Numbness in the fingers occurs for a variety of reasons. In young people, in most cases, quickly passing numbness is a consequence of physiological causes that can be established independently; this pathology does not require specific treatment. However, loss of sensitivity in the fingers can also be an initial symptom of serious diseases, which are best treated at an early stage. Therefore, if numbness occurs frequently and for a long time, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor.
Main reasons
There are two large groups of causes of numbness in the fingers on the left hand, which you can learn about below.
The main ones.
- Doctors say that such symptoms cause problems with the musculoskeletal system: osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, injuries and heavy loads on the vertebrae. All this causes compression of blood vessels and nerve processes. The person feels pain and goosebumps.
- Cerebral ischemia. Due to impaired blood flow, a deficiency of oxygen appears in the cells, which a person feels as numbness.
- A non-physiological posture may also be an explanation.
- Non-pathological reasons: carrying a child or squeezing the wrist with accessories.
Additional.
When wearing backpacks and bags, at low temperatures, or with the arm positioned for a long time above chest level, the plexus of nerve processes and blood vessels is compressed, which disrupts blood circulation and causes spasm of the arteries.
When is surgery needed?
There are a number of situations when conservative therapy does not allow one to get rid of the numbness in the fingers and other symptoms that bothers the patient, or the disease that provokes it poses a serious threat to the life and health of a person. In such cases, patients are recommended to undergo surgical intervention, the nature of which directly depends on the type of pathology detected.
So, the operation could consist of:
- removal of peripheral nerve tumors;
- neurolysis;
- decompression of compressed nerve structures;
- performing nerve plastic surgery for traumatic injuries;
- removal of cervical ribs;
- removal of aneurysms;
- removal of intervertebral hernias, etc.
Peripheral nerve tumor removal
This operation is required when benign or malignant tumors are detected that compress the peripheral nerve trunks. In the first case, it can be carried out by blunt desquamation from a capsule formed by connective tissue. Sometimes it becomes necessary to remove the damaged nerve fragment, after which it is repaired or sutured.
If fingers become numb as a result of the formation of neurofibromas, especially with multiple neurofibromatosis, surgical intervention is indicated only in cases where this benign neoplasm compresses the nerve trunk. This is due to the fact that the removal of one of the tumors can become an impetus for the formation of others, which can complicate the patient’s condition.
When diagnosing cancerous tumors, the operation involves removing the entire tumor, including healthy tissue and nearby lymph nodes. After this, patients are prescribed radiation therapy.
Neurolysis
Neurolysis or release of the nerve from the surrounding connective tissue scar tissue is used for:
- injuries of various types that caused nerve damage;
- compression of the nerve trunk by scar tissue;
- compression of the nerve by an aneurysm;
- failure of the nerve suture.
The goal of the operation is to restore normal nerve conduction. Therefore, it can act as a separate type of surgical intervention, or be only one of its stages.
Decompression of nerve trunks
This operation is performed when carpal tunnel syndrome develops as a result of compression of the nerve in the musculoskeletal canal of the wrist, etc. It is used when pain in the hand persists and there is a significant risk of developing muscle atrophy. The essence of this type of surgical intervention is to dissect the tissue that is compressing the nerve, and sometimes to move the nerve itself, followed by restoration of the anatomy of the musculoskeletal canal.
Plastic surgery and suture of nerve trunks
A nerve suture or neurorhaphy is required when the nerve trunk is ruptured as a result of a traumatic factor or after resection of its fragment during surgery. The essence of the method is the precise comparison of cross sections of the dissected nerve, followed by suturing its sheath or individual bundles.
Nerve repair is indicated when it is impossible to apply a suture due to the remote location of the remaining ends. It consists of using grafts taken from the patient’s other superficial nerves innervating the skin and using them to connect the remaining fragments of the injured nerve trunk. The autograft is fixed with sutures.
Removal of cervical ribs
If the fingers become numb due to the presence of an additional rib at the cervical vertebra, it is recommended to remove it in parts, but entirely along with the periosteum. For this purpose special forceps are used.
Aneurysm removal
The operation can be performed using different techniques, the choice of which directly depends on the location of the aneurysm:
- installation of a vascular stent or coil;
- applying a clip at the base of the aneurysm neck.
Removal of intervertebral hernias
Operations of this type are performed when fingers become numb as a result of the formation of protrusions or hernias in the intervertebral discs of the cervical spine. They can be carried out in different ways, including by:
- hydroplastics;
- nucleoplasty;
- endoscopic hernia removal;
- microsurgical operation.
In all cases, by removing the protrusion of the disc, decompression of the spinal root responsible for the innervation of the arm and fingers is carried out.
Thus, numbness of the fingers can be either a harmless situation, or be a consequence of an injury, or indicate the development of quite dangerous diseases, including the spine. Therefore, when this symptom appears, it is important not to hesitate and immediately contact a neurologist or spinal surgeon.
What is the body saying?
Suddenly my fingers lost sensitivity. If this is a rare phenomenon and it disappears after 2 - 3 minutes, then there is nothing to fear. If such sensations bother you often, then this is a signal of a developing disease.
- Little finger. Paresthesia indicates chronic heart failure and other cardiac pathologies.
- Forefinger. Goes numb with diabetes, occupational stress, inflammation in the joints.
- Thumb. Metabolic processes in the spine are clearly disrupted. You may feel pain in the forearm and weakness in the arm muscles.
- Middle finger. Raynaud's disease, hernia, articular deformity, osteochondrosis of the 7th vertebra.
- Nameless. Numbness due to the fact that the nerve endings in the bend of the elbow are compressed.
Provoking factors
A completely healthy person rarely experiences numbness; they may indicate a hidden pathology in the form of:
- consequences of injuries;
- various diseases of the spinal column;
- joint inflammation;
- degenerative or destructive diseases of the cartilage and ligaments of the hand;
- nervous and mental disorders;
- persistent decrease in blood pressure;
- diseases of the endocrine glands.
There are currently no clear scales that determine the severity of hand numbness. If the unpleasant sensations bother you from time to time and go away after simple movements or rubbing, then you hardly need to worry. However, in case of frequent repetition of numbness, when it happens several times a week or the discomfort increases, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible, as this may be the beginning of the disease.
Treatment methods
In modern medicine, there are several effective methods for treating numbness in the fingers of the left hand.
- Drug therapy. This method involves the use of products selected by a specialist, in the form of ointments, preparations and creams. Which can relieve inflammation, swelling and pain.
- Therapeutic massage and manual therapy.
- Using ultrasound or laser. This will help restore damaged tissue and lost sensitivity.
- Special exercises and health-improving physical education. This will help improve blood circulation and the general condition of the body.
Why does the little finger on my right hand always go numb?
A common culprit in the development of numbness in this case is overexertion. Most people are right-handed, and carpal tunnel syndrome occurs on the right side. Compression of the median nerve occurs in seamstresses, programmers, and sign language interpreters, whose work involves small, monotonous movements.
In second place is cervical osteochondrosis, in which most often the little and ring fingers on the hand go numb . Inflammation of the spinal root leads to disruption of the innervation of the upper limb.
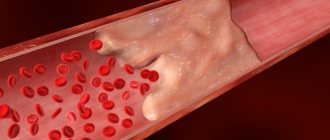
The third is vascular disorders. This is a blockage of the lumen of small vessels by a thrombus, cholesterol plaque (with atherosclerosis), spasm.
On the fourth - damage to the ulnar nerve due to neuritis.
Other root causes of paresthesia:
- fresh and old injuries;
- metabolic disorders;
- hypo- and vitamin deficiencies;
- neoplasms.
Preventing finger numbness
As with most neurological diseases, preventive measures boil down to the following:
- Maintain an active lifestyle. Do exercises and don’t forget about daily physical activity;
- Listen to your body and undergo timely medical examinations to identify pathology at an early stage;
- Periodically get tested and undergo examination of the vascular system;
- Try to eat healthy and balanced. Don't forget to take your vitamins.
The main thing to remember is that the body always warns in advance about changes, and does not suddenly get sick. Few people notice problems that are just beginning; most often they do not pay attention to it, hoping that everything will go away on its own. Lack of time, fear of doctors and injections, reduction of the importance of what is happening ultimately lead to the disease becoming much worse, treatment time taking much longer, or the consequences can cost lives.
How to treat?
For numbness of the hands, there is a universal drug treatment (venotonics, B vitamins, vascular drugs), but in most cases it is not very effective.
The most effective is local (local) treatment:
- shock wave therapy - stimulates blood flow in the area of nerve compression;
- injection of an anti-inflammatory drug (Diprospan, Flosteron) into the area of nerve compression;
- electromyostimulation - with the development of muscle weakness.
All these types of treatment are actively used in the Clinic.
In rare cases, when the course is prolonged and conservative treatment is ineffective, surgical treatment is used.
Make an appointment
Or call us for a consultation
Advantages of treatment at the Professor Kinzersky Clinic
- Specialized care: we are one of the few clinics in the country that specializes in this problem, offering a comprehensive diagnostic and treatment program.
- Application in diagnostics of electromyography: this is a complex diagnostic technique that requires highly specialized education for a neurologist.
- Application of ultrasound of peripheral nerves in diagnostics: we are the first clinic in the Chelyabinsk region that performs these techniques; such a study can only be obtained at CITO (Central Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics) in Moscow)
- Highly qualified doctors : three of our doctors studied at the specialized world congress on ultrasound of peripheral nerves IPSNI (International Society of Peripheral Neurophysiological Imaging)
- Unique capabilities of ultrasound navigation in treatment: Ultrasound navigation allows you to deliver anti-inflammatory drugs to the site of nerve compression as accurately as possible.
The course of treatment can be completed at a convenient time, without interruption from work.
The article was checked by Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Alexander Yuryevich Kinzersky
Diagnostic procedures
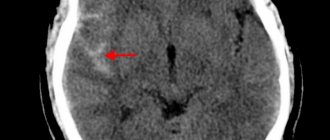
When contacting doctors, it is necessary to exclude preconditions for a stroke and take preventive measures. For this purpose, the doctor prescribes MRI, X-ray, CT and EEG. When the diagnosis is not confirmed and pathological processes in other systems are excluded, doctors identify abnormalities in the functioning of the limbs and the spine.
To determine a diagnosis that facilitates proper therapy, a specialist will have to restore a full picture of the disorder and determine the causes of its occurrence. Various procedures and tests may be used for this purpose.
A complete blood test can reveal the amount of cholesterol in the blood.
What does the electrocardiography procedure consist of:
- X-ray of the spine in the problem area.
- Testing the functioning of muscles and nerve tissues using electroneuromyography
- CT scan to determine disorders of the circulatory system.
- For a detailed diagnosis, you will have to contact highly specialized doctors such as a cardiologist or neurologist.