The implantation of an electrical pacemaker in Tver is carried out by a cardiovascular surgeon, candidate of medical sciences, Ilya Borisovich Lukin.
To make an appointment with a cardiac surgeon, as well as to find out the cost of the appointment, you can call:
- 8 (Research Institute “Phlebology”, Tver, 2nd Krasina St. 49)
- 8 (University Clinic, Tver, Peterburgskoye Highway, 115 building 2)
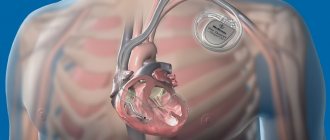
Implantation of an electrical pacemaker (Pacemaker) is the most reliable and often the only method for treating bradycardia. In the Tver region, about 1,000 people annually need this operation. Unfortunately, the capacity of Tver healthcare is only sufficient for 200 implantations per year.
Medtronic pacemaker
The first pacemakers from the middle of the last century were large and could not work for a long time without recharging. They were located outside the patient's body and stimulated the heart through the skin. Such devices were not very convenient, had a lot of shortcomings, and yet they helped save thousands of lives. A modern pacemaker is a small device that is sutured under the skin, usually in the collarbone area, and connected with wires to the heart. It is not noticeable at all, does not interfere with everyday activities, and can work for a long time without recharging. A pacemaker helps to significantly improve the quality of life of a person suffering from arrhythmia, get rid of painful symptoms, and prevent life-threatening complications. The main difference between different types of pacemakers is the number of wires that come from the device. Depending on this, pacemakers are: • Single-chamber. They have only one wire, which is installed in the wall of the right atrium or right ventricle. • Two-chamber. They are equipped with two wires: one is installed in the wall of the right atrium, the other in the wall of the right ventricle. Thanks to this, the Medtronic dual-chamber pacemaker can control and stimulate the work of two chambers of the heart at once. • Three-chamber. ECS of the latest generation.
Three electrodes are installed in the heart: in the wall of the right atrium, right and left ventricles. This ensures consistent propagation of excitation to different chambers of the heart. It was Medtronic pacemakers that at one time became the first devices that could be implanted. All previous models were powered from an outlet, so using them in everyday life was very inconvenient.
At the moment, the Medtronic external pacemaker is one of the most popular foreign pacemakers in Russia. In our country, the following models of dual-chamber pacemakers are often used: • Sensia, • SureScan, • Adapta.
What does the price depend on?
The cost of the operation depends on the chosen clinic and package of services . In a regular hospital, a surgeon will install a pacemaker for free, but it is the patient’s job to buy it.
In private clinics, in addition to the pacemaker, you will also need to pay for the services of a surgeon. Since there are pacemakers of various equipment, the price of modern models with greater functionality will be higher.
Main features of Medtronic pacemaker:
According to the manufacturer, they stimulate the heart in a completely physiological mode. • all device functions are automated; • constant monitoring of electrode polarity, impedance, stimulation thresholds is carried out; • the device automatically monitors the electrical activity of the heart and adjusts its work to it.
A cardiologist-arrhythmologist at City Clinical Hospital No. 31 checks and adjusts an already installed Medtronic pacemaker and installs an pacemaker.
If you already have a pacemaker , please provide the model when making your appointment so that your doctor can prepare the necessary equipment to test the pacemaker.
If you do not know whether you need a pacemaker, but you are concerned about heart failure , make an appointment with an arrhythmologist, and the doctor will select the necessary treatment.
You can read about how to prepare for an appointment with an arrhythmologist
What is a pacemaker
With age, the heart, like any muscle, wears out . Decreased quality of life can be corrected by installing a pacemaker. It is a small microprocessor in a sealed titanium case.
The pacemaker is inert in relation to the biological environment of the body, which means the risk of rejection is minimal.
The pacemaker has several parts:
- The power supply can be compared to a battery. The service life is about 7 years.
- Microprocessor – converts electricity into impulses to stimulate the heart.
- A block with conductors and electrodes are impulse conductors. They come into direct contact with the surface of the heart.
- Programmer – controls the operation of the stimulator. It is used to adjust the device settings for various changes in heart rhythm - tachycardia, bradycardia, fibrillation.
The implant is placed under the skin or muscle. It helps maintain a normal heartbeat. Modern models are autonomous - they detect the electrochemical activity of the heart and, in case of deviations, create an additional electrical charge. Doctors call this method “resynchronization therapy.” The entire operation lasts 1.5–2 hours .
Cost of services of an arrhythmologist
| Payment code | Nomenclature of the Ministry of Health and Social Development | Name | Price, rub.* |
| 1089 | B01.043.003 | Appointment (examination, consultation) with a doctor for X-ray endovascular treatment of cardiac arrhythmias | 4 300 |
| 1090 | B01.043.004 | Appointment (examination, consultation) with a doctor for X-ray endovascular treatment of cardiac arrhythmias with checking the operation of the pacemaker | 6 100 |
| 9004 | A05.10.006 | Electrocardiogram registration | 1 600 |
| 9006 | A05.10.008 | Holter heart rate monitoring (HM-ECG) | 4 800 |
| 15023 | A16.10.014.003 | Implantation of a two-chamber pacemaker (pacemaker), without the cost of the electrode and pacemaker | 125 000 |
Sign up for a paid appointment
What is needed for preliminary diagnosis?
- ECG in 12 leads;
- Echo-CG;
- Holter ECG monitoring for 1-2 (sometimes more) days;
- Stress ECG.
- or chest x-ray.
- Ultrasound examination of the heart.
- Coronary angiography.
- Dopplerography.
- Endocardial electrophysiological study.
- Consultation with a cardiologist;
- Consultation with an arrhythmologist to determine indications for surgery and select the type of pacemaker;
- Standard list of preoperative tests.
Efficiency forecast and service life
Pacing is the only effective long-term treatment for symptomatic bradycardia. The clinical benefit of PM therapy in patients with symptoms of atrioventricular block was evident from the very beginning.
Because of the magnitude of the treatment effect, there was no need for randomized trials to prove its effectiveness.
Later, the use of PM therapy was expanded to include other types of bradycardia such as SSS and AF. These arrhythmias represent a heterogeneous combination of conditions characterized by varying degrees of severity and a variety of symptoms, ranging from intermittent syncope to acute cardiac arrest.
No rigorous clinical trials have ever been conducted to determine the clinical effectiveness of PM therapy in these settings. International recommendations are mainly based on expert opinion. For some indications, such as SSS with prolonged ventricular pauses complicated by recurrent syncope, indirect evidence indicates a clear symptomatic benefit.
However, for conditions such as slow AF and lower levels of AV block, especially in patients who have no or mild pacing symptoms, the benefit of pacing is less clear.
Randomized trials of PM therapy were conducted in the 1990s and early 2000s, but these only compared the clinical effectiveness of different stimulation modalities
(eg, single or dual chamber stimulation), and they did not consider the actual effectiveness of the method.
In 2005, NICE published a technology assessment of the use of dual-chamber PM17s. She concluded that dual-chamber pacing is generally preferable to single-chamber pacing, except in certain groups of patients in whom, after complete evaluation, there is no evidence of AV conduction abnormality.
A 2004 Cochrane review found that pooled data from parallel studies showed a statistically significant preference for stimulation for the prevention of stroke, heart failure, and all-cause mortality, and a statistically significant benefit for the prevention of AF.
Pooled data from cross-sectional studies showed a statistically significant trend that pacing was more beneficial in terms of exercise performance.
The service life of modern pacemakers is 8-10 years. this applies to both classic models with electrodes and electrodeless ones.
What complications occur after implantation of pacemakers? And how can you prevent them?
Like any surgery, pacemaker implantation carries certain risks.
1. By making a skin incision, an infection . In order to prevent possible infection, before the operation the doctor administers an antibacterial drug to the patient, and the surgical field is treated with modern antiseptics. 2. In very rare cases, if the pleura, the film that ensures the tightness of the chest cavity, is damaged, air can penetrate into the latter due to the negative pressure inside. This condition is called pneumothorax . The air compresses the lungs, prevents them from expanding and makes breathing difficult. This can be eliminated by installing pleural drainage and pumping out air. In order to make sure that there is no such complication, or to detect and eliminate it in time, the doctor prescribes a chest x-ray after the operation. pain may occur when moving your arm , but usually it is not severe and passes quickly. If necessary, painkillers are prescribed for several days. 4. Next to the subclavian vein is the subclavian artery. Due to the individual anatomy of each patient, the surgeon can inject it with a puncture needle. Then there will be a hematoma (bruise) in the subclavian region, along the biceps and under the chest, which, as a rule, resolves after 7-10 days. 5. Some patients develop allergic reactions to medications or materials used during implantation. If a severe allergy (anaphylactic shock) occurs, doctors will interrupt the operation and provide assistance . Surgical treatment is carried out accompanied by an experienced anesthesiologist and resuscitator. 6. Hemorrhage under the skin . It will go away in a few days, there's nothing to worry about.
Modern technologies and small sizes of pacemakers make it possible to minimize risks, make implantation quick and painless, less traumatic, and reduce postoperative rehabilitation time. Still, this is a serious procedure. The quality of life of the patient in the future depends on how successfully it is performed.
4.Can electrical devices affect the operation of a pacemaker?
A pacemaker is an electrical device. And there are certain rules for its interaction with other electrical appliances:
- Electric blankets, heating pads, and microwave ovens will not affect the pacemaker;
- The cell phone must be used on the side opposite to the place where the pacemaker is implanted. The phone should not be worn directly on the chest (for example, on a lanyard) or on the same side of the body where the pacemaker is implanted;
- You will have to avoid strong electric or magnetic fields. For example, some industrial equipment, large electrical generators, power plants, radio frequency towers and arc resistance welders.
- You cannot undergo a medical examination with an MRI.
In any case, the doctor will tell you about this specificity in more detail.
Complications in the future
Pacemaker complications include failure due to mechanical factors such as pneumothorax, pericarditis, infection, skin erosion, hematoma, lead migration, and venous thrombosis.
Treatment depends on the etiology. Pneumothorax may require medical observation, needle aspiration, or even chest tube placement.
Late procedure-related complication
- Pocket erosion
- Electrode offset
- Hematoma
- Phlebitis/deep vein thrombosis
- Infection
- Hemothorax
- Atrioventricular fistula
- Subclavian crush syndrome
Late device-related complications
- Pacemaker/oscillator infection.
- Systemic infection.
- Myocardial perforation.
- Twiddler syndrome.
- Pacemaker syndrome.
- Allergy or sensitivity to unit components or electrodes.
- Electrode fracture.
- Breast muscle stimulation.
- Intercostal or diaphragmatic stimulation.
- Endocarditis.
- Right atrial thrombus.
2.How to prepare for implantation, implantation methods
Before having a pacemaker implanted, talk to your doctor about the medications you take on an ongoing basis. Your doctor may ask you to temporarily stop taking them 1-5 days before your procedure.
Do not eat or drink after 12:00 am immediately before your procedure. If you must take the medicine, take it with a small sip of water.
Pacemaker implantation methods
Pacemaker implantation can be performed in two ways:
- Endocardial method of pacemaker implantation.
It is used most often. A local anesthetic is used to numb the area where the pacemaker is implanted. An incision is made in the chest and the device is inserted into the desired area. Pacemaker wires are inserted through an incision into a vein and then guided toward the heart using fluoroscopy. One end of the wire is attached to the heart muscle, and the other to the pulse generator. - The epicardial pacemaker implantation method
is more often used in children than in adults. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
Visit our Cardiology page
approximate price
- The cost of an operation to install a temporary pacemaker in a public hospital starts from 13,500 rubles .
- The price for the service of permanent implantation of the device starts from 24,700 rubles .
- The indicated prices do not include the cost of the device itself; you must pay for it separately. Its minimum cost is 25,000 rubles . The patient may not pay for the services of a surgeon in a regular hospital if he has undergone a waiting list as prescribed by the doctor or has benefits.
- In a private clinic, you need to pay for the services of a surgeon (around 30,000 rubles ), and for a doctor’s consultation (from 1,000–3,000 rubles ), separately for a pacemaker and for staying in the ward during the rehabilitation period (approximately 5,000 rubles for two days) .
How are electrodes placed in the heart?
In order to install electrodes into the heart muscle through which the pacemaker will send impulses, it is not necessary to undergo severe traumatic open-heart surgery. The pacemaker and electrode are installed through one small incision. The electrode is passed into the chambers of the heart through blood vessels, usually the subclavian vein. In this case, an incision is made in the upper chest, under the collarbone. Once the end of the electrode is in the right place, it is attached to the wall of the heart using a special fixation system: anchors in the form of a hook (passive fixation) or using a corkscrew-shaped spiral (active fixation). Sometimes electrodes are inserted through other vessels: axillary, internal jugular vein, etc.