- Gallery
- Reviews
- Articles
- Licenses
- Vacancies
- Insurance partners
- Partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule for receiving citizens for personal requests
- Online consultation with a doctor
- Documentation
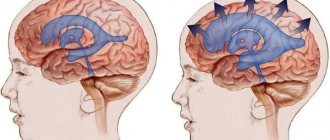
Increased intracranial pressure occurs with an increase in the volume of brain tissue, cerebrospinal fluid, or a voluminous pathological process in a relatively closed cranial cavity.
You need to imagine that the head is, first of all, the tightly connected bones of the skull, inside which the brain is located. And naturally, an increase in internal volume increases pressure on the bones of the skull and, accordingly, on the tissues and vessels of the brain.
The accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the cranial cavity is called hydrocephalus. It can be either external, i.e. accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid around the brain and internally (enlarged cerebral ventricles). This pathology can occur at any age - from newborns to the elderly. Each age interval has its own causes, there are age-related characteristics of manifestations and age-related characteristics of treatment.
Causes of increased intracranial pressure or hydrocephalus may include:
- congenital abnormalities of brain development;
- perinatal infectious, hypoxic, traumatic processes;
- tumors;
- meningitis;
- injuries;
- hereditary metabolic and degenerative brain diseases, etc.
In any case, intracranial hypertension syndrome has similar clinical manifestations . This is a headache, mainly in the morning, without clear localization, bursting, intensifying in paroxysms, often accompanied by vomiting, not associated with food intake. The headache intensifies when coughing, sneezing, or straining. Additional symptoms: a feeling of “fog” before the eyes after being in a bent position, lethargy.
Intracranial hypertension in children
January 30, 2017
Unfortunately, today intracranial hypertension in children (in other words, increased intracranial pressure) is not uncommon. Many parents have probably heard this term. Often, but not necessarily, intracranial pressure and cerebral palsy become companions.
Features and causes of occurrence Intracranial hypertension occurs due to an increase in the volume of cerebrospinal fluid (fluid of the ventricles of the brain), tissue fluid or blood. This phenomenon is also possible in cases of the appearance of a tumor and foreign tissue in the brain, and the pressure is not observed in any specific part of the brain, but covers it entirely.
Increased intracranial pressure can be caused by:
-congenital defects or anomalies, genetic predisposition; - hydrocephalus (water on the brain); - unfavorable course of pregnancy suffered during this period ———infectious diseases and/or difficult childbirth leading to birth injuries; -prematurity, intrauterine hypoxia or prolonged oxygen starvation during childbirth; - neuroinfections, inflammation of the membranes of the brain - meningitis, encephalitis.
The child cannot talk about his well-being, so the main task of parents is to carefully monitor the baby.
The symptoms are different:
profuse vomiting (several times a day), regurgitation in a fountain; superficial, restless sleep with frequent hysterical or monotonous crying for no reason; disproportionately large head size, rapid increase in skull size, inappropriate for age; swelling of the fontanelle and divergence of the sutures, failure to hear pulsations; irritability, lethargy, loss of appetite; muscle hypertonicity. convulsions, loss of consciousness, increased anxiety.
Intracranial hypertension itself is not a disease, but a symptom, so the goal of medical diagnosis is to identify the causes that led to the negative condition. Treatment begins immediately after the diagnosis is made.
Depending on the complexity of the symptoms, several methods and ways to eliminate them are used:
-the surgical route is used in the most severe cases, for example, with hydrocephalus - the essence of the surgical intervention is to install a shunt through which excess fluid is removed. It can be either temporary or lifelong and ensures rapid recovery for the patient. -drug treatment is practiced in cases of moderate severity. In this case, diuretics or combinations thereof are used, applied according to certain schemes. The results are monitored by neurosonography, so a significant improvement can occur within a week; - in mild forms of the disease, non-drug forms of treatment are prescribed, which may include the following procedures: a special drinking and eating regimen (diet); therapeutic swimming in the pool; a cycle of massage sessions and a complex of therapeutic exercises; physiotherapy and acupuncture; taking diuretic preparations and decoctions (at an older age and in the absence of an allergy to their components).
Thus, special attention should be paid to small children who can silently endure poor health for a long time, and if symptoms are detected, it is better not to delay a visit to a specialist. Any disease at an early stage is much easier to treat, and it is quite possible to prevent the consequences.
Back
Indications and contraindications for osteopathic therapy
Here is just a small list of body ailments for which a specialist appointment is indicated:
- various injuries;
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- dysfunction of childbirth;
- pain of various etiologies;
- pain in internal organs;
- states of the nervous system;
- curvature of posture;
- intracranial vascular disorder;
- increased intracranial hypertension;
- pregnancy planning.
Contraindications for manipulation:
- strokes, heart attacks;
- bleeding in the brain;
- cardiac, renal, hepatic, respiratory failure during decompensation;
- infections in the acute stage;
- open form of tuberculosis;
- untreated hematomas;
- mental illness;
- blood diseases;
- oncology, tumors.
The doctor will not be able to immediately cure high blood pressure and pain in adults and children, but after an acute period of the disease, during the rehabilitation stage, he will help to recover faster. In our Center, every visitor is treated with close attention and care. An individual approach and an atmosphere of trust between doctor and patient are proof of successful healing.
Craniosacral methods for relieving ICP
At first, the most superficial opinion, it seems that a session with a specialist in craniosacral therapy looks like an elementary massage of the head and face area. However, this statement is incorrect.
Real healing of pressure on the brain using a procedure can only be carried out by a modern qualified osteopath with extensive experience, who can listen to the so-called “primary rhythm” and adjust the techniques of the hands and fingers to it. In addition, the doctor must perfectly know the structure of the human brain. High efficiency and security of the session are guaranteed only if these conditions are met.
During the massage, the client is placed on a horizontal couch. Then the specialist begins to slowly press on the scalp with his fingers. With such movements, the intracranial pressure of the brain is first opened and then corrected. The doctor's movements are very light, painless, smoothing, almost imperceptible. There will be no discomfort during the session.
On the contrary, almost 100 percent of people indicate pleasant sensations: the disease goes away and fresh strength increases. The first procedure immediately entails that pain, increased pressure on the brain, and visual disturbances are relieved. The whole condition is normalized. The therapist spends about one hour, but this time is enough to achieve the identified effect in ICP and maintain it. Then you will need several sessions, because ICP requires quite a long treatment.
The above approach is absolutely effective in healing the symptoms of any disease. It is absolutely not dangerous to health and becomes the only possible option of salvation when the patient is not ready to take medication for any reason.
Diagnostic methods
A unique and most reliable way to measure the intracranial pressure on the patient’s brain in a few minutes is a puncture of the cerebrospinal fluid: a special puncture is made and a catheter is inserted into the lower back or into the brain. CSF flows out under pressure and measurements are taken. The normal value is from 60 to 200 mm of water column in a supine position.
There are also indirect studies:
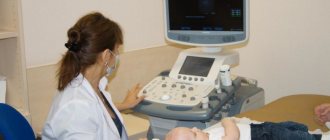
- The ultrasound radiation method is carried out exclusively for babies whose fontanel has not yet fused and the brain is visible through the sensor;
- A method of computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, where the image shows the brain in full three-dimensional layout;
- The echoencephalography method allows you to determine the coefficient of filling and beating of arteries in the brain;
- Rheoencephalogram method - examines the outflow of blood from the veins in the vessels of the brain;
- X-ray - used for a sluggish diagnosis of hydrocephalus, mostly performed in adults and children over one year of age.
Traditional treatment of pathology
It is best to treat a patient with blood pressure in a hospital setting.
At home, it should be prescribed based on the results of diagnosing hypertension. After a TBI, the patient should be given complete rest, offered light food, drink more fluids, and take anti-inflammatory drugs. In situations of hematomas and brain tumors, surgery is required.
Similar measures should be taken for hydrofecal cerebral effusion. To drain excess fluid during ICP, a catheter is installed. Liquor should be removed several times depending on the child’s growth, and the latter should be constantly monitored. Gradually, interference with blood pressure will disappear.
Treatment with medications during pathology is prescribed to make you feel better:
- hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- agents that protect neurons - affect blood flow and gas exchange in the brain;
- diuretics - for the outflow of excess contents;
- osmodiuretics - reduce the volume of cerebrospinal fluid.
However, the drugs affect the intracranial disorder signal itself, and not its cause. At the same time, an important stage of treatment is the treatment of the pathogenesis of intracranial pressure.
Features of the development of a child with increased ICP
First of all, parents need to understand that abnormalities in intracranial pressure do not cause mental retardation in the baby. The baby will develop like other children, able to develop intelligence and intelligence, have special talents, good memory, and perhaps musical or artistic abilities. In general, such children become good and excellent students, like other schoolchildren.
When helping your child reach the top, do not go too far, remember the characteristics of your beloved child:
- he needs not only to work, but also to rest a lot;
- the nervous system is easily excited;
- You don't have to be great at school to be happy.
How is ICP diagnosed in infants?
A correct diagnosis can only be made if appropriate diagnostics are carried out. While the fontanel is open in the youngest children, measurements can be easily made using an ultrasound examination - this technology is called “neurosonography”.
The ophthalmologist also makes his contribution to determining an accurate diagnosis - he always examines the condition of the fundus. The fact is that if intracranial pressure increases, the retinal veins immediately expand, which means that the optic disc becomes swollen.
If required, the pediatrician prescribes a number of additional examinations:
- tomography;
- echoencephalogram of the brain.
It is necessary to do these studies to determine the condition of the ventricles of the child’s brain. Adults who are diagnosed with increased ICP are also prescribed to undergo a spinal tap and spinal tap; in infants, such studies can cause the most unexpected consequences, so they are performed extremely rarely.