What is the clinical picture
There are no specific symptoms of narrowed blood vessels in the brain, with the exception of acutely developing pathologies, such as stroke. Chronic spasm and symptoms of contraction develop gradually. Some chronic diseases (encephalopathy) develop from 2 to 10 years. However, any pathological narrowing can be recognized in the early stages of development using the following symptoms:
- General cerebral signs: headache, dizziness, fatigue from simple work, irritability, sleep disturbance, increased sensitivity to light, sound or smell, drowsiness, lack of desire to engage in work.
- Autonomic disorders: sweating, constipation, diarrhea, paresthesia, shortness of breath, palpitations, decreased appetite, pain in the right hypochondrium, difficulty urinating, erectile dysfunction.
These symptoms are characteristic of many brain diseases and are therefore called nonspecific. If you find such signs in yourself or your loved ones, contact a neurologist and undergo brain examinations.
Folk remedies
List of common household questions:
Does coffee constrict or dilate blood vessels in the brain?
Coffee is a typical tonic drink due to the fact that it contains caffeine, a psychostimulant that increases the tone of the central nervous system. Caffeine constricts blood vessels in the brain. The drink is indicated for people suffering from hypotension. However, the reaction to coffee is individual and can be paradoxical: in some people, with small volumes of the drink, the blood vessels can dilate and even cause drowsiness.
Does alcohol dilate or constrict blood vessels in the brain?
Alcohol and elements containing it have a sedative effect on the central nervous system, dilating the blood vessels of the brain.
Does cognac constrict or dilate blood vessels in the brain?
Cognac, as a representative of strong alcoholic drinks, has an inhibitory and sedative effect on the nervous system, which causes the blood vessels in the brain to dilate. It lowers blood pressure and relaxes the arteries.
Does glycine dilate blood vessels?
Glycine is a nootropic drug. This pharmacological group affects brain cells, protecting them from damage and oxygen starvation. Nootropics improve metabolism in brain tissue. However, glycine has no effect on vascular tone and does not lower blood pressure.
What dilates blood vessels and what folk remedies can be used:
- Green tea contains catechins. This flavonoid has a mild dilatation of cerebral blood vessels. Green tea also lowers blood pressure. If you have high blood pressure, you can drink 2-3 cups of the drink per day.
- Valerian herbal decoction. How to prepare: add 10 g of plant roots to 200 ml of boiling water and leave for 2-3 hours. You should take one tablespoon 4 times a day.
- Garlic oil. How to prepare: Peel one head of garlic and crush it. Pour 100 ml of sunflower oil over fine garlic. Place the mixture in the refrigerator for a day to let it sit. The next day, add a teaspoon of fresh lemon juice to the mixture and mix. Take the resulting liquid 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
Herbs for dilating blood vessels in the brain:
- Collection of plants: chamomile, birch buds, St. John's wort, immortelle and millennial. All parts must be proportional (1 to 1). Mix the dry parts of the plants and pour 300 ml of boiling water over them. Leave for an hour. It is recommended to take in the morning and evening 30 minutes before meals.
- Hawthorn. The plant lowers blood pressure and relieves vascular spasm. How to prepare: 20-30 g of dry fruit, pour 100 ml of boiling water and cook for 5 minutes. After cooking, strain the liquid and let it cool and put it in the refrigerator. The next day, take 1 tablespoon before meals. It is recommended to drink for 3 months.
Exercises to dilate blood vessels in the brain can be performed at home. The following gymnastics are recommended to dilate blood vessels:
- Starting position – standing. Feet are shoulder-width apart. Make circular movements with your head clockwise and counterclockwise for 2-3 minutes.
- The situation is the same. Raise your arms fully and interlock your fingers, making a lock. Now do 4 forward bends and 4 backward bends.
- Starting position – lying on your back. Extend your arms to your sides. Now you need to raise your legs without bending your knees. When raising your legs at the hip joint, you must ensure that the lower limbs and torso form a right angle.
- Starting position – sitting. Place your palm on your forehead and press on it, while simultaneously exerting resistance with your neck muscles. You need to stay in this position for 10-15 seconds. This exercise warms up the neck muscles, dilates the main arteries and improves blood flow to the brain.
The healthiest foods for the human brain
The brain is one of the most complex organs of the human body. Without it, neither mental work nor normal physiology is possible. Its functioning requires a variety of amino acids, polyunsaturated fats Omega 3 and Omega 6, vitamins (especially vitamins E and C), water and many other substances and compounds.
The most beneficial foods for the brain
Sea fish and seafood are an essential component of the diet, aimed at improving the functioning of the brain and the entire nervous system. Phosphorus, iodine, minerals, Omega-3 fatty acids help the brain maintain efficiency and youth. They affect the reduction of the level of “bad” cholesterol, cleansing the walls of blood vessels from fatty plaques, and actively saturating brain cells with oxygen and nutrients.
Eggs. The yolk of an egg contains choline, which nourishes brain cells and neurons, without which they cannot form and exist. If you eat eggs regularly, it is enough to eat 1-2 eggs a day.
Milk. Milk is necessary for the brain because it contains tryptophan, a substance that is a source for the synthesis of serotonin, the hormone of joy. In addition, the antioxidant glutathione, which researchers recently discovered in milk, improves neuronal function and helps maintain sanity into old age.
Cereals. Oats, wheat, barley, brown rice and bran from them contain a lot of folic acid and thiamine, that is, vitamin B6. Thus, porridge and whole grain bread are useful not only as a means of improving metabolism, but also as an excellent stimulator of blood circulation and improvement of brain activity.
Nuts. Seeds and nuts are used both as an independent snack and as an additional ingredient in dishes. They contain everything that brain cells need: vitamins E and B; folic acid; Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids, etc., minerals, including magnesium and potassium. Nuts such as almonds, walnuts, cashews, peanuts, hazelnuts, pecans, and all types of seeds nourish the brain, provide a lot of energy, improve memory, elevate mood, and even reduce signs of depression.
Green and leafy vegetables, herbs. Greens contain so many vitamins important for mental activity that even a single loading dose can help: remember or remember a large amount of valuable information; increase the productivity of mental activity; relieve fatigue. Greens owe these results to a large amount of B vitamins and folic acid.
Berries. Vitamins, sugars, fiber, antioxidants, flavonoids from berries help with heavy mental stress, improve coordination and memory, preserve youth and increase cell performance.
Dried fruits. The rich vitamin and mineral composition makes dried fruits an essential product for those who want their head to work quickly and well. Dried apricots, raisins, prunes, figs, dates and other dried fruits and berries reduce the level of “bad” cholesterol in the blood, cleanse the blood vessels of the brain from cholesterol plaques, improve memory and concentration, and help maintain good coordination.
Honey. Honey is a recognized healer of the cardiovascular and nervous system. With constant mental work, it is definitely needed in the diet as a means of cleansing the blood and blood vessels from “bad” cholesterol and improving cerebral circulation.
Tea. Both black and green teas contain catechins. These unique substances help improve brain activity, remember information well, relax, and restore strength faster. It is better to drink tea in the morning and afternoon.
Turmeric. Turmeric is useful for the brain because it can relieve inflammation in brain tissue, restore neurons, destroy sodium benzoate, which interferes with connections between brain cells, act as an antioxidant that protects cells from aging, and give a positive mood due to the production of the hormones dopamine and serotonin.
Ginger. A spice with a pungent taste and fresh aroma is very beneficial for the heart, blood vessels and brain cells. Ginger is used as a blood thinner, improves cerebral circulation, and with regular use significantly improves memory, preventing the development of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.
Lemon. The value of lemon for the brain is associated primarily with its high content of vitamin C, potassium, magnesium and other minerals. Lemon helps cleanse blood vessels of cholesterol build-ups, prevent fatigue and relieve stress.
Plain water. The brain cannot function normally without sufficient fluid in the body. Often, a feeling of chronic fatigue and drowsiness are signs of a lack of moisture in the body. The best way to replenish fluid reserves and thereby protect the brain from dehydration is to drink regular drinking water: it is best absorbed without carrying additional calories, such as fruit juice.
Nutrition
Products that dilate blood vessels:
- Garlic. It contains essential oils and allicin. These biologically active substances relieve arterial spasm and strengthen the walls of blood vessels. In addition, allicin prevents the formation of cholesterol plaques.
- Ginger. It also contains allicin, only in smaller quantities. In addition to dilating blood vessels, ginger enhances immune defense and has a detoxifying function.
- Lemon. The citrus plant has a weak effect on vascular tone, but in combination with the vitamins it contains, lemon strengthens the wall and reduces the risk of developing atheromatous plaques.
- Honey. The product does not have a direct effect on tone, but thanks to trace elements and compounds, honey normalizes the rheological properties of the blood.
- Kalina. The fruits of the plant should be consumed fresh for expansion. Viburnum lowers blood pressure. Please remember the limit: 50 g of product. So, if you consume more, viburnum, on the contrary, increases blood pressure and heart rate per minute.
- Green tea. Expands the lumen of arteries. For best results, drink with lemon. It's better to drink in the morning.
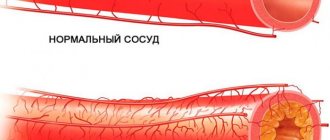
Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels (cerebral atherosclerosis) - symptoms and treatment
Treatment of cerebral atherosclerosis consists of influencing three groups of factors:
- Local factors, which include narrowing of the arteries of the brain by atherosclerotic plaques.
- Systemic factors, such as sudden changes in systemic blood pressure.
- Provoking factors, such as traumatic situations and infections [9].
Treatment of arterial hypertension
Features of the treatment of hypertension in patients with cerebral atherosclerosis:
- it is necessary to control even a slight increase in blood pressure (BP) and strive to reduce it in the morning - the pressure rises an hour before waking up and remains elevated for 4-5 hours after it;
- treatment should be ongoing, and not just when your health worsens;
- avoid sudden changes in pressure; for this it is better to use long-acting antihypertensive drugs with a 24-hour effect and, if necessary, combine drugs from different groups;
- fight hypertensive crises - find out the cause, select drugs for prevention, adequately eliminate crises, avoiding a sharp and excessive decrease in pressure.
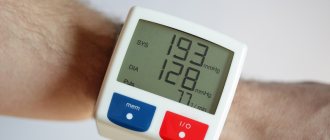
When taking antihypertensive drugs, you need to regularly monitor changes in blood pressure. It is measured after waking up, before going to bed and during the day if symptoms of the disease appear. It is recommended to record the measurement results in a diary.
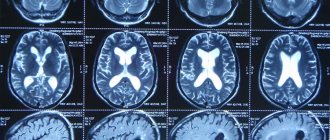
When monitoring blood pressure, it is important to consider how much blood is supplied to the brain. Signs of poor blood supply include a history of strokes and transient ischemic attacks, narrowing of the brachiocephalic arteries and the presence of foci of leukoaraiosis (damage to the deep white matter) on MRI, cognitive impairment, left ventricular hypertrophy and coronary heart disease. In order not to aggravate chronic cerebral ischemia and to avoid circulatory disorders, the pressure in such patients is reduced gradually, which may take from a month to six months.
The target level of systolic blood pressure differs for different groups of patients:
- in young and middle-aged people without severe atherosclerosis, it is 130–140 mm Hg. Art.;
- in elderly and senile patients with transient ischemic attacks or a history of stroke - 140–150 mm Hg. Art.;
- in patients with third-degree hypertension with severe atherosclerosis - 150–160 mm Hg. Art.
Systolic blood pressure measures the pressure on the walls of blood vessels at the moment when the heart contracts and pushes out blood. On the tonometer this is the first or top number.
Basic therapy for lowering blood pressure includes the following groups of drugs:
- angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) - Ramipril, Lisinopril, Perindopril, etc.;
- sartans - Telmisartan, Candesartan, etc.;
- beta blockers - Bisoprolol, Metoprolol, Nebivolol;
- calcium antagonists - Amlodipine, Lercanidipine;
- diuretics - Chlorthalidone, Indapamide, thiazides.
Regulation of lipid metabolism
In the initial stages of atherosclerosis, cholesterol is reduced through diet.
You should eat less:
- easily digestible carbohydrates - sugar, sweets, jam, white bread, cakes, etc.;
- animal fats - butter and fatty meats;
- table salt - less than 5 g per day, preferably 2-3 g;
- pickles and smoked meats;
- fried foods.
It is recommended to include in the diet:
- fresh vegetables and fruits (for example, kiwi [15]);
- dairy products;
- barley, soybeans and almonds;
- wholemeal bread;
- vegetable or olive oil.
If atherosclerosis progresses, statins are prescribed - drugs that lower cholesterol levels (Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin, Simvastatin). The doctor selects their dosages individually. At the same time, it is important not only to monitor cholesterol levels, but also to monitor liver function, i.e., evaluate the effectiveness and safety of the drug at the prescribed dose.
Target LDL levels:
- with extreme cardiovascular risk - up to 1.0 mmol/l;
- with high and very high cardiovascular risk - up to 1.8 and 1.4 mmol/l;
- with moderate risk and low cardiovascular risk - up to 2.6 and 3.0 mmol/l [6].
Cardiovascular risk increases with diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, and heart and vascular diseases. The risk level is considered extreme if cardiovascular diseases have already developed against the background of atherosclerosis, the patient takes statins at the maximum tolerated dose, but despite this, he suffered two severe attacks (for example, a stroke) over the past two years.
Taking statins allows you to strengthen the plaque cover, reduce the likelihood of its rupture, thrombosis and complete blockage of the vessel. A beneficial effect is often observed already in the first weeks of treatment. During this period, it is associated with improved blood flow, normalization of the blood coagulation system and the production of nitric oxide, which has a beneficial effect on the vascular wall.
When triglycerides (TG) increase, fibrates are prescribed: Clofibrate, Bezafibrate, Fenofibrate. They can be used either together with statins or separately. They are often used for diabetes mellitus, in which TGs are often elevated. For high TG levels in combination with gout, Fenofibrate is preferable - it reduces the content of uric acid, which damages the vascular wall.
To enhance the effect of statins, as well as in case of intolerance to them, the drug Ezetimibe is used, which suppresses the absorption of cholesterol in the intestine. You can also effectively and safely reduce cholesterol levels with the help of monoclonal antibodies - inhibitors of the PCSK9 enzyme (Evolocumab, Alirocumab).
Antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapy
To prevent the formation of blood clots and blockage of blood vessels, antiplatelet agents are prescribed: Aspirin, Clopidogrel, Prasugrel, Ticagrelor, Dipyridamole. They are especially recommended for women over 55–65 years of age who suffer from hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, as well as patients with carotid artery stenosis. These drugs are taken for life.
In case of cerebral atherosclerosis in combination with atrial fibrillation, it is recommended to take anticoagulants for the prevention of thrombosis and ischemic strokes: Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban, Apixaban. These drugs thin the blood more than antiplatelet agents. They are also accepted for life.
For the prevention of stroke, myocardial infarction and acute limb ischemia with coronary artery disease or lesions of peripheral arteries, Rivaroxaban is used in a reduced dosage in combination with Aspirin.
Symptomatic therapy
Symptomatic therapy slows down the development of cognitive disorders and dementia, reduces the severity of existing disorders, which improves the quality of life of patients and their relatives.
For the treatment of cerebrovascular insufficiency the following are used:
- Vasoactive drugs - Cavinton, Vasobral, Bilobil, Tanakan, Sermion. They improve microcirculation and are taken in courses 1–2 times a year.
- Cortexin, Cerebrolysin - have a positive effect on metabolic processes and the plasticity of brain cells. Plasticity allows neurons to recover and create new synaptic connections. The medications are taken in a course of 1–2 months.
- Drugs with neurometabolic effects - Citicoline, Ginkgo biloba, Piracetam, Pantogam active. They increase the brain’s resistance to hypoxia and the effects of toxic substances, and help nerve cells recover. They are taken for 1–2 months.
- Antioxidants - Cytoflavin, coenzyme Q, L-carnitine (succinic acid derivatives). They improve the transmission of nerve impulses, the plasticity of neuronal membranes, the functioning of receptors, blood flow in the vessels of the brain and metabolic processes. They are also taken for 1–2 months.
In addition to drug treatment, patients will benefit from physical activity. Walking and moderate exercise have a beneficial effect on the entire body, including the cognitive sphere. It is also important for patients to adhere to a diet: eat less fat, easily digestible carbohydrates, salt, and more foods containing antioxidants.
Medication
Medications for dilating cerebral blood vessels are divided into the following pharmacological groups:
- Drugs that act directly on vascular smooth muscle. They relax the walls of blood vessels, reduce the peripheral resistance of arteries and veins, regulate tone and lower blood pressure. Drugs: Dibazol, Apressin, Sodium nitroprusside.
- Calcium channel blocking drugs. These drugs block channels that allow calcium to pass through and trigger excitation. These tablets prevent calcium from entering the membrane and developing an action potential. Drugs: Verapamil, Nifedipine.
- Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. These drugs prevent the passive form of angiotensin I from turning into the active form, angiotensin II. Medicines: Captopril, Enalapril.
- Angiotensin II receptor antagonists. They block the receptors that perceive angiotensin II. Representatives: Losartan.
- Potassium channel activating drugs. The drugs widen the channels so that as much potassium as possible enters the cell, as a result of which the excitability of the cell membrane decreases and the cell’s action potential is blocked. Representatives: Lonitel, Hyperstat.