Home — For the public
- Map of medical organizations
- Vaccination
- Clinical examination
- Fluorography
- Addresses and opening hours of clinics
- Emergency rooms
- Oncology
- Where to take an HIV test
- Healthy child's office
- Services
- Prevention of CVD
- Disease Prevention
- World Patient Safety Day
- Newspaper "Medical News"
- specialist
- School of Health
— Disease prevention
- HIV infection
- All about vaccination
- All about proper nutrition
- Hepatitis
- Flu
- Dementia
- Schoolchildren's health
- STD
- Tick-borne encephalitis
- Whooping cough
- Measles
- Legionellosis
- Meningococcal infection
- Oncology
- Acute intestinal infection
- Pediculosis
- First aid
- Pneumococcal infection
- Pneumonia
- Prevention of rabies
- Dependency Prevention
- Rotavirus infection
- Diabetes
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Injuries
- Tuberculosis
- Tularemia
- Physical activity
- Obstructive pulmonary disease
- Exotic infections
- Ecology
- Why is swimming in ponds dangerous?
— Cardiovascular diseases — Diagnosis of CVDs
The widespread prevalence of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) and the continued high mortality rate from them necessitate the introduction into clinical practice of modern effective methods for the early diagnosis of these pathologies.
In recent years, there has been a steady trend of “rejuvenation” of CVD, including myocardial infarction, both among men and women of working age.
Diagnosis of CVD
The level of modern diagnostics makes it possible to identify most diseases of the cardiovascular system at an early stage, when the pathological process is reversible and responds well to therapy.
Methods for studying heart disease are divided into physical, laboratory and instrumental.
Physical examination methods performed by the doctor at the first appointment include:
- examination of the skin and mucous membranes;
- palpation - palpation;
- percussion - tapping;
- auscultation - listening.
Despite their simplicity, physical examination methods allow the doctor to make a preliminary diagnosis and outline the range of necessary laboratory and instrumental tests.
- During the examination, changes in the color of the skin (pallor, cyanosis, yellowness) are noted; the presence or absence of pastiness or swelling of the extremities, pulsation of the cervical arteries.
- Using percussion, the boundaries of the heart are determined, which, in case of myocardial pathologies, go beyond normal limits.
- Using a phonendoscope, auscultation is performed - listening to heart sounds and noises and assessing their sonority and rhythm.
- Blood pressure is measured.
Currently, these methods are relegated to the background, since there are modern, faster and more effective ways to detect pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
Radiography and fluoroscopy
In radiography, X-ray beams are passed through to produce a two-dimensional image of organs and tissues. Images are formed due to differences in the ability of different tissues to absorb radiation. The study is used mainly in traumatology, orthopedics, and to assess the condition of the skeleton.
Fluoroscopy also uses x-rays, but with its help, not individual images are taken, but long-term shooting. Used to visualize heart rate, intestinal motility, passage of an injected contrast agent through the esophagus, etc. Fluoroscopy is rarely used due to the relatively high doses of x-ray radiation. If possible, ultrasound or other research methods are used instead.
Laboratory research
Laboratory tests for diagnosing CVD are divided into general clinical and special.
General clinical tests include general and biochemical blood tests, which allow doctors to assess the general state of health, as well as find out the presence or absence of pathological changes in the body. But the changes that occur in the blood are nonspecific and can appear during pathological processes in different organs. Special tests have been developed to confirm diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Blood tests to identify cardiac pathologies allow you to:
- assess risk factors for developing heart and vascular diseases;
- identify early and hidden CVD lesions.
The lipid profile helps diagnose atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease.
Lipid profile indicators:
- Total cholesterol.
- Triglycerides.
- Cholesterol fractions: low-density lipoproteins (LDL), high-density lipoproteins (HDL).
A coagulogram is a study of the amount of substances responsible for blood clotting. An increase in blood viscosity is evidence of an increased risk of developing complications of hypertension, coronary heart disease, heart attack or stroke.
Serum enzyme tests:
Aspartate aminotransferase (AsAt) is an intracellular enzyme involved in the metabolism of amino acids in the liver and heart. An increase in the rate increases the risk of heart attack.
Elevated levels of creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase also indicate the development of acute myocardial infarction.
Blood for a cardiac profile is taken from a vein in the morning on an empty stomach.
Magnetic resonance imaging
This diagnostic method uses a magnetic field to obtain high-resolution images of internal organs or tissues. For the examination, a device with a camera is used, inside which the patient is located. This device provokes an electromagnetic response from atomic nuclei. The response is recorded and translated into a two-dimensional or three-dimensional image.
MRI allows you to obtain layer-by-layer images of organs and tissues. Used in the diagnosis of diseases of the spinal cord, brain, and internal organs. Gives high accuracy. The procedure takes about half an hour, it is painless, but is not suitable for people with a fear of closed spaces. Not used for diagnosing heart disease.
Instrumental diagnostic methods
Electrocardiography (ECG)
Electrocardiography (ECG) is one of the basic methods for diagnosing cardiac pathologies, without which not a single examination can be performed.
ECG - a method of studying the electrical activity of the heart has several varieties:
- ECG – standard.
- ECG – mapping.
- Holter monitoring ECG.
- Bicycle ergometry.
Using an ECG, electrical potentials are recorded in all parts of the heart, as well as the characteristics of the passage of impulses through the conduction system of the heart.
The ECG technique reveals:
- rhythm disturbances;
- change in heart rate;
- heart attack;
- ventricular hypertrophy;
- ischemic and cardiodystrophic changes.
To measure the electrical potentials of the heart muscle, a special device is used - a cardiograph. Sensors are placed on the patient's body, and the signals received from them are displayed on paper or film using recorders.
Electric potentials are shown on a graph as different lines. For each line on the ECG tape, strict normal parameters are defined, deviations from which indicate disturbances in the functioning of the heart.
The graph is studied using mathematical methods (advanced models of cardiographs perform this work automatically). Based on the results obtained, the doctor gives a conclusion indicating the parameters of the heart and its conduction system: heart rhythm, heart rate, electrical axis of the heart, conductivity, pacemaker.
ECG mapping
ECG mapping is a modern modified ECG method in which the recorded cardiac impulses are recorded in the form of cartograms. The method is based on recording multiple (from 64 to 224) ECG leads from the entire surface of the chest. When analyzing the data obtained, distribution maps are compiled, consisting of successive phases of the cardiac cycle. This significantly increases the diagnostic capabilities of the ECG, especially if the pathological process is difficult to detect with standard 12 leads.
Bicycle ergometry is a testing technique during which the patient performs dosed physical exercise on an exercise bike or treadmill while recording electrical potentials. The method makes it possible to detect latent heart failure or rhythm disturbances. Symptoms in such cases appear only with increased physical activity.
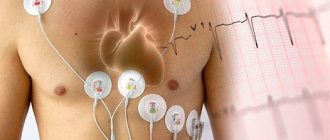
24-hour Holter blood pressure monitoring
24-hour Holter blood pressure monitoring is an examination in which blood pressure measurement is combined with an electrocardiogram recording.
The device for measuring pressure consists of a cuff, a sensor that captures the pulse waves of the artery, a connecting tube and a recorder that records pressure readings over time. A cuff connected by a tube to a microprocessor is fixed on the patient's shoulder. The device operates automatically: air is pumped into the cuff at specified intervals. The air is then gradually released and pressure levels are recorded on an electronic storage device.
Additionally, electrodes are installed on the patient’s chest, which send data about the electrical impulses of the heart to the device’s memory card.
Holter ECG monitoring for 24 hours or more allows you to detect heart rhythm disturbances and assess their frequency. Holter cardiac monitoring is a method of continuously recording an ECG during a person's normal daily activities. During the examination, the patient keeps a diary in which he records all types of activities (morning exercises, walk, rest, and so on). The doctor, analyzing the ECG readings, compares them with the patient’s records. This allows you to find out quite accurately what actions provoked certain changes in the cardiogram.
Echocardiography
Echocardiography is a study of the heart using ultrasound. Through a special sensor, which is applied to the chest in the area of the projection of the heart, ultrasonic waves propagate deep into the organ. The waves reflected from the tissues return to the sensor and are converted into electrical signals, which, after computer processing, are displayed on the monitor screen in the form of an image.
Echocardiography reveals:
- Congenital, acquired heart defects.
- Intracardiac thrombi.
- Damage to valve flaps.
- Hypertrophy or hypotrophy of the heart chambers.
- Free fluid in the pericardium (the sac around the heart).
- Pathologies of large vessels (aortic aneurysm).
- Changes in the speed and direction of internal blood flow
- Neoplasms in the heart muscle.
In addition, the method makes it possible to assess the anatomy and functional state of the heart: the shape and size of the organ, the thickness of the heart wall, the volume of the cavities of the atria and ventricles, the condition of the valves, pressure in the cavities, blood flow speed and other characteristics.
The procedure does not require special preparation. It is recommended several days before the ultrasound to limit the consumption of strong drinks, tea, coffee, alcohol and other energy drinks that affect the functioning of the heart. To obtain reliable results on the day of the procedure, the patient should avoid psycho-emotional unrest, physical stress, and quit smoking.
The most common in medical practice is the transthoracic method, when the examination is carried out through the anterior wall of the chest. If there are contraindications to this method (obesity, pulmonary emphysema, prosthetic heart valves), when acoustic barriers prevent the free passage of ultrasound waves to the object of study, echocardiography is performed by placing the sensor in the esophagus.
Transesophageal echocardiography provides a clearer image of the heart structures due to the proximity of the transducer and the absence of dense tissue or bone in the ultrasound path.
Doppler examination of the heart and blood vessels
The study is based on the Doppler effect, when ultrasonic waves are reflected from moving blood cells (erythrocytes) with a changed frequency.
The Doppler mode of echocardiography allows you to assess blood flow in the chambers of the heart and great vessels, identify reurgitation, determine the ejection fraction and stroke volume.
Angiocardiography
Angiocardiography is an X-ray diagnostic method that involves introducing a contrast agent into the vascular bed and taking a series of images of the heart and blood vessels. The method combines three studies:
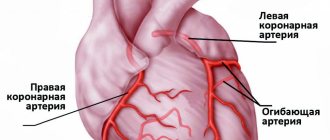
coronary angiography - an image of the coronary arteries supplying the heart;
left-sided ventriculography – obtaining images of the cavity of the left ventricle when it is filled with contrast;
examination of the right heart (atrium and ventricle) and pulmonary artery.
The method is invasive and is performed according to strict indications for the diagnosis of congenital and acquired defects of the heart and great vessels. often before heart surgery to clarify myocardial parameters.
Description of ECG
The ECG graph analyzes:
- An isoelectric line is a horizontal line recorded during a period when no excitation of activity is noted in the heart). It is the starting point for the changes listed below;
- teeth - deviations from the isoelectric line (the upper tooth is called positive, the lower - negative); The teeth in the figure are: P, Q, R, S, T, U
- a segment is an isoelectric line between teeth; the figure shows the segment ST and PQ
- intervals are fragments of the ECG graph that include ……… and the adjacent tooth; The figure shows the QT and PQ
In the ECG display we see (from left to right):
- P wave - characterizes depolarization of the atrial muscle
- segment PQ – reflects the time of depolarization through the atrioventricular node
- PQ interval - reflects the time of depolarization from the sinoatrial node to the atrioventricular node
- QRS complex – corresponds to depolarization of the ventricular myocardium
- QT interval - reflects the time of the action potential of the ventricular myocardium (depolarization + repolarization)
- ST segment – reflects the period of ventricular repolarization
- T wave - corresponds to ventricular repolarization
- U wave - not observed in practice
Endoscopy
The study is performed using an endoscope - an instrument with a flexible fiber-optic tube with a diameter of 8 to 15 cm. It allows you to “see” organs from the inside, obtain an image of the bronchial mucosa, stomach, etc.
Some equipment allows you to take tissue samples during the study. Endoscopes are used in gastroenterology, pulmonology, urology and gynecology, cardiology, etc. You have questions?
We will call you back within 30 seconds
or call the number
Clicking the "Submit"
, you automatically consent to the processing of your personal data and accept the terms of the User Agreement.
- Preventative medical examination for the elderly
- Types of instrumental examinations
- Laboratory diagnostics: main types of tests
- Examination by a neurologist and psychiatrist for the diagnosis of dementia and Alzheimer's disease
Electroencephalography
Method for assessing electrical activity of the brain. The procedure is carried out in several stages; the examination plan can be drawn up individually. To record brain activity, sensors are attached to the patient's head. Electrical activity is read at rest. Next, the EEG is carried out using additional stimuli (rapid breathing, flashes of light, etc.).
The result of the examination is a set of broken lines reflecting the activity of different parts of the brain. Based on their structure, epilepsy, age-related changes, and disorders of the brain are diagnosed.