Blood is the liquid tissue of a living organism.
Each person is filled with it individually: from four to five liters, and each person has their own, special composition.
The blood of an adult healthy person is 55% plasma and 45% other chemicals.
The bone marrow is responsible for how fluid tissue is created, filled, and distributed.
When the bone marrow is injured or its functions are impaired, the entire body suffers.
Both the quantitative and chemical composition and analysis parameters change. While a person is alive, the composition of his liquid tissue in the body is periodically updated. Sometimes there are more of some elements, sometimes of others. All elements are interconnected, and none can do without the other.
What will the results tell us?
As soon as a malfunction occurs in the body, we are sent for a blood test. Laboratory assistants examine her condition under a microscope. Based solely on the results of this main analysis, the doctor prescribes treatment. In this case, it focuses on 9 main components:
- Hemoglobin. Red pigment, the main filler of red blood cells. Reduced hemoglobin levels will indicate anemia and possible blood loss. An increased level of hemoglobin will let the doctor know that not everything is okay with the cardiovascular or circulatory systems.
- Red blood cells. Their increase means the presence of steroid hormones in the body. If less - about anemia, the presence of inflammation and infections that have settled permanently (chronic diseases). Sometimes red blood cells increase in the last months of pregnancy.
- Leukocytes. If the indicator is exceeded, then there is an infection in the body and inflammatory processes occur. Often the level of white blood filler increases due to stress, physical or mental stress. But most of all, an excess of leukocyte levels indicates allergic manifestations, leukemia, and bacterial infections. If the indicator is low, then there is a viral infection, the permissible norm of analgesics or anticonvulsants used is exceeded.
- Platelets. They are responsible for how blood clots. An increase in the norm is a signal for concern. There is reason to believe that a disease has settled in the body: cirrhosis of the liver, ulcerative colitis or tuberculosis. When there are not enough platelets, there are suspicions of diseases of the blood, liver, and spleen. Severe alcoholic and other poisoning, as well as hormonal disorders, are noticeable in the state of platelets, as well as drug abuse: antibiotics, nitroglycerin, hormones.
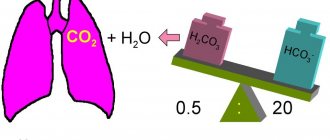
- ESR or ROE. An increase in ESR gives an idea of how the disease progresses. On the second to fourth day, the ESR rises. ESR levels increase to the highest values when the disease recedes. ESR increases with post-traumatic, anaphylactic or post-operative shock, after childbirth, acute or chronic kidney disease, during menstruation, with anemia, and impaired blood circulation.
- Glucose. Glucose levels below normal indicate poor, insufficient and chaotic nutrition. Exceeding normal levels means that diabetes has crept in and is carrying out its destructive work.
- Total protein. Its indicators are sometimes sharply reduced. This means that the body should be brought back to normal after an intensive and long-term diet.
- Total bilirubin. Yellow liver pigment. When the bilirubin level is higher than normal, there is a suspicion of jaundice or cholelithiasis. Together with other pigments, acids and cholesterol, bilirubin promotes normal digestion and regulates the functioning of the pancreas. An increase in bilirubin often occurs with jaundice and other liver diseases.
- Creatinine. It accumulates in muscle mass, and then enters the bloodstream and is excreted from the body by the kidneys.
It is better not to allow its content to increase. Kidney failure is no joke. If the indicators of this element are below normal, then you should change your lifestyle and strengthen the immune system: add vitamins to your diet, exercise, and avoid stress. These are the main blood indicators that indicate our health. Knowing them, you can read the test results yourself and make sure how well and harmoniously the organs work.
At the clinic you can take blood tests and consult with an experienced therapist.
We work with the diagnostic laboratory “Hemotest“
For an accurate diagnosis of your health, we offer the author’s program of Nadezhda Grigorievna Mironyuk (a therapist of the highest category) “Mandatory examination”
Medical Internet conferences
Blood is the mirror of health
Lavrentieva O.I.
Scientific supervisor: Tepaeva A.I.
GBOU VPO Saratov State Medical University named after. IN AND. Razumovsky Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation
Medical College
Blood is a liquid tissue of the body, which consists of plasma (water with proteins, fats, carbohydrates, salts, hormones, etc. dissolved in it) and three types of cells: erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets. The cellular composition of the blood of a healthy person is usually constant. Therefore, any changes indicate certain diseases. A blood test studies the cellular composition and helps the doctor make a diagnosis and serves as an indicator of the effectiveness of treatment.
The most commonly used general blood test is a general blood test. It includes determination of hemoglobin concentration, counting the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, counting the leukocyte formula and determining ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate).
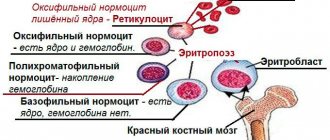
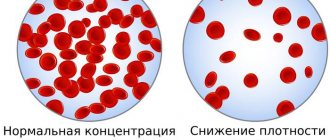
Red blood cells are red cells that serve to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the cells of the body due to the hemoglobin they contain. If a decrease in red blood cells (erythropenia) is detected, this indicates anemia and blood loss. If an increase in the number of red blood cells (erythrocytosis) is detected, this indicates dehydration of the body and tumor diseases of the hematopoietic system.
An accelerated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) indicates the appearance of inflammation, acute and chronic infections, poisoning, anemia, bleeding, and allergic conditions.
Slow ESR occurs with fluid loss due to diarrhea, vomiting, and viral hepatitis.
Leukocytes are white cells that protect the body from the invasion of foreign viruses, bacteria and poisons (leukocytes are divided into monocytes, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils). Leukocytosis may indicate inflammation, bacterial infections, poisoning, allergies, liver diseases, blood diseases (leukemia). Leukopenia characterizes the course of some viral infectious diseases. Non-infectious leukopenia is associated with increased radioactive background and radiation sickness.
Platelets - blood platelets, together with plasma proteins, ensure the functioning of the blood coagulation system, thanks to which bleeding is stopped and dangerous blood loss is prevented. Thrombocytopenia may indicate blood clotting disorders in hemophilia, bleeding, and can also be observed in viral and bacterial infectious diseases. Thrombocytosis is observed in chronic inflammatory diseases (for example, tuberculosis), some types of anemia, and malignant neoplasms.
Blood test
Blood tests are of great diagnostic importance. The study of the blood picture is carried out according to many indicators, including the number of blood cells, hemoglobin level, the content of various substances in plasma, etc. Each indicator, taken separately, is not specific in itself, but receives a certain value only in combination with other indicators and in connection with the clinical picture of the disease. That is why every person repeatedly donates a drop of his blood for analysis throughout his life. Modern research methods make it possible to understand a lot about human health based on the study of this one drop.
Author: Olga Gurova, Candidate of Biological Sciences, Senior Researcher, Associate Professor of the Department of Human Anatomy of the RUDN University
2.Leukocytes
Lymphoma
– a disease in which malignant white blood cells attack the lymphatic system. By multiplying uncontrollably, they displace healthy leukocytes. At the same time, the changed blood cells themselves are no longer able to perform the necessary functions.
Leukemia
. Bone marrow cancer caused by a mutation in stem cells. As a result, the production of healthy leukocytes is disrupted, which are gradually replaced by cancerous ones. There is an acute course (leukemia) and a chronic course (leukemia).
Leukopenia.
This is a symptom characterized by a decrease in the content of leukocytes in the blood. Leukopenia can be temporary and be a reaction to some internal and external factors (infections, radiation received, vitamin deficiency). It is rare as an independent disease.
Leukocytosis
– too high level of leukocytes in the blood. There are physiological and pathological increases in the number of white blood cells. The first is possible under certain conditions, stress, and infections.
Pathological leukocytosis manifests itself in severe diseases (oncological, inflammatory, autoimmune). With leukocytosis, weakness, subcutaneous hemorrhages, pain in the extremities, weight loss, and blurred vision are observed.
Most diseases associated with a violation of the number of leukocytes are oncological. Treatment is carried out by bone marrow transplantation, chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Visit our Oncology page
Blood clotting
Blood clotting
Blood clotting is the most important protective mechanism that protects the body from blood loss. This is stopping bleeding by forming a blood clot (thrombus), tightly plugging the hole in the damaged vessel. In a healthy person, bleeding when small vessels are injured stops within 1–3 minutes. When the wall of a blood vessel is damaged, platelets stick together and adhere to the edges of the wound; biologically active substances are released from the platelets, which cause vasoconstriction.
With more significant damage, bleeding stops as a result of a complex multi-stage process of enzymatic chain reactions. Under the influence of external causes, blood coagulation factors are activated in damaged vessels: the plasma protein prothrombin, formed in the liver, is converted into thrombin, which, in turn, causes the formation of insoluble fibrin from the soluble plasma protein fibrinogen. Fibrin strands form the main part of the thrombus, in which numerous blood cells are trapped (Fig. 3). The resulting blood clot clogs the site of injury. Blood clotting occurs in 3–8 minutes, but in some diseases this time may increase or decrease.
Red blood cells
Blood diseases
are considered to be the most serious disorders, since blood is involved in the work of all organs and tissues, providing communication between different systems of the body. Every component of blood is vital. Their correct structure, precise functioning and the necessary proportion are the three elements of healthy blood. Disturbance of any part of this balance is a hematological disease. In addition to the blood cells themselves, the cause of the disease can also be plasma (the liquid “base” of blood). Some blood particles do not have specific quantitative standards, since their appearance and concentration depend on the conditions in which the body finds itself. These are, for example, antibodies, antitoxins, immunoglobulins.
Let's consider blood diseases (causing changes in the structure and ratio of blood cells), for which there are standard indicators.
Anemia
– reduction in the amount of hemoglobin or particles transporting it – red blood cells. The consequence of this disease is a weakening of the oxygen supply to tissues and organs. Anemia can be caused by a violation of the shape of red blood cells, a decrease in their production, accelerated destruction or a lack of iron and a number of vitamins in the body. Some diseases in this group are genetic, others are acquired during life. Signs of low hemoglobin: pallor, drowsiness, shortness of breath, fatigue, headaches and heart rhythm disturbances.
Polycythemia
– production of excessive red blood cells. The consequence of this is a synchronous increase in the content of other blood cells, which carries the danger of blood clots, since the blood thickens greatly.
Thalassemia
– accelerated death of red blood cells associated with a failure in hemoglobin synthesis. This is a hereditary disease that requires only symptomatic medical care.
Malaria
– damage to red blood cells by tiny parasites. As a result of infection, red blood cells begin to burst, the general condition worsens, and damage to internal organs is possible. Modern medicine has effective means of combating malaria.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
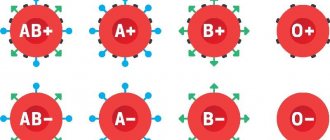
Rh factor
When transfusing blood, the Rh factor is also taken into account. Like blood groups, it was discovered by the Viennese scientist K. Landsteiner. 85% of people have this factor; their blood is Rh positive (Rh+); Others do not have this factor, their blood is Rh-negative (Rh-). Transfusion of blood from a Rh+ donor to a Rh- person has serious consequences. The Rh factor is important for the health of the newborn and in case of re-pregnancy of an Rh-negative woman from an Rh-positive man.
Blood groups
Knowledge of blood type is of practical interest. The division into groups is based on different types of combinations of erythrocyte antigens and plasma antibodies, which are a hereditary trait of blood and are formed at the initial stages of development of the body.
It is customary to distinguish four main blood groups according to the AB0 system: 0(I), A(II), B(III) and AB(IV), which is taken into account when transfusing it. In the middle of the 20th century, it was assumed that blood of group 0(I)Rh- is compatible with any other groups. People with blood group 0(I) were considered universal donors, and their blood could be transfused to anyone in need, and only group I blood could be transfused to them. People with blood group IV were considered universal recipients; they were injected with blood of any group, but their blood was administered only to people with group IV.
Now in Russia, for health reasons and in the absence of blood components of the same group according to the AB0 system (with the exception of children), transfusion of Rh-negative blood of group 0 (I) to a recipient with any other blood group in an amount of up to 500 ml is allowed. In the absence of single-group plasma, the recipient can be transfused with group AB(IV) plasma.
If the blood groups of the donor and recipient do not match, the red blood cells of the transfused blood stick together and their subsequent destruction occurs, which can lead to the death of the recipient.
In February 2012, scientists from the United States, in collaboration with Japanese and French colleagues, discovered two new “additional” blood groups, including two proteins on the surface of red blood cells - ABCB6 and ABCG2. They belong to transport proteins - they participate in the transfer of metabolites and ions in and out of the cell.
To date, more than 250 blood group antigens are known, combined into 28 additional systems in accordance with the patterns of their inheritance, most of which are much less common than ABO and the Rh factor.