Among diseases that can suddenly worsen and lead to extremely negative consequences, myocardial infarction is especially dangerous. Treatment should be started as early as possible. At the initial stage, it may consist of first aid, and the rehabilitation stage can last for several months. The patient is provided with comprehensive care, including drug treatment, surgical and non-surgical methods, and rehabilitation therapy aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease. With a professionally designed recovery program, life after a heart attack can return to normal, subject to certain restrictions.
Stages of treatment of myocardial infarction
- At the prehospital stage, if there are symptoms of the disease, the patient is given first aid and transported to the clinic.
- The hospital stage involves carrying out medical measures aimed at maintaining body functions and combating negative consequences.
- The rehabilitation stage is carried out in sanatoriums where special conditions have been created.
- At the stage of dispensary observation and outpatient treatment, the patient periodically visits the cardiology clinic and the doctor at his place of residence.
The high professionalism of doctors and the technical equipment of the clinic where you are being treated after a myocardial infarction are extremely important. With qualified specialists and high-quality rehabilitation, you will avoid complications and continue to live a full life.
Features of rehabilitation
The most acute period usually lasts up to six hours from the moment of the attack, the acute period - up to seven days. Scarring takes 28 days. Rehabilitation after a heart attack takes place in several stages, requiring the patient to give up bad habits and review all the main aspects of life:
- lifestyle;
- physical activity;
- diet.
The psychological attitude is of great importance. The duration of rehabilitation at the inpatient and outpatient stages depends on the patient’s condition. The final stage has no deadline - it lasts a lifetime.
First aid for myocardial infarction
Every person should be able to provide emergency care for myocardial infarction, because most people suffer from cardiovascular diseases, and the risk of developing this pathology is extremely high.
At the first symptoms, you must immediately call an ambulance, preferably a specialized cardiac team equipped with a defibrillator, pacemaker, and medications.
While you are waiting for the doctors, give the patient nitroglycerin under the tongue, analgesics, aspirin, Corvalol or Valocordin. If the patient suffers from arrhythmia, antiarrhythmic drugs will be needed.
If acute myocardial infarction is accompanied by cardiac catastrophe and loss of breathing, resuscitation should be started immediately. Lay the patient down, open his mouth slightly and cover him with a handkerchief. Exhale deeply through the handkerchief into the patient's lungs. Pinch his nose to prevent air from escaping.
While the patient's chest spontaneously lowers, straighten up, take a breath and repeat the manipulation several times. If there is no pulse in the carotid artery, indirect cardiac massage is necessary. The classic formula includes 15 chest compressions for 2 consecutive air injections. Actions must be continued until the patient’s skin turns pink, the pupils constrict, and a pulse appears.
Drug treatments for myocardial infarction
The purpose of using medications in the hospital is to restore and maintain circulatory functions, as well as relieve unbearable pain.
- Painful sensations can be eliminated with the help of analgesics, and the feeling of fear can be eliminated with tranquilizers.
- To prevent the formation of a blood clot, acetylsalicylic acid and anticoagulants are used.
- If a blood clot has already formed, powerful thrombolytics are used to dissolve it.
In the treatment of acute myocardial infarction, a special place is given to thrombolytic therapy to eliminate the risk of new blood clots. Arrhythmia is a common occurrence in this disease, so the patient is offered antiarrhythmic drugs, adrenergic blockers, nitrates, and vitamin E.
Rehabilitation after acute myocardial infarction involves taking medications to maintain normal blood pressure and prevent blood clots.
Physical activity
After illness, physical activity should increase gradually; forcing events often causes very serious complications. After several days after the acute period, the patient can slowly (on his own or with the help of others) get out of bed, holding the supports with his hands. The first steps can be taken only after transfer to a regular ward. You can only walk on a flat surface and avoid shortness of breath or feelings of fatigue. The duration and distance of walking increases gradually.
In a hospital, a doctor must supervise exercise therapy classes. The same exercises can be performed at home after leaving the hospital. In this case, you should constantly remember to monitor the condition. One of the important indicators of a successful rehabilitation course is pulse and blood pressure. After normal physical exercise, the frequency of contraction of the heart muscle should not exceed 100–120 beats per minute.
Angioplasty and coronary artery stenting
One of the effective and widespread methods of treating acute myocardial infarction throughout the world is coronary angioplasty with the possibility of installing a stent. The advantage of the operation is that it is extremely minimally traumatic: a small puncture is sufficient to insert a catheter into a peripheral vessel (usually the femoral artery serves as a transport vessel). The goal of high-precision manipulation is to widen the coronary artery in the place where it is blocked.
The catheter, under the control of X-ray equipment, is passed through the vascular system to the site of narrowing of the coronary artery. At the end of the catheter there is a miniature balloon, which is in a compressed state. An X-ray contrast agent is injected into the vessels, and the doctor has the opportunity to observe the manipulations on monitors in the operating room. The cardiac surgeon places a balloon in the affected area of the vessel and inflates it with special equipment, thereby restoring blood flow.
To prevent the walls of the artery from narrowing again, a cylindrical stent is inserted into it in the same way and secured. Thus, it replaces the affected area of the vessel.
How is coronary stenting different from open surgery?
Coronary stenting is a type of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Unlike open-heart surgery, coronary stenting is characterized by a minimal degree of trauma to the patient: the stent is implanted through a small puncture in a vessel of the thigh or upper limbs. This type of surgery does not require the use of general anesthesia: the patient is conscious and watches what is happening on the angiograph screen. In addition, treatment using endovascular surgery techniques is quick and comfortable, and the patient goes home the very next day after stenting the heart vessels.
If the stent implantation is successful, the patient feels relief almost immediately. Since normal blood flow to the heart is restored, heart pain, shortness of breath and other unpleasant signs of IHD disappear. Coronary artery stenting normalizes blood flow by widening and opening up narrowed and blocked arteries. As a result, chest pain decreases or completely disappears; physical activity does not provoke painful conditions.
Successful surgery minimizes the need for coronary artery bypass graft surgery in the future, where a vein or artery is removed from a part of the body and sutured directly to the heart to avoid affecting the affected area. Such an intervention requires an incision in the chest, but the risks are greater and the recovery period is longer. In addition, the price of cardiac stenting is much lower than bypass surgery.
Coronary artery bypass grafting
It is also a very effective method of treating myocardial infarction. The purpose of this operation is to create a new path for the blood, bypassing the vessel affected by atherosclerosis. For this, a special shunt is used - a part of the patient’s own vessel, taken from the thoracic artery or radial artery of the arm. It is sewn into the narrowed or blocked artery above and below the site of the lesion. Thus, the volume of blood required for heart function is normalized. Doctors are able to restore blood circulation in the affected area of the heart muscle in a short period of time.
The operation eliminates the very cause of the heart attack and is often performed as planned so that the patient can avoid a heart attack. The risk of developing a heart attack after surgery is significantly reduced, and the patient regains ability to work with a normal amount of physical activity.
Coronary artery bypass grafting is a type of open intervention for a beating heart. That is, to carry it out it is necessary to open the chest. There are options for surgery with or without artificial circulation.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptom is acute chest pain that does not go away after taking nitroglycerin. It occurs suddenly and gets worse quickly. The attack may be accompanied by shortness of breath, cough, and arrhythmia. If the pain lasts more than 15 minutes, you must call an ambulance. The sooner the blood supply to the heart is restored, the smaller the size of the dead area will be.
In a third of patients, myocardial infarction occurs in an atypical form, which significantly complicates early diagnosis and leads to the loss of precious time. Experienced caregivers know about this and can predict the development of an attack based on indirect symptoms. Patients with diabetes may not feel pain. In women, it is often localized in the arm or neck and is accompanied by fatigue. Atypical forms of heart attack also appear:
- pain in the abdomen, throat, lower jaw;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- confusion;
- cold sweat;
- swelling;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure.
In many cases, the only symptom of a heart attack is sudden cardiac arrest. In such cases, only urgent resuscitation measures can save the patient.
A delay in treatment of myocardial infarction can cause complications such as:
- cardiogenic shock,
- acute and chronic heart failure,
- arrhythmia,
- arterial hypotension,
- heart aneurysm.
If you suspect an attack, the patient must first be seated and removed from constricting clothing. Then you need to measure his pressure, give crushed aspirin or nitroglycerin (for high blood pressure) and call an ambulance. The services of a nurse significantly increase the chances of patients undergoing surgical treatment. Regular care after a heart attack reduces the likelihood of a recurrence.
Myocardial infarction: rehabilitation and life after an attack
At the rehabilitation stage, it is important to gradually expand the patient’s activity. For this purpose, professional cardiology clinics and sanatoriums use modern programs aimed at preventing and treating muscle atrophy and pulmonary congestion. They include physical therapy and physiotherapy.
Life after a myocardial infarction does not end at all if the patient is offered a competent and effective rehabilitation program. In some cases, the patient will have to change his job if it involves physical or emotional stress.
Condition assessment
After carrying out exercises and various activities, a number of parameters are assessed:
| Index | Change |
| General state | Moderate fatigue Severe fatigue that does not go away for a long time |
| Angina pain | No Moderate, goes away on its own Severe, require medicinal correction |
| HELL | The increase for the upper one is no more than 40 mm Hg. Art., lower - no more than 12 Or a decrease in indicators of no more than 10 units |
| Heart rate | Increase by no more than 20 per minute or decrease by 10 units maximum |
| Breathing problems | An increase of no more than 6 per minute is acceptable. |
| Changes on the cardiogram | Signs of impaired blood flow (decreased ST segment) Violation of the rhythm of contractions Blockade of impulse conduction |
Diet after myocardial infarction
Life after a heart attack involves following a diet with foods that do not put a strain on the vascular system. Nutrition after myocardial infarction should include easily digestible food, and it should be taken 5-6 times a day in small portions. The diet should include cereals, low-fat dairy products, juices, vegetables, and dried fruits.
The most strict diet is during the hospital period. It includes unsalted liquid porridges, vegetable soups made from ground products. In the future, nutrition will be normalized. Coffee, tobacco, and alcohol are strictly prohibited!
Nutrition
Depending on the period of illness, three different diets are recommended.
- The first week after an acute attack. When preparing food, salt is completely excluded; you can only steam or boil it; you are prohibited from eating fried foods. To facilitate the work of the intestines, food is pureed, the number of meals is increased to seven times a day, and the size of portions is reduced. You are allowed to drink up to 800 ml of liquid.
- Second and third week. Still, salt is not used and fried foods are prohibited. There is no need to wipe, just finely chop. The number of receptions is reduced to 5, and the size of portions increases slightly. The amount of liquid you drink increases to a liter.
- Fourth week (period of myocardial scarring). When cooking, salt is not used; dishes are steamed or boiled. The number of meals is reduced to four, and the portions increase. It is allowed to take large pieces of food, the volume of liquid drunk increases to 1.1 liters. If the doctor considers it possible, then a little (up to 4 g) table salt is allowed.
Treatment and rehabilitation after myocardial infarction using shock wave therapy
One of the effective methods of treating coronary heart disease, allowing you to avoid a heart attack or restore the body after the disease. It is used in cases where traditional methods of coronary artery bypass grafting and stenting are contraindicated or do not produce any effect.
Specialized equipment uses an ultrasound scanner to focus acoustic waves onto the area of myocardial ischemia. With non-contact exposure, new vessels are formed, resulting in a bypass effect - the blood supply to the heart improves, the number of angina attacks decreases.
The method is attractive due to its absolute painlessness. During the procedure, blood pressure does not change and heart rhythm is not disturbed. No side effects were recorded. After a course of procedures, you will be able to increase physical and emotional stress, and reduce the amount of medications consumed.
On the topic “Shock wave therapy for coronary heart disease,” watch the recording of the program “About the Most Important Thing” on Russia 1 channel, which was filmed with the participation of our cardiologist Elena Pisanko. The filming contains a clear example of the procedure itself, which took place in our clinic.
Indications
In what cases is stenting of coronary vessels performed? Often the reason for this is atherosclerosis. It begins due to the accumulation of cholesterol molecules on the walls of the arteries, gradually forming plaques. This complicates blood flow in this area, and the heart muscle experiences a lack of oxygen. As a result, the patient develops coronary disease, the symptom of which is angina pectoris. Retrosternal pain or pain in the heart area, shortness of breath, weakness, make themselves felt during physical activity. Read more about the characteristic signs of an angina attack here.
Cardiac stenting helps prevent the dangerous consequences of coronary artery disease: heart attack and acute coronary syndrome. Coronary stenting is a help for advanced stages of the disease or for emergency treatment of acute coronary syndrome. However, if both vessels are affected or the diameter of the vascular lumen is too small, bypass surgery, an open operation, will give better results.
Treatment and rehabilitation after myocardial infarction using enhanced external counterpulsation
UNC is an effective alternative to coronary artery bypass grafting, a modern and safe procedure. This non-surgical treatment method is widely used in modern medicine and professional sports. Its goal is to improve the blood supply to the heart without causing any surgical trauma to the patient. For this purpose, special cuffs are used that are placed on the patient’s limbs. Air is injected into the cuffs at a certain rhythm (coordinated with the contractions of the heart muscle) and then removed.
The effect is a 4-fold increase in blood supply to the affected areas of the heart and the formation of new vessels in it. High rates can be achieved in 90% of patients in whom the risk of heart attack is reduced or its consequences are reduced. Your body's metabolism, cholesterol levels and blood pressure will be normalized, and you will be able to increase the amount of physical activity.
On the topic “Enhanced external counterpulsation”, watch the recording of the program “About the Most Important Thing” on the Russia 1 TV channel, which was filmed with the participation of our cardiologist, cardiovascular surgeon Alexei Utin. Also, the filming contains a clear example of the procedure itself, which took place in our clinic.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
They are considered an important addition to physical rehabilitation methods and significantly speed up the process of restoring important vital signs. Most often it is recommended to do self-massage and breathing exercises. If the course of rehabilitation is favorable, gradual exercise with measured loads and time is allowed. These types include ordinary walking over longer distances, race walking, swimming, and cycling.
Hypoxic therapy - effective recovery after myocardial infarction
This is an effective non-surgical way to restore the functionality of the body, improve the quality of life after acute myocardial infarction, as well as the ability to prevent it. The procedure takes place in a special room. The hypoxicator device reduces the amount of oxygen in the air by several percent, maintaining normal atmospheric pressure. The oxygen delivery system in the patient’s body begins to work more actively, as a result of which the level of hemoglobin increases, and new blood vessels form in the myocardium.
Hypoxytherapy allows you to partially “revive” heart muscle tissue that has become dead during a heart attack. And in patients at risk of developing this disease, oxygen saturation of the heart improves. This eliminates the very cause of the heart attack.
Your body will be able to tolerate physical activity 70-80% easier in case of heart failure and coronary artery disease. In 75% of cases, positive changes are recorded after a course of treatment.
Life after stenting
Doctor - cardiologist of the cardiology department (for patients with myocardial infarction) No. 1 Artemyeva A. I.
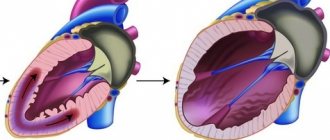
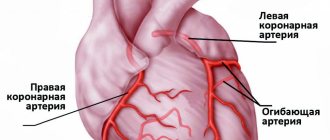
Coronary stenting is a method of intravascular prosthetics of the heart arteries for various pathological changes in the structure of their wall. Stents are used to reconstruct the corneal arteries.
A stent is a metal frame, which is a small metal tube made of wire cells (Fig. 1). A stent is inserted into the artery after it has widened and is placed at the site of the artery lesion. The stent supports the walls of the artery.
Figure 1 – Stent in a coronary vessel
Stents are placed on balloons, which allows them to have very small dimensions when unexpanded, and after the balloon is inflated inside the coronary artery, they expand, remaining in this position forever. Currently, a variety of stent models are used in interventional cardiology, differing from each other in certain design features. All of them are absolutely compatible with human organs and tissues, have a flexible structure and are elastic enough to support the artery wall. In addition, they are all made from radiopaque materials, which is a prerequisite for subsequent monitoring of their condition.
Recently, in order to prevent restenosis, specialists have begun to actively use drug-eluting stents, from which, after implantation into the coronary vessel, a pharmacological drug is released within several weeks, preventing excessive growth of the intima (inner lining) of the artery and an increase in atherosclerotic plaque. Taking into account modern capabilities, successful results of stenting are observed in 95% of patients who have undergone it. The feasibility of performing this operation and the choice of a specific type of stent is determined by a cardiac surgeon based on diagnostic data obtained during a preliminary examination of the patient.
Stenting can be either planned or emergency. It is carried out under the control of X-ray equipment, under local anesthesia, through a skin puncture on the wrist, forearm or thigh, without the need for large incisions, anesthesia and connection to a heart-lung machine. This intervention does not require strict bed rest and is quite well tolerated by patients.
During the intervention, a stent attached to a balloon catheter is inserted into the artery and advanced directly to the site of narrowing of the vessel. The balloon is then inflated under high pressure and the stent is deployed. The correct installation of the stent is monitored on the monitor screen.
Usually the results of the operation are good, it is relatively safe and the risk of complications after it is minimal. Sometimes an allergic reaction of the body to a substance introduced during the operation for x-ray observation is possible. There is also a hematoma or bleeding at the site of arterial puncture. To prevent complications, the patient remains in the intensive care unit with bed rest. Within a few days, after the wound at the puncture site has healed, the operated patient is discharged from the hospital. After this, restrictions are usually lifted, the person returns to normal life, and observation is carried out periodically by a doctor at his place of residence.
The bloodlessness and apparent simplicity of the operation, the short postoperative period and the effectiveness of coronary stenting make it a modern and popular solution to the problem of many cardiovascular diseases. Unlike surgery, which is performed using artificial blood circulation, the stenting procedure lasts 30-40 minutes and has virtually no complications.
Stenting is not completely effective; in approximately 15-20% of cases the reverse process occurs, and the vessel narrows again. One of the reasons for this process is excessive growth of muscle tissue, and, as a result, narrowing of the vessel wall. However, research by cardiologists does not stop, improving the technology of coronary stenting and achieving increasingly stable positive results statistics.
Currently, about 400 different models of stents have been developed, and the development of the method leads to their constant modernization. These stents differ in the alloy from which they are made, length, shape of the holes, coating of the surface in contact with the blood, and delivery system to the coronary vessels. So, in addition to balloon-expandable stents, there are self-expanding stents, etc.
However, it is worth remembering that even the most advanced methods of cardiac surgery do not replace the need for prevention and careful attention to your health and the health of your heart. Regular physical activity, commensurate with age and physical capabilities, fresh air, a balanced diet, enriched with vitamins and excluding weight gain, limiting the consumption of foods containing cholesterol - these are concepts that never lose their relevance.
The apparent simplicity of stenting, the absence of the need for long recovery after it, as well as the noticeable therapeutic effect of the operation often create in patients the illusion of a complete recovery. However, stenting is aimed only at eliminating the symptoms of the disease. The cause of coronary heart disease - atherosclerosis - continues to exist and progress, creating a threat of recurrence of angina, the development of myocardial infarction, heart failure and other very serious problems.
For this reason, a person who has undergone surgery must be fully aware of all the possible dangers of his situation and the need for further treatment.
Physical activity is one of the most important lifestyle requirements after stenting. Regular exercise slows down the development of atherosclerosis, trains the heart muscle, helps stabilize blood pressure, and has a general health effect on the body. It is important that sport helps the body burn fat, which means maintaining normal weight and blood cholesterol levels.
There are no sets of exercises that would suit every single patient after stenting. The training regimen and intensity are tailored individually, depending on the person’s condition, the list of his diseases, and exercise tolerance. All this is determined by a cardiologist.
The patient who has undergone this operation should be prepared for the fact that from now on he will play sports at least 4-5 times a week. Among specific types of loads, special physical therapy exercises, walking, cycling, swimming, and jogging are recommended. Sports that are accompanied by “explosive” loads, require significant physical effort and potentially pose a risk of injury (weight lifting, boxing) are not recommended.
Speaking about physical activity, it is important to mention sexual activity after stenting. Sexual activity can be carried out as usual; it can be resumed at any time as soon as the patient feels the need for it. On the recommendation of a doctor, you can take nitroglycerin before sexual intercourse, as well as before any other type of exercise. However, this is not always required.
The second extremely important component of therapy is diet.
"Food is medicine." These words are attributed to Hippocrates, and even today we can still attest to their authenticity. Special nutrition after stenting is not just a prevention of heart problems that may or may not arise in the future. This is treatment.
It’s sad, but not all patients adhere to the recommended nutritional rules. And we can say without a doubt that this plays a big role in the high incidence of recurrent angina and repeated stenting.
Diet therapy after stenting of coronary vessels should be based on the following principles.
- restriction in the diet of animal fats. This means reducing the consumption of foods such as fatty meats (lamb, pork), lard, processed foods, margarine. You should not eat butter, cheeses, sour cream, or cream in large quantities. It is also worth limiting your egg consumption to 3-4 eggs per week. All fatty foods are future cholesterol plaques that will resume the symptoms of IHD after stenting.
- limiting refined carbohydrates and sweets. From the foods that are often on your table, you will have to cross out sweets (it is better to replace them with dried fruits), excess sugar, pastries, carbonated drinks, etc. In the body, carbohydrates are converted into fats, which is why you should avoid sweets as much as possible.
- salt restriction. It causes fluid retention and increased blood pressure. Many patients with coronary artery disease who undergo stenting have hypertension. They should pay particular attention to this recommendation. The amount of salt should be reduced to 3-4 g per day (half a teaspoon). Be careful: many prepared foods (canned food, bread, etc.) contain salt, so you should limit its consumption more or less depending on what foods are present in your diet.
- limiting the consumption of coffee and other drinks and products containing caffeine (strong tea, chocolate, cocoa). Caffeine causes vasospasm and increased heart function, which creates increased stress on the cardiovascular system and harms patients with coronary artery disease and stenting. However, it is worth understanding: the diet does not require a complete abstinence from coffee; with controlled blood pressure and the absence of severe symptoms, it can be consumed in small quantities. It is better to choose natural Arabica beans - they have less caffeine than robusta and, especially, than instant coffee.
- adding vegetable oils, fresh vegetables and fruits, fish to the diet (consume at least 2 times a week). All this prevents the development of atherosclerosis. Dietary fiber from plant foods binds and removes cholesterol from the intestines, omega-polyunsaturated fatty acids from fish and vegetable oils reduce the content of harmful lipids (low-density lipoproteins, triglycerides) in the blood and increase the content of beneficial ones (high-density lipoproteins).
If your cardiologist recommends taking medications, you must follow this advice. The volume of drug therapy after surgery will decrease, but it is impossible to completely abandon medications for IHD. Follow the treatment regimen and do not forget: your good health after surgery is largely maintained due to the fact that you follow the therapy regimen.
If any complaints appear or the condition worsens, you should definitely consult a doctor for examination and treatment correction.
After undergoing stenting, it is recommended to quit smoking. Actually, this should be done before the operation, and it is best to never start smoking at all. However, if you have undergone surgery and still smoke, you can be given advice that will definitely help: quit cigarettes immediately!
Some patients console themselves with the thought that two or three cigarettes a day is quite a bit, and there will be no harm from them. This is wrong. Any type of smoking (active or passive) with any number of cigarettes smoked negatively affects the heart and blood vessels. It increases blood pressure, has a cardiotoxic effect, accelerates the progression of atherosclerosis, increases the likelihood of developing arrhythmias and the risk of heart attack. The pleasure derived from smoking is in no way justified by the enormous harm it causes.
Now about alcohol. It is a known fact that dry red wine has a healing effect on the heart. In some places you can even find information that it protects against atherosclerosis and almost causes the resorption of cholesterol plaques in the vessels. Indeed, small amounts of such wine have a beneficial effect on the course of atherosclerosis. However:
- we are talking about small quantities of the drink, no more than 1 glass of wine per day.
- only high-quality, expensive alcohol provides benefits, and not those types of alcohol that can be bought in any supermarket
— the benefits of red wine are not so obvious that it is mandatory to drink it regularly. The notorious cessation of smoking will bring many times greater benefits.
After the stenting operation, the patient will be able to return to normal work. The specific time frame for restoration of working capacity may vary; it depends on the person’s condition (the severity of coronary artery disease, the presence of a recent heart attack, etc.) and his profession. Intellectual workers can start working almost immediately after stenting, and those whose specialty is related to physical activity are allowed to start working later.
The stenting operation eliminates the symptoms of coronary artery disease, the person’s condition improves after it, therefore, it is quite rare to talk about registering disability for patients who have undergone it.
In the event that stenting does not lead to improvement, the patient’s angina returns early, or a heart attack occurs after the operation, assigning a disability group to the person is possible. However, this operation is not performed on people at risk of deterioration and complications, so usually stenting still gives a positive result and contributes to the restoration of a person’s performance, and not its final loss.
When a person’s condition stabilizes after surgery, he is allowed to travel by any means and without restrictions. The main thing is that a person regularly takes medications and follows other doctor’s recommendations. Among all types of recreation, it is better to choose an active one, taking into account your tolerance to physical activity. Patients are most often not contraindicated from visiting baths and saunas, although a more specific opinion on this matter should be given by a cardiologist.
A cardiologist is a doctor who often sees and observes his patients for years. Coronary heart disease is a chronic phenomenon, so this is not surprising.
Sometimes you come across such stories: a person develops hypertension, angina, then suffers a heart attack and undergoes stenting. However, even after this, the “adventures” do not end: periodically the patient is hospitalized with hypertensive crises, after some time his angina pectoris returns, he again undergoes stenting or even coronary bypass surgery... Repeated heart attacks and heart failure are not uncommon phenomena even after repeated operations. As a result, a person feels much worse than he could, and his life expectancy is reduced.
Why does this happen? The reason is not only the insidiousness and danger of the disease, although, undoubtedly, both are fully inherent in coronary heart disease. Most often, an unfavorable outcome of the disease is determined by the fact that a person makes insufficient efforts to improve his condition and prolong his life.
If you have had stent surgery and you are not following all the lifestyle recommendations, it is time to consider changing your attitude towards treatment. All the tips listed above are clear, simple and doable; you just need to follow them, constantly and conscientiously.
After stenting, hemodynamics change in the heart and throughout the body, so the body needs time to adapt to this. In addition, with stenting, a foreign body is actually installed in the coronary vessel. This causes a reaction from the immune system and blood clotting, creating an increased readiness in the body to accelerate the development of coronary atherosclerosis, the formation of blood clots in blood vessels, etc.
The period of hospital treatment is not enough for the body to fully recover, so cardiac rehabilitation is recommended for patients after stenting.
A set of health procedures will consolidate the results of therapy and improve a person’s condition. A special training program will help the patient get used to the new lifestyle.
Ultraviolet irradiation of blood
This method of treating the consequences of myocardial infarction, used in CBCP, also improves the quality of life after this disease. Does not require any surgical intervention in the patient's body. In this case, no blood is drawn: a special needle connected to a UV emitter is inserted into the patient’s vessel. The device affects a small volume of blood with low-power radiation, which is not felt at all by the patient.
Under the influence of UV radiation, a photochemical reaction occurs in the blood and plasma, as a result of which their composition and functionality improves. It is possible to achieve a significant reduction in blood viscosity (eliminate the risk of blood clots), activate metabolism, improve oxygen delivery to heart tissue, and dilate blood vessels.
Ultraviolet irradiation of blood attracts, first of all, its restorative effect. If you want to “rejuvenate” your heart without resorting to surgery, this method opens up wide possibilities for you.
Stationary stage
At this stage, it is not so much the physical recovery of the patient that is important, but the moral one. He must believe that not everything is lost, that a healthy lifestyle can be completely restored, that the disease has receded for a long time and there is no need to be afraid of relapses. But the desired result can be achieved only under one condition - the patient himself will make every effort and unconditionally follow all medical recommendations.
During the stationary stage of physical rehabilitation, the sick person must fully take care of himself and take walks of two to three kilometers. In addition, exercise therapy efforts should ensure:
- localization and elimination of complications that arise after prolonged bed rest. Consequences of outpatient treatment may include intestinal disturbances (atony), thromboembolism, and congestive pneumonia. Restoring movement makes it possible to restart the vital functions of the body;
- the maximum possible restoration of the performance of the cardiovascular system at the initial stage, training of peripheral circulation. In this case, the load on the heart is selected as sparingly as possible, the patient is constantly monitored;
- orthostatic stability, restoration of simple motor functions.
As soon as the patient is convinced of the progress of the results of the fight against the disease, he will have positive emotions and confidence in his future. Normalization of mental state also plays a very important role in the process of returning to a normal lifestyle.
Infusion therapy
Drug drips are an integral part of treatment for symptoms of myocardial infarction. In particular, with this disease, ventricular tachycardia may occur, for which infusion solutions are indicated. In some cases, the Bezold-Jarisch reflex occurs in the myocardium, which is also suppressed by drugs administered through IVs. Anticoagulants and antiarrhythmic drugs are also administered. The method allows drugs to be distributed throughout the vascular system in the shortest possible time.
Therapeutic exercises are a necessary element in the rehabilitation complex after myocardial infarction
Physical activity after myocardial infarction, along with a proper diet, is necessary for the full restoration of the functions and functioning of the heart and the body as a whole. In the absence of complications, the doctor creates an individual set of exercises for each patient. Therapeutic exercise is carried out even during bed rest - starting with movements of the hands and feet and ending with turns on different sides, moving to a sitting position. After discharge from the hospital, recommendations for rehabilitation and lifestyle after an attack necessarily include daily walking a certain distance.
Prevention of complications
To avoid relapse, you must:
- give up alcohol, nicotine, and other bad habits;
- have a good rest;
- exclude sauna and steam bath;
- avoid stress, maintain emotional stability;
- do not ignore dosed sports activities;
- control weight (BMI – within 25-27 kg/m);
- visit a cardiologist, get tested, undergo stress tests, ECG, ultrasound.
Rehabilitation after a heart attack requires iron discipline. The state of health in this serious disease depends on how correctly the doctor’s recommendations are followed. In old age, it is difficult to keep everything under control, and difficulties arise with self-care. If it is difficult to provide care for an elderly relative, you should seek professional help.
The Vita boarding house network has all the conditions for full recovery. A convenient infrastructure has been created for people with disabilities. Qualified personnel work. The implementation of medical prescriptions is monitored and rehabilitation is carried out according to individual programs.
Guests are provided with six meals a day, taking into account the recommended diet. Hygienic and sanitary care is provided. The closed area of the nursing home and video surveillance guarantee safety.