Women of childbearing age (especially during pregnancy) often encounter varicose veins of the uterus. Diagnosis and, as a result, proper treatment of this disease has become possible in the last thirty years, when clinics began to be equipped with high-precision diagnostic equipment. If varicose veins are not treated in time, the woman may subsequently become infertile. To avoid this, you should contact a phlebologist at the first suspicion of the disease. Your obstetrician-gynecologist can also refer you to a phlebologist after an examination.
Diagnosis of uterine varicose veins
If uterine varicose veins are suspected, the doctor should refer the woman for examination. In modern medicine, various diagnostic methods are used for this:
- radiography;
- Ultrasound using a transvaginal sensor (echography);
- laparoscopy;
- Doppler ultrasound;
- CT scan.
Progressive diagnostic methods used in well-equipped clinics eliminate inaccurate diagnoses.
Varicose veins of the pelvis in women: treatment, medications, recommendations from specialists
There are 2 directions in the treatment of varicose veins of the pelvic organs: conservative and invasive. In the first stages of the development of the disease, in the absence of visible changes in the venous vessels, drug therapy is prescribed, consisting of venotonic drugs of various effects. The main goal of the method is to eliminate symptoms and improve the current condition of the veins. The following groups of drugs are indicated for varicose veins:
- Phlebotonics are drugs to improve venous tone, strengthen the vascular wall and normalize blood circulation, which are the main causes of the disease. The main component of the drug is the substance diosmin;
- Coagulants are blood thinners that reduce blood viscosity and prevent the formation of blood clots;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Vitamin and mineral complex of preparations to maintain general vascular health.
Drug treatment should be combined with physiotherapeutic exercises and compression garments. Regularly wearing compression allows a woman to normalize blood flow, reduce the load on the venous vessels and improve the physiological processes of the body.
In cases where the disease is too advanced, minimally invasive surgeries are more effective methods of treatment. Varicose veins can be removed using the following procedures:
- Sclerobtilation – blockage of a vessel with a special liquid;
- Ovarian vein embolization;
- Crossectomy is a surgical intervention, the essence of which is ligation of the great saphenous vein.
The most effective cure for varicose veins is a healthy lifestyle with moderate physical activity and regular preventive measures if there is a predisposition to this disease.
Treatment of varicose veins of the uterus
Uterine varicose veins are treated in several ways. In the early stages of the disease, it is enough to undergo a course of medication, combining it with wearing compression garments and performing a set of physical exercises to improve blood circulation. Varicose veins during pregnancy sometimes go away after childbirth on their own without much effort.
In an advanced stage, when treatment does not bring results, surgery will be required. In particularly severe cases, the uterus must be amputated, but usually the disease can be cured simply by removing the problematic veins. The operation is carried out using various methods - it can be a conventional surgical or laser phlebectomy. The main thing is that healthy veins are not affected.
Varicose veins of the pelvis: features of the disease and symptoms
Varicose veins of the pelvic venous vessels in most cases affect women of childbearing age. The development of pathology is facilitated by a hereditary predisposition, which provokes degeneration of the walls of blood vessels and failure of the valve apparatus. Secondary factors in the progression of varicose veins can be pregnancy and childbirth, endocrine and gynecological diseases.
Varicose veins of this type are difficult to diagnose in the first stages, because the symptoms are very similar to inflammatory processes or hormonal disorders. Only a thorough ultrasound diagnosis and a series of clinical tests will help identify the problem. Based on the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes special medications and physiotherapeutic procedures indicated for varicose veins.
Varicose veins of the pelvis, depending on the location and severity of symptoms, can develop according to two scenarios:
- Dilation of the vessels of the vulva and perineum is a visible change in the venous vessels in the woman’s genital area, accompanied by bursting pain, itching and heaviness in the lower abdomen. Thinning of the wall of the venous vessel can lead to bleeding during sexual intercourse, which is quite difficult to stop. Another complication of varicose veins is thrombophlebitis. Due to inflammation, the venous nodes become dense, swollen, and the temperature may rise. This pathology most often develops against the background of compression of the abdominal cava and iliac veins as a result of the growth of the uterus during pregnancy.
- Venous congestion syndrome is a chronic form of varicose veins of the pelvic organs, which is often confused with colitis, cystitis and radiculitis due to similar symptoms. Varicose veins are expressed by severe pain in the abdomen, radiating to the sacral region. The syndrome becomes most vivid in the second half of the menstrual cycle and during sex. Treatment involves serious drug therapy.
As a rule, both of these forms of varicose veins complement each other and contribute to the active progression of the disease. The nature of venous expansion can be natural (genetic) or acquired. The main factors for the deformation of damaged veins can be pregnancy, obesity, heavy physical activity or its complete absence, and hormonal imbalance in the body.
Symptoms of varicose veins of the pelvic veins
Symptoms of varicose veins in women are varied. Their manifestation depends on the type and location of the disease, as well as the complexity of the course. As for venous insufficiency of the genital organs and rectum, the symptoms here are quite nonspecific, especially in the initial period of development. For a long time, a woman may not know about the problem and attribute the malaise to gynecological issues or general malaise. How do you know if you urgently need treatment?
- Severe and frequent pain in the lower abdomen, not associated with the menstrual cycle. The more the vein is affected, the more intense the pain, which can radiate to the lower back, upper abdomen and perineum. The help of drugs in advanced cases will not be enough;
- Dysmenorrhea is a pronounced premenstrual syndrome, which is accompanied by intense pain during menstruation, a large amount of discharge, and emotional instability. Requires complex treatment;
- Dyspareunia – pain during sexual intercourse;
- Unpleasant sensations, pain and burning during urination.
To correctly prescribe a medicine, a gynecologist carefully examines the patient’s medical history and conducts a comprehensive diagnosis based on ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound and diagnostic laparoscopy.
Childbirth with varicose veins
Women with a predisposition to varicose veins also need medical supervision. Although the natural course of delivery is often accompanied by premature breaking of waters, short duration of contractions, postpartum hemorrhage, placental abruption, doctors strive to ensure the birth of the child naturally.
The uncomplicated course of varicose veins allows women to count on a natural course of childbirth. To prevent the backflow of blood into the veins during pushing, it is necessary to bandage both legs of the woman in labor with elastic bandages, or use compression stockings.
Expectant mothers must undergo laboratory tests to determine blood clotting. If a tendency towards increased coagulation is detected, the doctor prescribes medications to correct it and means to reduce platelet aggregation.
In the postpartum period, women need to get out of bed early, visit the physical therapy room, and continue elastic leg bandaging. If surgical delivery has taken place and there are significant disturbances in the blood coagulation system, drug treatment continues. In case of complex course of varicose veins, if the situation does not change after childbirth, they resort to surgical intervention.
To prepare for the birth of a child, it is useful for a woman to take walks lasting up to two hours, this helps improve blood circulation.
You need to give up heels and wear comfortable, stable shoes. Every day you need to give your legs a rest by placing your feet in an elevated position. For a good night's rest, it is advisable to place a small pillow under your stomach and legs. It is useful for a pregnant woman to visit the pool and use a contrast shower.
Pregnancy is characterized by changes in the hormonal background of the female body. A decrease in the amount of estrogen and an increase in the amount of hormones, relaxing the walls of blood vessels, leads to their varicose veins.
Regular visits to the doctor for examination help to promptly identify disorders that can lead to varicose veins. This may be an increase in venous pressure levels, slowing
blood circulation in the legs, which leads to the occurrence of disease. Varicose veins contribute to placenta previa or low position. This doubles the risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth. Regular examinations, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and following all medical recommendations contribute to the birth of a healthy baby during natural delivery.
How to prevent the formation of varicose veins?
If you need to stand or sit for a long time, walk every 30–40 minutes or at least stretch your legs, and in the evening, every hour, lie down for 15 minutes with your legs raised above your body. Don't cross your legs. When you lie down, place a pillow under your feet to elevate them.
- Try to move every day: regularly swim, do gymnastics or walk.
- Take care to massage your legs - this should always be done in the direction of the heart, that is, from the feet upward.
- Don't carry heavy things.
- Choose shoes with wide toes and low heels, and do not wear clothes that restrict movement.
- Avoid high temperatures (hot baths, sauna, solarium, prolonged tanning), as it quickly dilates blood vessels.
- Take preventative medications that strengthen the walls of blood vessels.
- Take over-the-counter anti-varicose capsules to improve vein tone. Swollen legs are wiped with gels containing Troxevasin or Heparin.
- Wear anti-varicose tights or stockings. You need to put them on before getting out of bed (before the blood flows to your feet). Good tights should have adequate compression, so you need to choose them based on a medical prescription.
How to determine whether a problem has occurred?
The first warning sign is the feeling of heavy legs - you feel them as if they were made of lead.
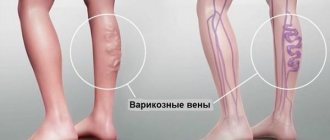
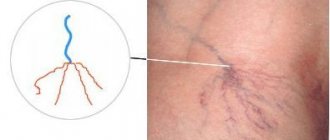
Often, during pregnancy, your feet become swollen and a little sore, especially at the end of the day. There is tingling, burning, itching, and sometimes cramps. Purple “webs” are small dilated veins or cracks in small capillaries. At the initial stage, the problem is more aesthetic than harmful to health, but the next stage is varicose veins. When the veins cannot withstand the pressure of the residual blood, they dilate, elongate and begin to resemble blue ribbons just under the skin. Then it is no longer just a beauty defect, but a medical problem.
Fortunately, after childbirth, when everything returns to normal, varicose veins often become less noticeable and sometimes even disappear without a trace, but they may appear during the next pregnancy, especially if little time has passed since the birth of the baby.
Venous thrombosis
Dilated veins can cause not only pain, but also a dangerous complication in the form of thrombosis. As a result of stagnation of blood in the vessels, a thrombus can occur, which, like a plug, clogs the vessel, preventing free blood flow. Thrombosis is further promoted by increased blood viscosity during pregnancy.
Venous thrombosis is manifested by severe pain, swelling of the leg, redness of the veins, and sometimes a noticeable thickening at the site of the blood clot. If you notice such ailments, do not delay visiting your doctor. Injections will be needed to reduce blood clotting. Don't blame these symptoms on tired legs or temporary worsening. If part of the clot is not removed, it can travel through the bloodstream and clog important blood vessels.