any contraindications. It is allowed to drink any alcoholic beverages without mixing, no more than 20 g for women and 30 g for men, translated into pure alcohol content.
Weight control
Constant control of body weight reduces the risk of heart attack. Excess weight puts additional stress on the myocardium, which provokes attacks. It is also important to avoid underweight and sudden fluctuations in weight, as this leads to malfunctions of the body.
The main indicator for weight control is the BMI formula. Also, when taking measurements, it is worth taking into account individual characteristics and body type.
Pressure control
Pressure control is an important preventive way to prevent a heart attack. For people suffering from hypertension, it is important to pay special attention to blood pressure, since elevated values place an increased load on the myocardium, which impairs its performance.
It is recommended to use a device for measuring blood pressure (tonometer), regularly take measurements and check the instructions for normal blood pressure indicators. It is necessary to ensure that it does not rise above 140/90 mmHg, and if there is a tendency for pressure surges or a strong increase, be sure to consult a doctor and start taking medications to normalize it.
Positive emotions
Positive emotions are important for healing many diseases, and heart attack is no exception. It is necessary to tune in to favorable results and prognosis of therapy, try to avoid stressful situations and disorders.
If it is difficult for a patient to control emotions, it is recommended to take sedatives of herbal origin, for example, motherwort tincture.
Taking blood tests
An important criterion for preventive therapy is monitoring the results of blood tests, in particular, glucose levels and cholesterol levels, LDL. These values make it possible to check the state of lipid balance in the body, which deviates from the norm in the case of atherosclerosis, and to identify the development of diabetes mellitus, which increases the risk of myocardial infarction.
Timely doctor visits
Visiting a doctor for people at high risk for heart attack is mandatory and should occur regularly. It is the doctor who, after interviewing the patient and analyzing the studies performed, can determine the development of the disease and its stage, as well as prevent complications.
Secondary prevention
Secondary preventive measures primarily require taking medications previously prescribed by a doctor after the first attack of a heart attack. Also, in the absence of contraindications, it is recommended to combine drug therapy with the use of folk remedies.
Secondary prevention of myocardial infarction occurs with constant monitoring of the condition using ultrasound, ECG with stress, and Holter monitoring.
Use of medications
To prevent recurrence of a heart attack, the doctor prescribes medications from the following groups:
Anticoagulants and antianginal agents that lower blood cholesterol levels.
The main medications to prevent recurrent attacks are Aspirin. The use helps to stop the formation of blood clots, which are the main cause of myocardial infarction.
The effectiveness of Aspirin for ischemia depends on the dosage, in particular, low dosages are recommended for stable health conditions, and increased amounts of the drug should be taken by people suffering from periodic pain and fever.
Acetylsalicylic acid can help not only avoid relapses, but also reduces the chances of initially experiencing a heart attack. The main thing is to avoid overdose. The maximum amount taken per day is from 75 to 150 mg.
Anti-cholesterol diet. The diet does not allow the presence of animal fats, fatty meats, any sausage, or sweets on the table. The basis of the diet is cereals, vegetables, dietary dairy products, fruits, chicken, and rabbit. Complete cessation of tobacco and alcohol. The very first cigarette or drop of alcohol can cause severe vasospasm. Physiotherapy. The load is prescribed by a specialist based on data on your well-being. Fast walking is allowed with a gradual increase in the distance covered by the patient, exercises in the gym under the guidance of an instructor. Sex is allowed 2 months after illness, if the patient is able to climb 2 floors up, and his pulse does not exceed 120 beats per minute.
In addition to basic medications, it is recommended to include vitamin supplements in your treatment to maintain health and immunity. These include:
"Magnesium B6", actively involved in the normalization and restoration of heart rhythm. Its use is especially important for people suffering from such a complication of a heart attack as heart disease, which is necessary to maintain heart health and maintain its functionality.
“L-Carnitine”, which affects overall well-being and provides a boost of vivacity and energy. Its influence helps to endure the disease with less physical and mental costs.
Fish oil, which contains fatty acids that prevent the development of blood clots.
Complications and methods of dealing with them
Since myocardial infarction is a condition in which damage is caused to the most vital organ, it is often accompanied by negative consequences, including:
- risk of stroke or recurrent heart attack,
- heart failure,
- aneurysm,
- arrhythmia,
- arterial hypertension,
- ventricular fibrillation,
- violation of the integrity of the heart muscle.
Ventricular fibrillation and disruption of the integrity of the heart can lead to death in a short time and require extreme measures - the use of electric shock, artificial respiration.
When diagnosing other complications, it is important to begin therapy with drugs that affect the restoration of heart rate and blood pressure, prescribed for stroke. It is also important to maintain bed rest and avoid physical and mental stress until the condition improves.
Myocardial infarction is a serious heart disease, the complete cure of which is almost impossible. To avoid its occurrence, you need to adhere to the rules of primary and secondary prevention: take the necessary medications, balance your diet and stop smoking.
It is possible to prevent a heart attack if you take prevention seriously. This is easier than having a long and painful recovery from the disease, and then still returning to restrictions and taking medications.
Antiviral effect of interferon and drugs of its endogenous synthesis
Recently, interferon preparations and stimulators of its endogenous synthesis are increasingly called the drugs of choice for comorbid pathology. The antiviral activity of interferon has been comprehensively studied and proven. It is based on preventing the penetration of a viral agent into a cell, activating the synthesis of specific substances that disrupt viral replication and accelerated lysis of infected cells6. Release-active drugs Ergoferon and Anaferon help increase the production of endogenous interferons when the body comes into contact with a viral infection, and also improve the binding of the interferon molecule to its receptor, ensuring the normal course of the antiviral immune response. These drugs have a number of advantages: • They have almost no contraindications. • They have a favorable safety profile, and the risk of atopic reactions is much lower than when taking natural interferon • They can be easily taken with drugs of other pharmacological groups • Due to the combination of several mechanisms of action, the appointment of Ergoferon or Anaferon will minimize the dose of symptomatic drugs and, accordingly, the load to the liver. • Endogenous synthesis of interferon correlates with the content of the virus in the body, so there is no risk of hyperstimulation of the interferon system.
Prevention of heart attack in women
Women do not develop myocardial infarction as often as men. However, there are risk factors that increase your chances of encountering this terrible disease. These include:
- Endocrine pathologies – hypo-, hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus.
- Metabolic diseases, primarily obesity.
- Hormonal disorders caused by menopause, pregnancy, long-term use of oral contraceptives.
- Burdened heredity.
For women, normalization of the daily routine (sleep at least 8 hours) and diet - avoidance of fatty, sweet, salty and spicy foods - comes to the fore in the primary prevention of heart attack. In addition, it is important to learn to control stress levels and avoid overwork.
How release-active drugs work
The effectiveness of Anaferon and Ergoferon is due to the content of affinity-purified antibodies in a release-active form. Recent studies have convincingly shown that antibodies in the release-active form (RA Ab) to IFN-γ modify the spatial structure of IFN, causing conformational changes in precisely those parts of the molecule that are responsible for the binding of interferon-γ to its receptor. These drugs realize their therapeutic effects through their influence on regulatory molecules and mediators involved in the formation of the antiviral immune response and the development of infectious inflammation.
As viral particles are eliminated, the synthesis of endogenous interferon gradually decreases to normal values, and in case of exacerbation, it is activated again. This flexibility of action of drugs based on RA AT helps to avoid hyperstimulation and hyporesponsiveness of the interferon system.
Along with antiviral, immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects, Ergoferon also has an antihistamine effect due to the content of RA antibodies to CD-4 and histamine7.
Prevention of myocardial infarction
Details Published 02/05/2020 1:23 pm Emergency conditions in cardiology, including myocardial infarction, are the main cause of death for people aged 40 years and older, and, like all diseases, heart attacks are “getting younger.”
The number of people aged 25 to 40 years diagnosed with acute coronary insufficiency increases every year. Doctors believe that the reason is ignoring methods for preventing heart attacks, in particular, the lack of necessary physical activity, poor diet, and bad habits. Abroad, primary prevention of myocardial infarction is carried out almost from birth; its essence lies in early screenings, popularization of a healthy lifestyle and teaching children from school to monitor their own health indicators. Secondary prevention of myocardial infarction (after a previous illness) involves regular visits to the doctor, adherence to a diet and the use of supportive therapy. Unfortunately, many patients often do not comply with even these requirements, which results in a high mortality rate and numerous complications that could be avoided by paying attention to the prevention of heart attacks and one’s own health.
The statistics are sad: in 40-60% myocardial infarction leads to the death of the patient, with extensive forms the mortality rate reaches 90% or higher.
People die as a result of cardiac arrest, multiple organ failure, and repeated heart attack. Contents: 1. Prevention of heart attack in women 2. Prevention of heart attack in men 3. Prevention of early complications of myocardial infarction 4. How to avoid a recurrent heart attack? 5. Primary prevention of myocardial infarction 6. Secondary prevention of myocardial infarction
Prevention of heart attack in men
The main task for men is to combat bad habits, excess weight and physical inactivity. Myocardial disorders, in particular ischemia, more often develop in smokers, people who abuse alcohol and are obese. That is why a man can avoid myocardial infarction by doing physical exercise, giving up an unbalanced diet (fatty, meat dishes, fast food should be replaced with fruits and vegetables, cereals, etc.) and getting rid of bad habits. It is very important to control blood pressure, since hypertension dramatically increases the risk of developing a heart attack.
How to avoid another heart attack?
The goal of secondary prevention of heart attack is to prevent recurrence and in this case the emphasis is on drug therapy. The medications prescribed to the patient during the rehabilitation period should provide heart support, activate metabolic processes and blood circulation. The following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants with indirect action (usually the Aspirin group is used), the latter are prescribed with caution, since they can cause bleeding in 3-8% of patients.
- Beta-blockers are indicated for secondary prevention in the early stages of heart failure and a previous anterolateral infarction with a Q wave and ventricular arrhythmia.
- Calcium antagonists are prescribed in courses during the first 6 months.
- ACE inhibitors - slow down the expansion of the left ventricular cavity, reduce the risk of heart failure to improve blood flow in the coronary auxiliary arteries.


![Rice. 1. ACCOMPLISH study: the effect of the combination of ACE inhibitor* amlodipine and ACE inhibitor hydrochlorothiazide on the risk of primary endpoint events (CVE) [14]](https://expert35.ru/wp-content/uploads/ris-1-issledovanie-accomplish-vliyanie-kombinacii-iapf-amlodipin-i-iapf-330x140.jpg)