Diabetes mellitus requires a person to pay increased attention to health. In particular, the patient must keep the level of caxapa in the blood under control. The saturation of the body's cells with energy depends on this. Their starvation can lead to dangerous consequences, including diabetic coma and death.
To measure your sugar levels you no longer need to visit a clinic. There are special devices - glucometers that are suitable for home use. They do not require medical skills and allow you to track your sugar yourself. We will figure out what types of glucometers there are and what to consider when choosing.
Types of glucometers
The classification is based on the operating principle of the device. Devices for measuring blood sugar levels are divided into invasive and non-invasive. The first involves pricking a finger and collecting capillary blood. They are:
- photometric;
- electrochemical;
- coulometric.
Express test strips are considered separately from invasive glucometers. This is not a device, but rather an indicator of sugar content. Although you also need to pierce your finger to use it.
For children and elderly patients, it is more convenient to use non-invasive ones. They do not require blood for analysis, so the measurement is absolutely painless. This category includes sensor devices (or Raman devices), including laser ones. They determine glucose levels based on subjective factors, so their accuracy is somewhat lower.
Diacont Classic
This glucometer is as practical and budget-friendly as possible. There is no need to code Diacont Classic, so the risk of errors is reduced to zero. This glucometer has an electrochemical method for determining results, and for analysis you need just a little blood (0.5 microliters), which reacts with protein. The device is calibrated using plasma, and after measuring the sugar level, the display will show information whether there is a deviation from the norm. It takes literally 5 seconds to determine your blood glucose level. The only negative, according to reviews from Diacont Classic users, is that sometimes when sugar levels are high, the device increases the readings.
Diacont Classic
Genom Biotech, India; Panacea Biotec, India
Highly accurate, large-screen blood glucose meter with hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia warning, PC data port and no-coding test strip measurement system.
The measurement takes just 6 seconds, and only 0.7 µl of blood is required for analysis. The Diacont glucometer stores 250 measurements in memory, calculates the average value for 7, 14, 21 and 28 days, and turns on and off automatically. Supplied complete with test strips, lancets, blood drop device, automatic scarifier with alternate blood collection facility, control solution and storage case. from 118
5.0 1 review
14
- Like
- Write a review
Photometric glucometers
These devices read the change in color of a test strip onto which the patient's blood is applied. Such strips are coated with a reagent containing glucose oxidase. It gives specific responses to a particular level of glucose concentration, coloring the strip in the appropriate color.
You don't have to compare colors yourself. The scale is already stored in the device's memory. When a test strip is inserted into it, it compares its color with the values on this scale and produces a numerical result.
Such devices are easy to use, but quickly break down. In addition, their optical system is so fragile that there is a high probability of breaking the glucometer during operation. And if the lens becomes cloudy, the results may be distorted.
Electrochemical glucometers
Their action is based on the amperometric method of analysis. The test strips here are also lubricated with a reagent, but when they come into contact with blood, coloring does not occur. During the reaction, electric current is released. Its strength depends on the sugar level.
Electrochemical devices eliminate a number of disadvantages of photometric devices:
- increased strength;
- the accuracy of measurements has been increased (current strength is a specific value, as opposed to color);
- the required amount of blood for analysis has been reduced.
A child, an elderly person or simply a person with a low pain threshold will definitely prefer this type of sugar meter. The depth of the puncture depends on the required volume of blood. If less is required, the procedure is less painful.
Measuring blood sugar with a glucometer: norm, table of indicators, algorithm of operation
Patients with diabetes need to measure their blood sugar levels daily using a home glucometer. This allows the diabetic not to panic and provides complete control over his health.
Glucose is commonly called sugar. Usually this substance enters the blood through food. After food enters the digestive system, carbohydrate metabolism starts in the body.
With increased sugar levels, insulin levels can increase sharply. If the dosage is large and the person has diabetes, the body may not be able to cope, resulting in a diabetic coma.
Glucose is commonly called sugar.
What blood glucose numbers are considered normal?
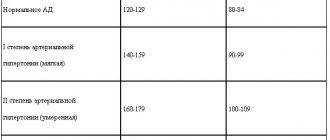
To determine the presence of pathology, you should know about the normal level of glycemia. With diabetes, the numbers are higher than in a healthy person, but doctors believe that patients should not lower their sugar to minimum limits. Optimal values will be 4-6 mmol/l. In such cases, the diabetic will feel normal and get rid of cephalgia, depression, and chronic fatigue.
Normal values for healthy people (mmol/l):
- lower limit (whole blood) – 3, 33;
- upper limit (whole blood) – 5.55;
- lower threshold (in plasma) – 3.7;
- upper threshold (in plasma) – 6.
The numbers before and after food enters the body will differ even in a healthy person, since the body gets sugar from carbohydrates in food and drinks. Immediately after a person has eaten, the glycemic level increases by 2-3 mmol/l. Normally, the pancreas immediately releases the hormone insulin into the bloodstream, which should distribute glucose molecules throughout the tissues and cells of the body (in order to provide the latter with energy resources).
As a result, sugar levels should decrease and return to normal within 1-1.5 hours. This does not happen against the background of diabetes. Insulin is not produced enough or its action is impaired, so more glucose remains in the blood, and tissues in the periphery suffer from energy starvation. In a diabetic, the level of glycemia after meals can reach 10-13 mmol/l with a normal level of 6.5-7.5 mmol/l.
In addition to the state of health, what numbers a person gets when measuring sugar is also influenced by his age:
- newborn babies – 2.7-4.4;
- up to 5 years of age – 3.2-5;
- school-age children and adults under 60 years of age (see above);
- over 60 years old – 4.5-6.3.
The numbers may change individually, taking into account the characteristics of the body.
How to determine sugar levels using a glucometer.
Regulating Blood Sugar Levels
– one of the fundamental foundations of our health. If it is impaired, the development of chronic diseases is only a matter of time. It turns out that measuring blood sugar levels is a powerful tool for monitoring health problems that everyone should use at least from time to time.
Dysglycemia (dysglycemia) underlies diseases such as metabolic syndrome, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative diseases.
At the same time, it can be difficult to understand that sugar regulation is impaired - even under the close supervision of doctors. The reason is that modern medicine tends to look for pathology in its measurements and is not concerned with optimal health indicators.
It turns out that when our indicators are far from optimal for health, but by medical standards do not yet fall into the intervals of prediabetes or diabetes, as a rule, we are not warned about this.
That is, prediabetes or diabetes can fall on a person almost out of the blue, as if there is no interval between the optimal blood sugar level for health and prediabetes.
However, dysregulation of blood sugar levels is a long process that usually develops over years. And it is precisely until this process has reached a stage that is recognized by medicine as a pathology that it is easiest to reverse it and prevent the disease.
This test asks a person to drink a solution containing 75 grams of pure glucose.
Glucometer device
A classic glucometer consists of the following elements:
- accumulator battery;
- instrument for piercing fingers - semi-automatic scarifier (lancet);
- electronic unit equipped with a liquid crystal display;
- unique set of test strips.
To record the results of measuring blood sugar, you can create a special table or use ready-made forms of self-monitoring logs.
Glucometers may differ in size, operating speed, memory and screen parameters, and cost. Modern glucometers are compact, accurate, have a high speed of obtaining results, do not require complex maintenance, and to use them you only need a small amount of capillary, i.e., blood taken from a finger.
Modern models can be equipped with useful additional functions:
- memory;
- computerization of results;
- the ability to save the latest results;
- separate maintenance of statistics;
- calculating the average blood sugar level for a certain period;
- control of ketone bodies in the blood;
- auto-encoding of test strips;
- voice function.
All glucose meters measure blood sugar differently and give different results. Each device is calibrated (set) using a standard glucose solution. After calibration, each batch of strips receives a unique digital code that is entered into the meter. The device must be calibrated according to the test strips. In some meter models, the code must be entered manually for each new batch of test strips; in other glucometers, the code is entered automatically.
To compare the results of different devices for measuring blood sugar, you need to know the true value of glucose in the blood, which can only be determined by a laboratory analyzer. The best way to check the accuracy of your home glucose meter is to compare the results obtained on your personal device with laboratory values at each doctor's visit.
Analysis algorithm.
Memo
It is best to determine your glucose level in the morning on an empty stomach or simply on an empty stomach. After eating, the answer may not be accurate.
Don't forget about the expiration date of test strips. They must be stored in a dry place at room temperature. Unusable test strips will give the wrong answer and will not help to detect the deterioration of the patient’s condition in a timely manner.
For insulin-dependent patients, testing is performed before each insulin injection. It is best to pierce the skin on the fingers on the side of the pads, as this place is considered less painful than the rest. Hands should be dry and clean. It is necessary to constantly change the place for puncturing the skin. Never use someone else's lancets for your blood glucose meter.
You can take out the test strip only immediately before the procedure for measuring blood sugar. The test strip and meter code must be identical. Do not pierce the skin too deeply to avoid damaging the tissue. A drop of blood that is too large can distort the result, so you should not deliberately squeeze it out or drop more than the required amount onto the test strip.
1 Wash and dry your hands thoroughly.
Glucometer readings: norm, table
Using a personal glucometer, you can monitor the body’s response to food and medications, control the required level of physical and emotional stress, and effectively control your glycemic profile.
The sugar norm for a diabetic and a healthy person will be different. In the latter case, standard indicators have been developed that can be conveniently presented in a table.
For a diabetic, an endocrinologist determines the normal limits according to the following parameters:
- Stage of development of the underlying disease;
- Concomitant pathologies;
- Age of the patient;
- Pregnancy;
- General condition of the patient.
Prediabetes is diagnosed when the glucometer reading increases to 6.1 mmol/l on an empty stomach and from 11.1 mmol/l after a carbohydrate load. Regardless of the time of meal, this indicator should also be at the level of 11.1 mmol/l.
If you have been using one device for many years, it is useful to evaluate its accuracy when taking tests in the clinic. To do this, immediately after the examination you need to take a second measurement on your device. If a diabetic’s sugar levels drop to 4.2 mmol/l, an error on the glucometer is allowed no more than 0.8 mmol/l in any direction. If higher parameters are assessed, the deviation can be either 10 or 20%.
When processing results electronically, important parameters will be the memory capacity from 30 to 1500 of the last measurements and the program for calculating the average value for half a month or a month.
About glucometers
The device for measuring blood glucose levels is a portable device equipped with a display and functional buttons. According to the technical characteristics, the following glucometers are used today:
- photometric – indicators are assessed by changes in the color indicator;
- electrochemical - according to current strength;
- non-invasive devices, i.e. without punctures of the skin (thermal, spectral, ultrasound, tonometric).
The latest version of glucometers allows you to avoid permanent injury to the skin and accidental infection of the puncture wound. The disadvantage of this type of device is the high price category. In addition, not all non-invasive models are certified in the Russian Federation. The most common assistant for Russian diabetics is an electrochemical glucometer.
The prerogative aspects of the device include:
- price;
- accuracy (minimum error of results);
- ease of operation;
- high speed of obtaining results;
- auto-encoding of strips (test strips);
- “blood drop” function (0.3 µl is enough to check sugar levels);
- memory function (you can save the results of previous measurements);
- customization function;
- availability of consumables (strips).
Depending on the specific model, the meter may be equipped with additional capabilities for measuring ketone bodies and cholesterol. Popular among diabetics are the functions of calculating the average glycemic value per day (week, month), and automatic connection with a home computer.
Devices differ from each other in color, shape, font size (numbers displayed on the display). Among domestic models, the Satellite Express glucometer (manufactured by Elta, Russia) is considered the leader. The device is distinguished by high accuracy of results and an affordable cost. Equipped with functions:
- auto-on;
- memory;
- uninterrupted use more than 2 thousand times.
Another plus is the Russian-language menu.
The most popular imported devices are glucometers of the AccuChek line (Accu-Chek), manufactured in Switzerland:
- Mobile;
- Assets;
- Performa.
The price of foreign devices is an order of magnitude higher than domestic ones.
After the procedure, the results and time of measurement must be recorded in the Diabetic Diary.
Coulometric glucometers
This is a type of electrochemical meters. The principle of determining glucose concentration is similar to amperometric. Only in this case, it is not the current strength that is assessed, but the electric charge. The required volume of blood for analysis is minimal compared to all other devices.
Amperometric instruments are more often used in laboratory practice, while coulometric instruments are usually used for home use.
The two subtypes differ in the price of consumables. Patients with type 1 diabetes need to measure their glucose more often. Therefore, it is more profitable for them to acquire an amperometric device with cheaper test strips. Coulometric tests are recommended for the control of type 2 diabetes.
Subtleties of choice
The type of disease is not important when choosing a glucometer. The device is a universal measurement tool for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. But there are other subtleties!
Vladimir Zhuvak says: “Those people who suffer from diabetes and at the same time have a high drug load, whose diet contains sugar substitutes, whose biochemical composition of the blood is not in order, is not recommended to choose glucometers, the instructions of which say that this type of glucometer is characterized by cases influence of interfering substances. If you use brands of glucometers whose operation is affected by oxygen, then you need to take into account that the less oxygen, the less intense the chemical reaction in the blood will take place, as a result, the readings displayed on the glucometer display will be underestimated. And vice versa. This information is especially relevant for people moving below or above sea level, climbing a mountain or, conversely, descending to lowland areas, and having respiratory diseases. Any user must responsibly study the information provided by the manufacturer before purchasing a device.”
Yuri Glukhov's opinion : “There are many nuances that must be taken into account when choosing a glucometer. The device must meet international standard accuracy, be easy to use, quickly produce results, and require a small volume of blood for analysis. Long-term warranty service is highly desirable (in our case it is unlimited). The measurement range is also important - it is necessary that the glucometer can detect both very low and high blood glucose levels. Typically, this range is from 0.6 to 35 mmol/L. I would also like to note that it is extremely important that the device gives a signal about the need to quickly replace the battery. This is necessary so that a person does not end up with a non-working glucometer at the most inopportune moment.”
In conclusion, one more piece of advice. Remember to check your meter every three years - this is the standard verification period. This is done in the manufacturer’s warranty service or in special laboratories. For example, in Moscow this is done at the center for checking glucometers ENTS (Moskvorechye Street, 1).
For reference:
Medtechservice is a Russian manufacturer of a full cycle of diabetic test strips for Gmate Life glucometers, created as part of the implementation of the National Healthcare Project. The company launched its production in mid-2019, gained a foothold in the domestic market and plans to export in 2022.
ELTA is the first Russian manufacturer of means for express measurement of blood glucose levels. The company's products are exclusively its own original developments. Exports glucometers to Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Belarus.
Text: Lydia Gromeka
Post Views: 3,104
Rules for using a glucometer
Anyone can use this device at home. The main thing is to have consumables (test strips) in stock if the measurement is carried out using an invasive method. It is important to monitor their expiration date: damaged products will not provide the required accuracy.
Using a glucometer comes down to a few simple steps:
- thorough hand washing;
- disinfection of the puncture site;
- pricking the fingertip with a lancet;
- applying blood to the test strip;
- inserting the strip into the device.
The sequence of the last two steps depends on the type of device. The photometric strip is inserted with blood already applied. It is placed clean in the electrochemical one.
There is no need to insert express strips anywhere. Just wait for the color to change. With non-invasive it is even easier. It is only necessary to ensure contact with the skin (the area depends on the type of device).
What else will you need besides a glucometer?
Buying a glucometer is half the battle. To measure glucose levels, you also need other components: a lancing pen , lancets , also known as scarifiers (cartridges for lancing the skin that are inserted into a lancing pen) and test strips . The range in cost of test strips in a package of 50 pieces, depending on the manufacturer, varies from 480 to 1,500 rubles per package. Patients with type 1 diabetes require 150-180 test strips per month, type 2 diabetes a little less. For the first days, the test strips included in the kit along with the glucometer will be enough.
Gmate LIFE Product Suite
If you can choose a lancing pen and lancets that go with it according to your taste and wallet, then for each glucometer, for accuracy of measurements, only certain strips from the same manufacturer are suitable; there are no universal ones for all models, so the choice of glucometer will affect how much money you will spend on test strips. Please note that you will have to buy additional consumables quite often in any case.
A comfortable piercing pen should have different puncture depth modes, since the skin of adults, the elderly and children differs in thickness and requires different piercing forces, manufacturers remind.
It should be noted that the primary kits accompanying the glucometer are practically the same from different manufacturers.
Vladimir Zhuvak talks about his own products: “The kit with our Gmate Life glucometers, which have a lifetime guarantee, allow you to store 500 measurements and have an auto-encoding function, also includes a case, 25 test strips, a lancing pen, ten disposable lancing lancets and instructions for application."
The Satellite Express kit, according to Yuri Glukhov, includes the device itself with a battery, a control strip that allows the user to independently diagnose the glucometer to ensure its serviceability, a case, test strips (25 pcs) with a code strip, and a pen - piercer, disposable scarifiers (25 pcs), instructions.
The Satellite Express kit includes the glucometer itself with a battery, a control strip for self-diagnosis of the device, a case, test strips (25 pcs) with a code strip, a lancing pen, disposable scarifiers (25 pcs), instructions
“Our pharmacy, like most others, offers both domestic and foreign glucometers. Buyers are still more likely to buy foreign ones, but I don’t see a fundamental difference between them. Russian glucometers are gaining more and more market share every year. They are cheaper, but at the same time practically not inferior in quality. An important argument in support of our glucometers is that patients registered with an endocrinologist in city clinics can receive free test strips for them. They are also issued to imported ones, but to ours much more often and in greater numbers.”
Natalya Brichkina, pharmacist
Is it possible to take blood from something other than a finger?
Traditionally, blood for testing is taken from a finger or from a vein. In the case of assessing sugar levels, venous is not very preferable. It contains more glucose than capillary, and there is a high risk of incorrect interpretation of the analysis. Therefore, blood for sugar is taken from a finger.
But there are many nerve endings in the fingertip. For many people, piercing is too painful. Therefore, there are high-quality glucometers that include the ability to analyze blood from:
- shoulder;
- forearms;
- shins;
- hips.
It's not that painful to pierce them. However, blood circulation in these parts of the body is slower than in the fingers. Therefore, changes in glucose levels do not always appear in a timely manner according to analyzes from alternative sites.
Device coding
This is a procedure on which the accuracy of the results depends. It allows you to bring the device itself and the test strips that come with it into maximum compliance. Older models required manual coding. It was replaced by electronic chips.
The most advanced devices do not require coding. It occurs automatically when the test strip enters the housing. The glucometer reads the code and configures itself.
No Coding technology was developed because it became apparent that most patients were not completing the necessary adjustments. The coding procedure cannot be ignored, as this reduces the accuracy of measurements. As a result, it is not possible to accurately determine the dose of insulin that needs to be administered to the patient.
Reading information
Each glucometer is configured to the parameters of a given pack of test strips and reads information in the following way:
- codeless glucometer. This type of device is perfect for older patients;
- glucometer device with manual coding input function. The test strip code must be entered manually. An affordable and accurate device, but this type of device is convenient for people with good eyesight;
- glucometer device with chip function. The patient simply inserts a chip into the device, which is sold with test strips;
- glucometer device with automatic fine-tuning function without patient intervention. But the cost of a glucometer with such test strips is significantly higher. Although this is a very convenient type, it is better to choose for the elderly, novice users, and medical institutions.
As a result of everything stated, we can say that the accuracy of glucometer measurements does not directly depend on the method of processing information, but may depend on the correctness of the manipulations.
How to choose the right glucometer
You can see many models on the market. Equally high-quality devices differ in the degree of convenience for a particular user. You can understand which glucometer is best to buy for your home by answering a few questions:
- Which type of device is most convenient for you?
- Does the required blood volume matter? For the elderly, children and especially sensitive people, the depth of the puncture is important.
- Is measurement time important? Faster ones cost more, but not everyone needs them.
- What test strips are available in pharmacies near you?
- Is additional plasma calibration required? In simpler devices it is carried out through capillary blood.
- How much memory is needed? This determines how many last measurements can be recorded.
It is important to decide whether additional features are needed. Modern sugar meters can have a lot of them. But their presence is not necessary.
Glucometer and laboratory analysis. What is the difference?
Portable analyzers are divided into hospital glucometers (they are used in hospitals of medical institutions) and individual ones, for personal use. Hospital glucometers are used for the primary diagnosis of hypo- and hyperglycemia, for monitoring glucose in hospitalized patients in endocrinology and therapeutic departments, and measuring glucose in emergency situations.
The main advantage of any glucometer is its analytical accuracy, which characterizes the degree of closeness of the measurement result of this device to the true picture, the result of the reference measurement.
A measure of the analytical accuracy of a glucometer is its error. The smaller the deviation from the reference values, the higher the accuracy of the device.
Owners of different models of glucometers often doubt the readings of their analyzer. Monitoring glycemia with a device whose accuracy is not certain is not easy. Therefore, it is important to know how to test your glucose meter for accuracy at home. Measurement data from different models of personal glucose meters sometimes does not match laboratory results. But this does not mean that the device has a manufacturing defect.
Experts consider the results of independent measurements to be accurate if their deviation from the indicators obtained during a laboratory examination does not exceed 20%. Such an error does not affect the choice of treatment method, so it is considered acceptable.
The degree of deviation may be affected by the configuration of the device, its technical characteristics, and the choice of a specific model. Accuracy of measurements is important to:
- Choose the right device for home use;
- Adequately assess the situation if you feel unwell;
- Specify the dosage of medications to compensate for glycemia;
- Adjust your diet and physical activity.
Laboratory tests check sugar both in capillary and venous blood. The difference between these readings is up to 0.5 mmol/l.
For personal glucometers, analytical accuracy criteria in accordance with GOST: 0.83 mmol/l for plasma glucose levels less than 4.2 mmol/l and 20% for results greater than 4.2 mmol/l. If the readings exceed the permissible deviation limits, the device or consumables will have to be replaced.
Reasons for distorting results
Inaccuracies can also arise from careless collection of biomaterial. You should not rely on the result when:
- A contaminated test strip if it was not stored in its sealed original packaging or in violation of storage conditions;
- A non-sterile lancet that is used repeatedly;
- For an expired strip, sometimes you need to check the expiration date of the opened and closed packaging;
- Insufficient hand hygiene (wash them with soap, dry them better with a hairdryer);
- Using alcohol when treating the puncture site (if there are no options, you need to give time for the vapors to erode);
- Analysis against the background of treatment with maltose, xylose, immunoglobulins - the device will show an inflated result.
How can I check if my glucometer is working correctly?
You can evaluate the operation of the device using a special liquid called a control solution. Each manufacturer produces a specific test solution for its models, this must be taken into account.
The bottles contain a known concentration of glucose. Components that increase the accuracy of the procedure are used as additives.
If errors are detected, the test is repeated. If the readings are the same or the glucometer shows different results each time, you should not use such a device.
Possible deviations
If you want to check your glucometer for accuracy, it is best to start with home diagnostic methods. But first, you need to clarify whether you are using consumables correctly. The device may be faulty if:
- Store the pencil case with consumables on the windowsill or near the radiator;
- The lid on the original packaging with stripes is not tightly closed;
- Consumables with an expired warranty period;
- The device is dirty: contact holes for inserting consumables, photocell lenses are dusty;
- The codes indicated on the pencil case with stripes and on the device do not match;
- Diagnostics are carried out in conditions that do not comply with the instructions (permissible temperature range from +10 to +45°C);
- Hands are frozen or washed with cold water (there will be an increased concentration of glucose in the capillary blood);
- Hands and equipment are contaminated with sweet products;
- The depth of the puncture does not correspond to the thickness of the skin, the blood does not come out spontaneously, and additional efforts lead to the release of intercellular fluid, which distorts the readings.
Before checking the accuracy of your glucometer, you need to check whether all conditions for storing consumables and collecting blood are met.
Manufacturers of glucometers in any country are required to test their devices for accuracy before entering the pharmaceutical market. In Russia, this is GOST 115/97. If 96% of the measurements taken fall within the error range, then the device meets the requirements. Personal devices are notoriously less accurate than their hospital counterparts. When purchasing a new device for home use, checking its accuracy is mandatory.
Experts recommend checking the performance of the glucometer every 2-3 weeks, without waiting for special reasons to doubt its quality.
If the patient has prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, which can be controlled with a low-carbohydrate diet and adequate muscle exercise without hypoglycemic medications, then you can check your sugar once a week. In this case, the frequency of checking the functionality of the device will be different.
An unscheduled check is carried out if the device has been dropped from a height, moisture has entered the device, or the package of test strips has been unsealed for a long time.
A blood glucose meter is an essential tool in the treatment of diabetes and should be taken with the same seriousness as medications.
Individual glucometers are intended only for self-monitoring of glucose in diabetics and patients with other diagnoses requiring such a procedure. And they should only be purchased at specialized retail outlets - this will help avoid counterfeits and other unwanted surprises.
What blood is used to determine glycemia
Blood sugar levels can be determined by venous (from a vein, as the name implies) and capillary (from vessels on the fingers or other parts of the body) blood.
In addition, regardless of the sampling site, the analysis is carried out either on whole blood (with all its components) or on blood plasma (the liquid component of blood containing minerals, salts, glucose, proteins, but not containing leukocytes, red blood cells and platelets).
What's the difference?
Venous blood flows away from the tissues, so the concentration of glucose in it is lower: primitively speaking, some of the glucose remains in the tissues and organs that it has left. And capillary blood is similar in composition to arterial blood, which only goes to tissues and organs and is more saturated with oxygen and nutrients, therefore it contains more sugar.
In whole blood, the sugar level is lower because it is diluted with red blood cells that do not contain glucose, and in plasma it is higher because it does not contain red blood cells and other so-called formed elements.
According to WHO standards 1999-2013, glucose levels are as follows:
The vast majority of modern glucometers for home use determine the sugar level using capillary blood, but most models are configured for capillary blood plasma.
There is an official international standard that will help convert the glucose concentration in whole blood to the equivalent in plasma and vice versa. For this, a constant coefficient of 1.12 is used.
How to convert the result from plasma to whole blood?
There are several ways to convert the If value on plasma indicators to capillary blood values:
- subtract 12% from the result obtained
- divide the result by 1.12
- multiply the result by 0.88
Permissible errors in the operation of the glucometer
According to the current GOST ISO, the following errors are allowed in the operation of home glucometers:
- ± 15% for results greater than 5.55 mmol/l
- ± 0.83 mmol/L for results not exceeding 5.55 mmol/L.
It is officially recognized that these deviations do not play a decisive role in the control of the disease and do not entail serious consequences for the patient’s health.
It is also believed that the greatest importance in monitoring the patient’s blood glucose levels is the dynamics of the values, and not the numbers themselves, unless we are talking about critical values. If a patient’s blood sugar level is dangerously high or low, it is necessary to urgently seek specialized medical care from doctors who have precise laboratory equipment at their disposal.
Where can you get capillary blood?
Some glucometers allow you to take blood only from your fingers, while experts recommend using the side surface of your fingers, since there are more capillaries on it. Other devices are equipped with special AST caps for collecting blood from alternative sites.
Please note that even samples from different parts of the body taken at the same time will vary slightly due to differences in blood flow rates and glucose turnover rates. The closest to the indicators of blood taken from the fingers, considered the reference, are samples obtained from the palms of the hands and earlobes. You can also use the lateral surfaces of the forearm, shoulder, thigh and calves.
Why do the readings on different glucometers differ?
Even the readings of absolutely identical models of glucometers from the same manufacturer will most likely differ within the permissible error, and what can we say about different devices! They can be calibrated against different types of test material (capillary whole blood or plasma). Medical laboratories may also have different equipment calibrations and uncertainties from your instrument. Therefore, it makes no sense to check the readings of one device against the readings of another, even identical, or laboratory ones.
What could be causing the difference in results?
- Glucose levels measured at the same time depend on how the device is calibrated: whole blood or plasma, capillary or venous. Be sure to carefully read the instructions for your devices!
- The time difference between sampling - even half an hour plays a role. And if, say, you took some medicine between samples or even before them, then it can also affect the results of the second measurement.
- Drops are taken from different parts of the body. Even the readings of samples from the finger and the palm will be slightly different, the difference between the sample from the finger and, say, the calf area is even greater.
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules. You should not take blood from wet fingers, since even residual liquid affects the chemical composition of a drop of blood. It is also possible that when using alcohol wipes to disinfect the puncture site, the patient does not wait for the alcohol or other antiseptic to wear off, which also changes the composition of the blood drop.
- Dirty scarifier. A reusable scarifier will carry traces of previous samples and “contaminate” the fresh one.
- Too cold hands or other puncture site. Poor blood circulation at the site of blood collection requires additional effort when squeezing out the blood, which saturates it with excess intercellular fluid and “thin” it. If you are drawing blood from two different places, restore circulation to them first.
- Second drop. If you follow the advice to measure the values from the second drop of blood, wiping the first with a cotton swab, this may not be correct for your machine, since the second drop contains more plasma. And if your meter is calibrated using capillary blood, it will show slightly higher readings than a plasma glucose meter, which requires the first drop of blood to be used. If you used the first drop for one device, and use the second from the same place for another, as a result of the additional presence of blood on the finger, its composition will also change under the influence of oxygen, which will certainly distort the test results.
- Incorrect blood volume. Glucometers calibrated using capillary blood most often determine the blood level when the puncture site touches the test strip. In this case, the test strip itself “sucks up” a drop of blood of the required volume.
- The test strips from one of the devices were not stored properly or their expiration date had expired. For example, the strips were stored in an environment that was too humid. Improper storage accelerates the decomposition of the reagent, which, of course, will distort the results of the study.
- The analysis is carried out under unacceptable external conditions. The correct conditions for using a glucometer are an altitude of no more than 3000 m above sea level, a temperature in the range of 10-40 degrees Celsius, and a humidity of 10-90%.
Why do my meter readings differ from my lab results?
The idea of using numbers from a regular laboratory to test a home glucose meter is initially wrong. If you want to ensure the accuracy of your glucometer, you must contact a specialized laboratory accredited by Rosstandart of the Russian Federation at the initiative of the manufacturer of your device.
If you do decide to compare your results with results in the laboratory, remember that equipment in the laboratory and at home can (and most likely will) be calibrated for different types of blood - venous and capillary, whole and plasma. It is incorrect to compare these values. Since the level of glycemia in Russia is officially determined by capillary blood, the laboratory readings in the results on paper can be converted into the values of this blood type using the coefficient 1.12 (or 12%) already known to us. But even in this case, discrepancies are possible, since laboratory equipment is more accurate, and the officially permitted error for home glucometers is 15%.
Important! All comparative measurements must be made simultaneously and from one drop of blood.
The DIN EN ISO 15197 standard sets the following requirements for glucometers:
- For values less than 4.2 mmol/l, the difference between 95% of the results and the standards should not exceed 0.82 mmol/l.
- At a concentration greater than or equal to 4.2 mmol/L, 95% of measurements are allowed to fluctuate from the reference values by no more than 20%.
When should you think about the accuracy of the device?
- When you turn on the device for the first time.
- If you suspect a malfunction.
- In case of long-term storage of control test indicators.
- If the device is suspected of being damaged: a fall from a height, exposure to low or high temperatures, moisture, ultraviolet rays, liquid or condensation.
- In case of prolonged non-use of the device.
In addition to the malfunction of the device itself, the accuracy of its readings is affected by compliance with operating rules, external conditions and proper storage of the device. Optimal conditions provide a reduction in error to 2%. The higher the glucose concentration, the less accurate the readings. In addition, performance is affected by both excessive and insufficient blood volume.
To diagnose the device, you should contact a certified service center of the manufacturer whose glucometer you are using.
What may influence the difference in results?
Additional functions of the meter
Typically, the device only measures the blood glucose concentration using a preset method. The kit includes the device itself, a set of test strips for the first time and a lancet for piercing the skin.
More expensive models come with statistical options, including separating measurements taken before and after meals. This is convenient for those who forget to fill out self-monitoring diaries.
A glucometer for an elderly or visually impaired person may have a voice assistant or a backlit display. The additional expense in this case is justified. You can also invest in an option with an auto-lancer, because not everyone has the fortitude to do it manually.
Options such as the ability to communicate with a computer or smartphone, the presence of extra control buttons and a timer are unimportant. Some sugar meters also analyze cholesterol levels.
iCheck
iCheck is one of the most budget-friendly electrochemical glucometers with the most necessary functions: minimal memory, choice of units of measurement, the ability to determine the average test result, connection to a PC. iCheck is suitable as a starter kit for those who only need a basic blood glucose measurement. Among the advantages are the ability to choose the depth of the puncture and a lifetime warranty on the device. Cons: few functions, slow operation, requires 2 microliters of blood.
iCheck
The iChek blood glucose monitoring system allows testing in just 9 seconds with a minimal blood sample, just 0.9 μl of fresh whole capillary blood taken from a finger prick.
The principle of the method is based on the use of biosensor technology. The use of the enzyme glucose oxidase as a sensor allows for a specific analysis of beta-D-glucose content. from 803
5.0 1 review
21
- Like
- Write a review
Rating of the best devices
A high-quality glucometer can only be purchased at a pharmacy or medical equipment store that has the appropriate license. There are numerous manufacturers on the market that receive positive reviews. Their ranking is as follows:
| Manufacturer | Popular models |
| Accu-Chek (Germany) |
|
| OneTouch (Switzerland) |
|
| Bayer (Germany) |
|
| Diamedical (Taiwan) |
|
| Bioptik (Taiwan) |
|
| 77 Elektronika Kft (Hungary) |
|
| iHealth (USA) |
|
| CareSens (South Korea) |
|
| Satellite (Russia) |
|
| AgaMatrix (Germany) |
|
Tokareva Lyudmila Georgievna, therapist, medical offices 36.6
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS, BEFORE USE YOU MUST CONSULT WITH A SPECIALIST