Every person is familiar with the feeling of numbness in the hands, when the loss of sensitivity in the area of the hands is accompanied by a slight burning or tingling sensation. This phenomenon is explained by a disruption of normal blood flow to the distal parts of the upper extremities, caused by compression of blood vessels or nerve fibers. In most cases, such changes are temporary phenomena. Sensitivity is restored immediately after changing body position, during movement and similar actions.
What is hand numbness and its causes?
Many people are familiar with the unpleasant feeling of tingling, “crawling on the skin,” as well as pain, decreased sensitivity and deterioration of mobility in the limb. All of these manifestations characterize numbness, which can occur in the arms, legs and other areas of the body. It is associated with impaired blood circulation in the tissues or compression of the nerves.
Along with numbness in the hands, the following symptoms may also occur:
- burning sensation;
- muscle spasms;
- tingling sensation;
- pain in hands, fingers;
- feeling of itching;
- tingling and numbness that gets worse when you move your fingers;
- increased sensitivity to touch;
- pain in the cervical spine.
Feeling like your arm is paralyzed - osteochondrosis or hernia?
With osteochondrosis, the arm on the affected side is lost. As a rule, this is a protrusion of the lateral segment of the intervertebral disc. As a result of a decrease in its height during head movements, temporary compression of the root nerve or its branches occurs. An acute pain syndrome develops, after which excessive tension in the muscle fiber is observed. This is a compensatory protective reaction of the body to remove pressure from the radicular nerve. Therefore, with osteochondrosis, most often the feeling that the arm is paralyzed is temporary. It goes away quickly after the pain is relieved.
With an intervertebral hernia, the arm is taken away a little differently. The feeling is very persistent and does not go away after some time. In this case, only the procedure of manual traction of the cervical spine and osteopathic reduction of the hernial protrusion can help.
You can find out exactly what causes the feeling that your arm is paralyzed only with the help of an MRI examination. It is this type of modern diagnostics that shows the condition of cartilage, muscle, tendon and other soft tissues.
Causes of numbness in the left hand:
- Cardiac ischemia. In addition to numbness in the left arm, there is discomfort in the chest. If after taking nitroglycerin or stopping the physical activity that caused the symptoms, these manifestations disappear, then it is angina pectoris. In addition to numbness of the left arm, it is accompanied by chest pain in the heart area, panic, pale skin, nausea, shortness of breath, and cold sweat.
- Myocardial infarction. Sometimes hand numbness is the only sign of this acute cardiovascular disaster. During an attack, the patient experiences intense pain and a feeling of constriction in the chest, shortness of breath, and interruptions in the functioning of the heart. The skin becomes covered with cold sweat. Along with numbness in the hand, a person experiences pain radiating to the lower jaw, stomach, and the area between the shoulder blades.
- Atherosclerosis. Due to atherosclerotic damage to the blood vessels, decreased strength and numbness in the arm may occur. Symptoms intensify when raising the limb upward.
- Stroke. Numbness in the left hand may indicate damage to the right hemisphere of the brain. In this case, the upper and lower limbs on the left side become numb, vision and speech are impaired. Along with numbness in the hand, a stroke can cause a complete loss of sensation in the hand. Other symptoms of cerebral hemorrhage include weakness in the limbs, loss of coordination, severe headache, blurred vision, nausea and vomiting, and irritation from bright lights and sounds.
- Vegetative-vascular, or neurocirculatory dystonia. This is a complex of autonomic disorders that is associated with disorders of nervous regulation. In addition to numbness of the left hand, it may be accompanied by headaches, insomnia, pressure fluctuations, arrhythmia, and panic attacks.
- Raynaud's disease. The pathology is accompanied by paroxysmal circulatory disorders in the arteries of the extremities. Along with the numbness of the hand, its rapid freezing is felt. In the cold and with excitement, a person’s fingers may turn blue. As Raynaud's disease progresses, not only the hands become numb, but also the legs, chin, nose, and ears.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency. This connection is extremely important for the normal functioning of nerve tissue. With its deficiency, a person not only experiences numbness in the hand, but also suffers from dry mouth and pale skin.
- Osteochondrosis (usually cervical and thoracic). First, the fingers go numb, then weakness develops in the upper limb, and the grip strength of the hand decreases. Sometimes pain is felt along the outside of the shoulder and forearm.
- Overstrain of muscles in the cervical-collar region. Pianists and PC operators suffer from hand numbness due to prolonged maintenance of the same position. The problem lies in the overstrain of the muscles, which compress the nerve fibers responsible for the sensitivity of the limbs.
- Insufficient blood circulation. The upper limb becomes numb due to impaired blood flow due to damage to the walls of blood vessels, for example, in diabetes mellitus.
- Stress and psycho-emotional overload can cause hand numbness.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome. When the median nerve passing through the wrist is compressed, the left hand may become numb. This problem is familiar to people of certain professions (programmers, musicians). Nerve compression can also occur in women during pregnancy due to swelling, as well as in patients after surgery, in obese people.
In what cases should you consult a doctor if you have numbness?
If the numbness has a physiological cause, that is, caused by a temporary disruption of the local blood supply, then it is enough to change the position and rub the numb area, and sensitivity will be restored. If the numbness does not go away, then the cause is more serious and you should consult a doctor.
It is necessary to get emergency medical help if numbness is accompanied by symptoms of damage to the central nervous system:
- headache, dizziness, attacks of weakness, double vision, loss of coordination;
- unexpected bowel movements or sudden urination;
- speech problems.
These symptoms may occur after a head, neck, or back injury.
You should also consult a doctor if:
- numbness occurs periodically and without an obvious reason;
- thermal perception is impaired (for example, the ability to distinguish between warm and cold water is impaired);
- Numbness is preceded by pain and loss of range of motion in one of the joints.
Numbness in the right hand may have the following causes:
- impaired blood flow, pinched nerve due to incorrect position of the limb (for example, during sleep);
- staying in an uncomfortable position for a long time (may be due to the nature of the work, for example, carpal tunnel syndrome);
- frequent carrying of bags, suitcases and other heavy objects;
- long exposure to frost or in a cold room;
- long-term muscle tension of the upper limb.
In pregnant women
During the period of bearing a child, a woman’s hands often become numb at night. The pregnant woman's body is focused on ensuring that the embryo develops normally. Therefore, a pregnant woman experiences difficulties due to the restructuring of the work of all organs and systems. Her metabolic processes are disrupted. Lack of vitamins and microelements leads to cardiac dysfunction. Most women are diagnosed with anemia.
Pregnant women rarely sleep fully, especially in the last stages before childbirth. It is difficult to assume a natural sleeping position due to a large belly. The consequences of stress and nervous strain are disturbances in the functioning of peripheral arteries.
Why does hand numbness occur?
When a patient says that his upper limbs are numb, he may mean:
- a tingling feeling that causes discomfort;
- sensation of “goosebumps” under the skin;
- decreased sensitivity of the skin.
Numbness of the hands does not always indicate pathology. It may be the result of wearing too tight clothes and jewelry that compress blood vessels and nerves.
The most common causes of numbness in the hands:
- Uncomfortable body position, monotonous mechanical work, disrupting blood flow. After changing the position of the limb, the unpleasant sensations disappear.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome (usually affects the working hand due to prolonged monotonous work).
- Atherosclerosis. Accompanied by tingling and numbness of the hands, in the future a decrease in their muscle strength is likely.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine (numbness, usually symmetrical, may intensify after physical activity).
- Diabetic neuropathy (usually both hands go numb).
- Intervertebral hernia in the cervical region (numbness is associated with compression of the spinal nerve roots).
- Ischemic stroke of the brain (threatens numbness and paralysis of the arm).
- Multiple sclerosis (if part of the postcentral gyrus of the brain is affected, the limbs may go numb).
- Thoracic outlet syndrome (compression of nerve trunks and blood vessels in the area of the upper chest opening).
- Brachial plexitis (numbness of the arm occurs due to inflammation of the brachial plexus).
- Damage to peripheral nerves due to alcoholism (alcoholic polyneuropathy).
- Brain tumor (the formation can compress the motor and sensory neurons responsible for the innervation of the upper extremities).
- Raynaud's disease (a disorder of the innervation of small arterioles, more common in women, manifested by numbness and pain in the extremities).
- Rheumatoid arthritis (inflammation and deformation of joints leads to compression of nerve fibers) and others.
Main services of Dr. Zavalishin’s clinic:
- consultation with a neurosurgeon
- treatment of spinal hernia
- brain surgery
- spine surgery
What is the body saying?
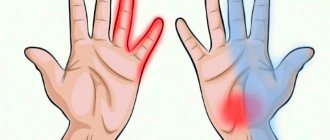
Suddenly my fingers lost sensitivity. If this is a rare phenomenon and it disappears after 2 - 3 minutes, then there is nothing to fear. If such sensations bother you often, then this is a signal of a developing disease.
- Little finger. Paresthesia indicates chronic heart failure and other cardiac pathologies.
- Forefinger. Goes numb with diabetes, occupational stress, inflammation in the joints.
- Thumb. Metabolic processes in the spine are clearly disrupted. You may feel pain in the forearm and weakness in the arm muscles.
- Middle finger. Raynaud's disease, hernia, articular deformity, osteochondrosis of the 7th vertebra.
- Nameless. Numbness due to the fact that the nerve endings in the bend of the elbow are compressed.
Diagnosis of the causes of hand numbness. How to identify?
At the appointment, the doctor examines and palpates the patient’s limb and asks the following questions:
- Where exactly is the numbness felt?
- When did the unpleasant tingling sensation and decreased sensitivity first appear?
- How long does numbness in a limb bother you?
- What actions and movements aggravate symptoms?
- Are there any other complaints, such as burning, itching, tingling, pain?
- How do your arms, hands, and fingers feel—cold or warm?
The main task of the doctor is to determine the causes of hand numbness. It is necessary to exclude systematic mechanical compression of blood vessels, as well as to determine household and industrial factors that could cause disturbances.
Numbness may be a harmless symptom, but it may also hide serious problems - myocardial ischemia, stroke, spinal problems, diabetes mellitus, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, etc. In this case, the doctor issues a referral to doctors of relevant specializations (cardiologist, endocrinologist, neuropathologist, etc.).
The main emphasis in identifying the causes of numbness is on detecting signs of osteochondrosis. For this, the patient is referred for magnetic resonance imaging, radiography, computed tomography, and electromyography. The purpose of imaging studies for arm numbness is to determine the height of the intervertebral disc, detect osteophytes, and clarify the presence of protrusion or intervertebral herniation.
Diagnostics
The etiology of hand numbness is determined by a neurologist. In case of vascular pathology, consultation with a vascular surgeon is required. The specialist examines the history of the disease, assesses the condition of the limb, pulse in the arteries, identifies swelling, signs of inflammation, and other changes. A neurological examination includes the study of sensitivity, reflexes, and muscle strength. Based on the results, the following are assigned:
- Electrophysiological studies
. ENG, EMG, evoked potentials are carried out to differentiate damage to nerves, muscles and structures of the central nervous system, to clarify the location and degree of damage to the nerve trunk. - Radiography
. Performed for injuries, suspected compression of nerves by bone growths, neoplasms. Visualizes fractures, dislocations, osteophytes, bone deformities. - Vascular studies
. Informative for scalene muscle syndrome, Takayasu's disease, thromboangiitis obliterans. To determine the localization and severity of occlusion, vascular ultrasound, angiography, and aortography can be performed. - Other visualization techniques
. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are performed for diseases and traumatic injuries. Prescribed in case of ambiguous results of basic studies and planning of surgical interventions. - Lab tests
. Recommended for confirming the infectious and dysmetabolic genesis of polyneuropathies and diagnosing Takayasu’s disease.
Acupuncture
Principles of treating hand numbness
The primary task of the doctor is to identify the root cause of this symptom. For this purpose, radiography, myelography, MRI, blood tests, etc. can be performed.
Depending on the nature of the disease that caused numbness in the hands, treatment methods are selected. First of all, the underlying disease is treated. Drug treatment is supplemented by:
- physiotherapy;
- physical therapy;
- reflexology;
- massage;
- diet therapy;
- lifestyle correction.
Vascular disorders
One of the complications of diabetes is diabetic neuropathy, damage to sensory, motor and autonomic nerves as a result of impaired blood flow in small vessels. One possible symptom is numbness in the limbs.
There is a large group of diseases - vasculitis. Autoimmune inflammation develops in the vessel wall, it thickens, becomes weakened, and scarring occurs. In the lumen of the vessel, areas of narrowing appear in which blood flow is disrupted. Various organs, including nerves, can suffer from this.
With one of the systemic connective tissue diseases - Raynaud's disease - a spasm of the small vessels that supply blood to the fingers and toes occurs. In response to cooling or stress, a feeling of coldness and numbness occurs in the fingers.
Preventing numbness in the hands
In order to prevent discomfort in the upper extremities, it is recommended:
- exercise regularly (discuss the type and nature of exercise with your doctor in advance);
- maintain the health of blood vessels, joints and the body as a whole (give up bad habits, eat rationally);
- dress according to the season, keep your hands warm;
- take breaks every 40 minutes if your profession involves working on a PC or performing monotonous hand movements.
Pain in bones, muscles, joints and forearm
Pain in the left shoulder joint and forearm often occurs with diseases of the heart, liver, spine, after a stroke, heart attack, with hepatitis, pneumonia, cervical osteochondrosis, tumors of tissues and organs of the chest, and with other diseases. Pain may indicate dysfunction of the bones, pathological changes in the tendons:
- The elbow is pressed to the side, the arm turns outwards with the inner side - severe pain indicates a pathological process in the infraspinal tendon.
- Severe pain in the left shoulder joint and forearm when moving the upper limb to the side or forward indicates damage to the supraspinal tendon.
- The elbow is pressed to the side, the arm is turned with the outer side towards the body. Pain in the shoulder with this position of the arm indicates a pathological process in the subscapularis tendon.
Treatment with folk remedies
The following recipes help with numb hands:
- as a compress or therapeutic bath, use a mixture of 2 liters of milk, 600 g of salt and 50 g of honey, heated to 60? C;
- apply an infusion of wild rosemary with apple cider vinegar (1:3) 3 times a day;
- infusion of garlic (several cloves) in vodka (400 ml) taken orally, 3-5 drops dissolved in water;
- for 1 liter of vegetable oil - 100 g of ground black pepper, cook for 30–40 minutes, rub the cooled product into the skin of the affected limb.
Treatment of hand numbness in specialized hospitals
Department of Neurosurgery, City Clinical Hospital named after. A.K. Yeramishantseva sees patients with complaints of numbness in their hands. Here, progressive methods of conservative and surgical treatment of diseases manifested by such symptoms are used. Advanced technical equipment and extensive professional experience of the medical staff guarantee good treatment results. Telephone.
Neurosurgeon Evgeniy Evgenievich Zavalishin treats diseases that cause numbness in the hands. Sign up for a consultation by calling 8 (499) 940-04-30.