Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
The umbilical cord is an organ that is quite simple in structure, but very important in significance. It plays a big role in ensuring the normal functioning of the baby during pregnancy. Accordingly, various anomalies and pathologies of its structure negatively affect the child’s condition and can lead to birth defects and even death. One of the problems that pregnant women face is a short umbilical cord in the fetus. This is a fairly serious pathology that can seriously complicate pregnancy and childbirth, up to its complete impossibility.
The umbilical cord and its role in childbirth
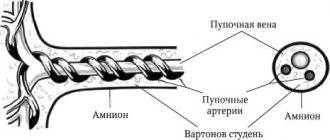
The umbilical cord is a hollow, flexible tube that connects the fetal abdominal wall to the placenta. Inside it lies:
- 1 vein, through which the baby receives blood enriched with oxygen and nutrients from the mother’s bloodstream;
- 2 arteries through which waste products of the fetus (urea, carbon dioxide, etc.) are discharged back;
- The vitelline duct connects the embryo's intestine to the yolk sac, which contains a supply of nutrients;
- The urachus is a duct that connects the fetal bladder to the placenta and serves to remove metabolic products.
The outer membrane (amnion) consists of strong connective tissue and protects blood vessels from damage. The space between it, the artery and veins is filled with Wharton's jelly - a jelly-like or mucous substance consisting of polysaccharides. It gives the umbilical cord elasticity and prevents it from twisting, thereby protecting the veins from the formation of kinks and mechanical damage.
Thus, the purpose of the umbilical cord is to provide nutrition, respiration and metabolism to the fetus during gestation. Since his own organs and systems are just being formed, their function is transferred to the mother’s body. During childbirth, the blood vessels in the umbilical cord, under the influence of the hormone oxytocin, “collapse,” gradually cutting off blood flow. This is how atrophy of the umbilical cord begins, which normally ends completely a few hours after the birth of the child. Under natural conditions, the umbilical cord dies and falls off on its own, but in the maternity hospital it is cut 1-3 minutes after birth. This allows you to minimize the risk of developing infection.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
What is the single artery of the fetal umbilical cord?
An anomaly in the structure of the umbilical cord, when instead of two arteries one is formed, is called a single umbilical cord artery.
The absence of one artery in the umbilical cord can be initial (congenital aplasia) or develop during pregnancy (artery atrophy, which occurs as a result of the complete cessation of its functioning).
A single fetal umbilical cord artery is considered a fairly common pathology: 1 in 200 singleton pregnancies – 0.5% and 1 in 20 multiple pregnancies – 5%.
Normally, the umbilical cord contains 2 arteries and 1 vein
Short umbilical cord during pregnancy: causes and symptoms
Normally, the length of the umbilical cord in humans is 50-70 cm. This size reduces the likelihood of it twisting, which can cause hypoxia and nutritional deficiency in the fetus. However, quite often pregnant women experience disturbances in the length of the umbilical cord - in particular, its shortening. If the length of the organ is less than 50-40 cm, it is considered abnormally short. Depending on the causes of the pathology and the size of the umbilical cord, two types of anomalies are distinguished:
- Relatively short umbilical cord. It initially has a normal size, but during gestation it shortens due to twisting or entwining around the fetus, and the formation of varicose nodes on the organ. Most often this happens if the expectant mother eats poorly, drinks alcohol and drugs, smokes, experiences constant stress, or suffers from chronic systemic and gynecological diseases. This pathology poses a danger to the health and life of the child due to impaired blood circulation and accompanying hypoxia. However, a shortened umbilical cord can unravel on its own and therefore has a more favorable prognosis.
- Absolutely short umbilical cord. This is a genetic pathology associated with a violation of the mechanism of placenta formation. Factors contributing to this condition are hereditary diseases and chromosomal mutations. It occurs in most cases and also poses a great threat to the fetus. However, unlike the previous type of pathology, an absolutely short umbilical cord cannot be treated.
The danger of this pathological condition is that outwardly it does not show itself in any way. The expectant mother does not experience any inconvenience or pain; her life is not in danger. Very often, a woman finds out that she has an abnormally short umbilical cord during childbirth. Typical signs of this pathology:
- Increased labor time. For patients giving birth for the first time, they can last up to 20 hours, for those who have previously given birth again - up to 15 hours.
- Early delivery of the placenta. Normally, she is born within 20-50 minutes after the fetus leaves the woman’s birth canal. If the umbilical cord is too short, the child “pulls” it along with him, which is often accompanied by its separation and bleeding.
- Fetal hypoxia. This symptom is not direct evidence of an abnormally short length of the umbilical cord, since this condition is also observed in some other intrauterine pathologies. However, in combination with the above symptoms, fetal hypoxia may indicate a violation of the development or structure of the umbilical cord.
- Fetal hyperactivity. With acute hypoxia, the child begins to make vigorous movements. His heartbeat first increases to 160 beats per minute, then becomes slow (no more than 120 heartbeats). In addition, in the amniotic fluid, as a result of increased activity of the fetal intestine, meconium may appear - primary feces, consisting of bile, mucus, prenatal hair, and amniotic fluid digested by it.
Thus, the presence of a short umbilical cord in a fetus can be judged either by the fact of birth, or by using modern diagnostic tools that make it possible to track the condition of the baby during the prenatal period.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Why is a short umbilical cord dangerous?
Both absolutely and relatively short umbilical cords are pathological anomalies that are potentially dangerous to the life and health of the child. The greatest damage is caused by chronic hypoxia, which develops due to insufficient oxygen supply to the tissues (including the brain). Its result is the death of the baby during pregnancy or childbirth, as well as congenital pathologies caused by the death of neurons in the brain or spinal cord. Also, a short umbilical cord during childbirth can cause the following complications:
- Slow movement of the child through the genital tract, which again causes hypoxia and too long compression of the skull bones, leading to death or developmental disorders;
- Placental abruption, which is accompanied by intrauterine bleeding, hemorrhagic shock due to large blood loss, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, which simultaneously leads to the formation of blood clots and massive hemorrhages that threaten the life of both the fetus and the woman herself;
- Incorrect presentation of the fetus in the uterus, which can lead to various birth injuries - ruptures, sprains, etc.
Thus, the consequences that arise from a short umbilical cord concern not only the child himself, but also the mother. In severe cases, this pathology can lead to the loss of a newborn, infertility and death of the woman herself.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Diagnosis of a short umbilical cord
As already mentioned, this pathology during pregnancy does not affect the condition of the woman herself, which significantly complicates its diagnosis. Often they find out about it only directly during childbirth, when complications begin. However, a short umbilical cord directly affects the condition of the fetus, and its changes can be recorded with modern diagnostic tools:
- Ultrasound. Ultrasound examination allows you to obtain a visual picture of the umbilical cord, from which you can judge the presence of knots and entanglements around the fetus. Unfortunately, this method does not accurately measure the length of the umbilical cord and, therefore, accurately diagnose the pathology.
- Ultrasound Doppler. Doppler ultrasound is a type of ultrasound, but it records the parameters of dynamic (moving) objects, while conventional ultrasound is used to study mainly static objects. This method is based on the fact that sound waves are reflected from moving objects with a change in frequency. Doppler ultrasound, in particular, allows one to determine the speed and direction of blood flow in the umbilical vessels. However, as in the previous case, these are only indirect signs that do not allow an accurate diagnosis to be made.
- CTG. One of the manifestations of a short umbilical cord in a child is hypoxia, which is accompanied by a reduction in his heart rate. To measure the fetal heart rate, cardiotocography is used, a type of Doppler ultrasound that records the heartbeat. In addition, this method also allows you to measure the frequency of uterine contractions. By synchronizing these two indicators, the doctor can judge the state of chronic fetal hypoxia and, therefore, the possible presence of a short umbilical cord.
- Gynecological examination. The standard of this procedure includes a visual examination of the cervix, which can be used to judge the position of the fetus, as well as an ultrasound scan, which monitors its heartbeat. Practice shows that gynecological examination quite often reveals indirect signs of a short umbilical cord.
The disadvantage of all of these methods for diagnosing a short umbilical cord is that they do not give an accurate result. However, by combining them with each other, the doctor can, with a fairly high degree of probability, make the correct diagnosis of a short umbilical cord.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Treatment of a short umbilical cord
There is currently no effective treatment for the pathology itself (both of its forms). If a short umbilical cord is suspected during pregnancy, the patient is hospitalized in a hospital for constant monitoring. Doctors use a wait-and-see approach, carefully monitoring the fetal heartbeat and mobility using ultrasound, ultrasound and CTG. The following are prescribed as maintenance therapy:
- Antispasmodics and mild sedatives that prevent vigorous fetal movements and umbilical cord twisting;
- Magnesium and iron preparations that improve oxygen supply to the blood and compensate for fetal hypoxia;
- Medicines that improve blood flow in the umbilical vessels.
Depending on the severity of the pathology, the predicted consequences of a short umbilical cord for the child and the woman herself, as well as the timing of detection, the following options are possible:
- Caesarean section - it is prescribed for a proven short umbilical cord and fetal hypoxia to prevent placental abruption and other complications during childbirth;
- Dissection of the perineum - this method is used to prevent fetal hypoxia in cases where a short umbilical cord is detected during natural birth.
A caesarean section can also be an emergency - for example, if bleeding, acute fetal hypoxia and other complications occur during natural childbirth with a short umbilical cord. In general, even with late detection of pathology, timely and correct use of CS allows to minimize the risks for both the woman and her child.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Material and methods
To achieve this goal, we conducted a Doppler study of the state of HD in the AP in 178 fetuses of healthy pregnant women with a physiological pregnancy - group 1 (control) and in 162 fetuses of pregnant women with diabetes - group 2 (main). The main group was divided into two subgroups. Subgroup 2a included 65 fetuses without ultrasound signs of diabetic fetopathy and subgroup 2b - 97 fetuses with ultrasound signs of diabetic fetopathy at 30 to 39 weeks of pregnancy without signs of hypoxia according to other research methods. Analysis of hemodynamics in the umbilical cord artery included the study of indices of peripheral vascular resistance (SDO, IR and pulsatility index - PI), peak (pressure in the vessel at the time of the peak of the systolic wave in a given segment of the vessel) and average (pressure in a given segment of the vessel at the average time of rise in systolic waves) pressure gradients, MO in the umbilical artery, its percentage of the minute volume of blood of the left ventricle of the fetal heart, the integral coefficient of elasticity of the AP wall (an indicator of the ratio of the peak pressure gradient to the blood flow velocity gradient). To describe the distribution of quantitative characteristics, the median (Me) and interquartile range (Q1-Q3) were used.
The study was carried out using ultrasound devices Accuvix XQ and Accuvix V20 (South Korea).
Prevention of a short umbilical cord
Since there is currently no effective treatment for this pathology, doctors recommend reducing the risk of its development even when planning pregnancy. If a woman cannot do anything about the hereditary physiological characteristics of her own body, then she is quite capable of the following actions:
- Avoid smoking, drinking alcohol and narcotic substances, which can cause disruption of the development of the placental apparatus;
- Prevent fetal hyperactivity by reducing the consumption of stimulating foods such as coffee, cocoa, chocolate, etc.;
- Be in the fresh air more often in order to maximally saturate your own blood with fresh oxygen, which will at least partially compensate for possible fetal hypoxia;
- Do not come into contact with toxic chemicals (varnishes, paints, industrial gases, etc.) during the period of preparation for pregnancy and gestation;
- Eliminate or minimize stressful situations - for example, changing jobs, leaving a dangerous urban area for a while, etc.;
- Make your diet more varied, rich in vitamins and other beneficial substances - especially iron and magnesium compounds, which will improve blood oxygen saturation;
- Avoid heavy physical activity and injuries, as they can lead to hyperdynamia of the fetus and the umbilical cord entwining around it.
Regularly scheduled medical examinations during pregnancy allow early diagnosis of possible pathology. If the expectant mother has relatives who were born with a short umbilical cord, or she herself had this anomaly, it is recommended to undergo examination by a geneticist.
If you suspect a short umbilical cord in the fetus, it is important to seek quality medical care. It can only be provided in licensed clinics staffed by qualified doctors. Also, the mother herself is required to completely trust the attending doctor and carefully follow his recommendations. You should not be afraid of such radical steps as a caesarean section - this is a long-established and simple operation that significantly reduces the likelihood of complications.
The correct tactics of behavior for a pregnant woman with this pathology
Many pregnant women, after diagnosing this anomaly, are at a loss. They do not know what to do and how this pathology can affect the intrauterine development and health of the baby in the future.
First of all, you need to calm down and understand that the only artery of the umbilical cord carries an increased load, and unnecessary worries, hard work and stress have an extremely negative effect on blood flow.
Therefore it is very important:
- maintain a certain daily routine;
- completely eliminate any psycho-emotional stress;
- free yourself from heavy work and heavy lifting;
- to walk outside;
- prevent the development of constipation.
In most cases, one umbilical cord artery rarely affects the health of the child in the future, and the birth of a baby with developmental abnormalities when this anomaly is diagnosed is extremely rare. If you follow all the recommendations of specialists and constantly monitor the condition of the fetus, the number of umbilical cord arteries does not matter at all for the child’s future life.