This macroelement is responsible for general health, participates in metabolism, bone tissue formation, regulates hormonal balance, ensures proper absorption of nutrients, and normal muscle contractility. Measuring calcium levels is necessary to diagnose dangerous conditions and prevent systemic diseases. Pathologies are indicated by both deficiency and excess of the mineral.
Calcium levels in the body
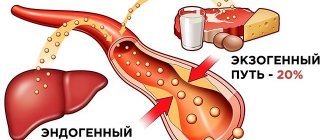
Blood contains only 1% of the total amount of calcium contained in the body. The rest is concentrated in tissue cells, forming combinations with phosphorus. Plasma is saturated with several forms of the mineral:
- ionized or free calcium (Ca2+), its share: 52–58%;
- associated with protein fractions: up to 38%;
- complexed: composed of salts with bicarbonates, lactates, phosphates and citrates: about 10%.
A normal general level of calcium ensures healthy metabolism, delivery and absorption of other minerals into cells, absorption of vitamins, synthesis of hormones, formation of structures of the skeletal system, teeth, and soft tissues. It is necessary for hematopoiesis, proper functioning of the central nervous system, and maintaining salt metabolism.
The overall level of an essential macronutrient in the body varies depending on age and physical condition. Its general indicators for different categories:
- 1.9–2.6 mmol/l: in newborns;
- 2.25–2.7 mmol/l: in children under 4 years of age;
- 2.1–2.55 mmol/l: in children and adolescents under 18 years of age;
- 2.15–2.5 mmol/l: in adults;
- 2.22–2.55 mmol/l: in elderly people over 65 years of age.
To maintain the normal level of calcium, it must be supplied to the body daily through food. In childhood, the need for the element is about 200 to 1000 mg. Adults need 1200–1400 mg per day. During pregnancy and lactation in women, its dose should be at least 1500 mg. The absorption of the mineral is affected by:
- hormonal background;
- Lifestyle;
- food quality;
- level of phosphorus, magnesium, parathyroid hormone, active form of vitamin D in the body;
- the presence of systemic diseases.
With age, the absorption and content of calcium in the body inevitably decreases. This is caused by a decrease in the activity of the intestines, kidneys, and changes in the endocrine functions of the glands. The mineral is constantly consumed, its salts are excreted through urine and metabolic products, so the development of deficiency is more common than excess. But hypercalcemia is also a likely condition. It occurs due to increased levels of albumin in the blood. This protein provokes the accumulation of bound calcium, which affects its overall level.
Prevention and treatment of deficiency conditions
Calcium deficiency can be avoided with a nutritious diet. Dairy products, especially artificially enriched ones, contain large amounts of calcium. Less of it is found in cereals, nuts and greens. The listed sources of calcium should be present in the diet daily.
However, to cover the daily requirement, diet correction is not always enough. In this case, taking calcium supplements is indicated. It is possible to use only this macroelement, or a complex of substances necessary for the body.
To prevent and eliminate calcium deficiency in the body, you can take the combined drug Calcemin Advance. In addition to calcium, it contains a number of other useful substances: magnesium, copper, zinc, vitamin D, manganese and boron. One tablet contains 500 mg of calcium; depending on the indications, you can take up to three tablets per day for a total dosage of 1500 mg. We should not forget that the daily norm is made up of calcium that enters the body with food, as well as taking into account the medications taken. In this regard, you should not increase the dosage yourself without the appropriate recommendation of a doctor.
L.RU.MKT.CC.03.2020.3102
Indications for analysis
The study of biochemical blood parameters allows you to study in detail the condition of the body, exclude or confirm the development of a number of diseases, adjust the prescribed therapy regimen, and more successfully carry out rehabilitation treatment after surgery. There are two types of calcium testing:
- to the general level;
- for ionized calcium: a highly specialized, expensive, but more informative study.
Calcium testing is indicated for the following conditions:
- muscle weakness;
- frequent numbness of various parts of the body;
- arrhythmic manifestations, other signs of heart disease;
- disruption of the production of hormones of the adrenal glands, thyroid and parathyroid glands, ovaries;
- kidney pathologies;
- intestinal inflammation and malabsorption syndrome;
- oncological diseases;
- decreased albumin levels;
- suspected development of osteoporosis;
- blood clotting disorders;
- symptoms of hypocalcemia: drowsiness, dizziness, deterioration of teeth and nails, hair loss.
A calcium test is recommended before surgery, during the recovery period after complex physical injuries, internal organ transplantation, and blood transfusions.
Increasing values
- increased production of parathyroid hormones due to its benign growth or malignant tumor;
- bone metastases in kidney, lung, and breast cancer;
- a special type of malignant tumor - carcinoma, which produces parathyroid hormone, while the primary cancer can be in the uterus, ovaries, thyroid gland or kidneys;
- injuries and illnesses in which a person is forced to remain motionless for a long time, causing calcium from the bones to move into the blood - bone fractures, spinal tuberculosis, Paget's disease or damage to bone tissue with improper formation and resorption, congenital hip dislocation;
- increasing vitamin D levels;
- adrenal disease, especially insufficiency;
- hemoblastoses or tumor diseases of the blood and lymph - especially myeloma, accompanied by destruction of bone tissue;
- Williams syndrome or “elf face” is a genetic disorder where several genes are missing;
- kidney failure;
- granulomatous diseases, especially sarcoidosis;
- excessive intake of medications containing calcium;
- milk-base or Burnett syndrome, when there is a lot of calcium in the blood, and the acid-base balance is shifted to the alkaline side;
- overdose of diuretics containing thiazide, or substances that potently remove potassium and sodium.
Preparing for testing
A week before the test, it is recommended to refrain from drinking alcohol, potent drugs, vitamin-mineral complexes, fried, smoked and excessively salty foods. Strong coffee, which promotes increased removal of calcium from the plasma, is also not recommended.
It is not advisable to smoke or engage in heavy physical work for 24 hours before the test. Instrumental examinations and infusion procedures are also prohibited. The last meal and drinks should be no later than 12 hours before taking the sample. Then only pure still water is allowed.
Blood should be donated in the morning: optimally from 8 to 12 hours.
Antitumor, anticonvulsant drugs, diuretics, antibiotics and steroid hormones can distort test results. These medications cause a temporary decrease in calcium levels in the body.
What medications are there?
There are several forms of calcium: gluconate, carbonate, citrate and chelate. Each type has certain properties and levels of digestibility.
- Gluconate. This type of element has the largest list of contraindications and side effects. It is absorbed by the body only 3%. With long-term treatment, stones form in the gall bladder and kidneys. Its only advantage is its low price.
- Carbonate. The most common form of calcium is absorbed by 17-22% at high and 0% at low acidity. Long-term use leads to the formation of calcium kidney stones. Taking a large amount of the element at a time can cause nausea, abdominal pain, and digestive tract disorders.
- Citrate. The absorption rate of the drug is 44%. Calcium can be taken at any time, even on an empty stomach. This form of the element is safe for humans and does not cause the formation of stones. Calcium citrate helps change the pH of urine, eliminating the development of diseases of the urinary ducts and genital infections.
- Chelated. On the world market this is the best form of calcium, which is also called “ionic”. The absorption of the drug is equal to 90-98%. The product has no side effects and does not irritate the digestive tract. The chelate is completely soluble in water, and the rapid release of calcium ions protects the blood from oversaturation with the element.
There is also calcium chloride in ampoules, which is used to more quickly saturate the body with the substance. Droppers are prescribed to people with increased secretion of the element and a deficiency in the functioning of the parathyroid glands.
What affects calcium absorption
Calcium is a difficult-to-digest macronutrient, since its absorption requires the presence of the following substances in the body: magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, manganese, silicon, chromium, vitamins D, etc. Moreover, an excess amount of the first two compounds prevents its full absorption.
The optimal ratio of calcium, magnesium and phosphorus in food or dietary supplements is 2: 1: 1. Considering that the mineral “transforms” into a bioavailable form only under the influence of gastric juice, taking it and alkaline substances that neutralize hydrochloric acid, including carbohydrates, leads to to reduce the absorption of the element in the intestines. At the same time, the combined use of the compound with rhubarb, spinach, parsley, cabbage, sorrel, radish and currants potentiates the formation of oxalate kidney stones.
Remember, calcium is well absorbed from dairy products due to the optimal ratio of nutrients and the presence of lactic acid bacteria in such products. Moreover, to increase the bioavailability of the mineral, it is permissible to use healthy fats. However, it is important to take into account that an excess or lack of lipids in the diet prevents the complete absorption of the “bone” substance, since in the first case there are not enough bile acids to break it down, and in the second - fatty acids.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
The optimal ratio of calcium to fat per serving of food is 1:100.
Calcium-rich foods
Dairy products are the most powerful source of calcium. The macronutrient is also found in greens, nuts, vegetables and fruits. The table shows foods by category that are high in calcium.
| Product, 100 g | Calcium, mg |
| Fruits, dried fruits | |
| Oranges | 35 |
| Dried apples | 45 |
| Dried apricots | 170 |
| Figs | 57 |
| Raisin | 56 |
| Vegetables | |
| Cabbage | 60 |
| Celery | 240 |
| Leek | 60 |
| Lettuce | 82 |
| Green bean | 40 |
| Olives | 77 |
| Nuts | |
| Peanut | 70 |
| Pecan | 73 |
| Almond | 254 |
| pumpkin seeds | 60 |
| Sunflower seeds | 100 |
| Dried soybeans | 225 |
| Sesame | 1150 |
| Fish (with bones) | |
| Sardine | 350 |
| Dried fish | 3000 |
| Milk products | |
| Cottage cheese | 95 |
| Milk 1% | 120 |
| Milk 3% | 100 |
| Natural yogurt | 120 |
| Fruit yogurt | 100 |
| Diet yogurt | 85 |
| Processed cheese | 300 |
| Swiss hard cheese | 600 |
| Sour cream | 100 |
| Pudding | 85 |
Almost all foods contain calcium, but in lower concentrations.
Interaction with other drugs
Before using several types of medications, you should consult a doctor. At least 2 hours should pass between taking calcium and sodium fluoride, bisphosphonates, tetracyclines, and glycosides. This is because the element can increase or decrease the therapeutic and toxic effects of drugs.
The absorption of calcium is reduced when taken simultaneously with zinc, while calcium does not allow the body to be saturated with manganese and iron. When using prednisolone, the excretion of the substance increases. Calcium absorption is facilitated by additional intake of magnesium and vitamin D.
Side effects of calcium supplements
With uncontrolled intake of the element, hypercalcemia is observed, which negatively affects the functioning of the entire body. Main side effects during self-medication:
- upset stool, bloating, constipation;
- formation of kidney stones;
- decreased effectiveness of other medications;
- numbness, muscle spasms;
- toxicity of the supplement's auxiliary components;
- increased irritability.
If you have any symptoms of calcium overdose, you should consult a doctor.
Natural springs
Considering that calcium is involved in the formation of bone, connective and nervous tissues, it is important to ensure a regular supply of the macronutrient with food.
Table No. 1 “Sources of calcium”
| Product name | Calcium content per 100 grams of product, milligrams |
| poppy seed | 1450 |
| Parmesan cheese | 1300 |
| Hard cheeses | 800 – 1200 |
| Sesame (unroasted) | 700 – 900 |
| Nettle (green) | 700 |
| Brynza | 530 – 600 |
| Common mallow | 500 |
| Basil (greens) | 370 |
| Sunflower seeds | 350 |
| Almonds (unroasted) | 260 |
| Sea fish | 210 – 250 |
| Parsley (greens) | 240 |
| White cabbage | 40 |
| Beans | 160 – 190 |
| Garlic, watercress | 180 |
| Dill (greens) | 120 |
| Milk, kefir, cottage cheese, whey, sour cream, yogurt | 90 – 120 |
| Broccoli | 105 |
| Peas | 100 |
| Walnuts | 90 |
| Shrimp, anchovies, oysters, crabs | 80 – 100 |
| Peanut | 60 |
| Chicken egg (1 piece) | 55 |
Calcium is found in small quantities in cereals, fruits, vegetables, berries, meat and honey. The content of the element in these products varies from 5 to 50 milligrams per 100 grams.