When the fetus's heart begins to beat
For the full development of the fetus, an autonomous circulatory system is necessary. Therefore, the cardiovascular system is one of the first to be laid down and formed. And at the very first ultrasound when confirming pregnancy, you can already hear the first beats of your baby’s heart. This will happen on the 22nd day. And in just 5 weeks the formation of the most important system of the body will be completed.
In the first trimester, the frequency of strokes can only be calculated using ultrasound, in the second - EchoCG, in the third - auscultation, and starting from the 32nd week, CTG is done. During each period of pregnancy, heart rate norms are different.
Pregnancy in an unknown place
Pregnancy in an unknown location is a term used to describe a transient condition of early pregnancy during which ultrasound does not reveal MB and the adnexa are normal—in other words, “normal” pelvic ultrasound findings. At this stage, the three main possibilities include early MB, occult ectopic pregnancy, and complete spontaneous abortion. Unfortunately, serum beta-hCG levels alone do not reliably differentiate between these possibilities.
.
In the case of a positive pregnancy test with low beta-hCG levels, it may be too early to visualize the site of blastocyst implantation. Despite a number of studies reporting a discriminatory beta-hCG level (the value above which an intrauterine ulcer is consistently visualized in normal pregnancies on ultrasound) of 1000–2000 mIU/ml (1000–2000 IU/L), the validity of the discriminatory level in exclusion of a viable pregnancy is less than initially reported. For example, studies have reported cases of fetuses with cardiac activity on follow-up ultrasound after an initial ultrasound that did not detect PU with beta-hCG levels greater than 2000–3000 mIU/mL (2000–3000 IU/L). In addition, multiple pregnancies result in higher beta-hCG levels at any gestational age compared with those in singleton pregnancies. Although the chance of an ectopic pregnancy increases significantly with an empty uterus and higher beta-hCG levels, especially if the level is above 3000 mIU/ml (3000 IU/L), the chance of a viable ectopic pregnancy is still 0.5%.
Thus, in a patient who is hemodynamically stable and has a pregnancy in an unknown location, it is less risky to wait, monitor beta-hCG levels, and ultrasound than to presumptively treat an ectopic pregnancy.
By explaining the limitations of this technology, healthcare providers can help patients appreciate the uncertainty of the diagnosis and the need for appropriate follow-up. As Doubilet and Benson (2010) so eloquently state: “Above all, do no harm.”(*I think this principle can be safely dated earlier than 2010 - primum non nocere - as it refers to the so-called oath Hippocrates).
How the heart develops
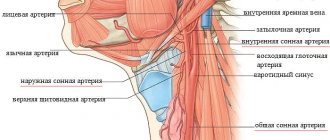
The rudiment of the organ is formed in the 4th week, and by the 5th week pulsating contractions first appear and autonomous blood circulation appears. While the blood circulates in one stream, representing one tube, in the bend of which there is a small motor - the fetal heart. By the ninth week of pregnancy, the small heart becomes four-chambered. It differs from the organ of an adult, but is still fully formed. These weeks are the most important stage when any disruptions in the formation of an organ lead to congenital defects.
Terminology
Accurate interpretation of ultrasound findings in the first trimester requires the use of appropriate and consistent terminology, as outlined in Doubilet et al. (2013). The criteria for viable and non-viable MBs are simple. However, MB of unknown viability is a broad category and can lead to confusion. To be precise, MB of unknown viability can apply to normal pre-embryo development situations with cardiac activity, including empty PU (PM with a yolk sac but no embryo), and PU with a yolk sac and an embryo smaller than 4 mm but without cardiac activity. activities. The second category of unknown viability is used when there is evidence of miscarriage (signs of poor prognosis). The authors of the publication found that using the term MB of unknown viability is more appropriate in this case because it conveys a sense of alertness. Alternatively, for small uterine ulcers, it is preferable to use the term “early intrauterine uterine ulcer at __ gestational age” instead of urinary tract of unknown viability, with a recommendation for follow-up ultrasound to confirm normal pregnancy development.
Pregnancy in an unknown location has several scenarios, and the authors encountered these scenarios while applying this terminology to their patient population. If the results of pelvic ultrasound are almost normal, a differential diagnosis of “very early MB”, “non-visualized ectopic pregnancy” or “complete spontaneous abortion” is provided. When vaginal bleeding and thickening of the heterogeneous endometrium occur, the authors used the term “pregnancy in an unknown location, the most likely scenario is spontaneous termination of pregnancy.” Detection of an area of low-resistance arterial trophoblastic flow may be useful to confirm the site of intrauterine implantation in these situations. However, spectral Doppler ultrasound should not be used in the first trimester if normal viable MB is likely (*And I keep hearing that these recommendations are often ignored...). The third scenario is vague intrauterine fluid accumulation. While intrauterine PO and early MB may be most likely, the differential diagnosis also includes a decidual cyst and localized intrauterine fluid. Thus, in these situations, it is recommended to monitor beta-hCG levels and control endovaginal (*transvaginal) ultrasound after 7-10 days.
How to listen to the fetal heart
You can hear the baby’s heartbeat on your own or during a visit to the gynecologist. You can do this at home no earlier than the 2nd trimester, with a doctor - earlier. An experienced gynecologist will use the device to help you find out the sex of the baby by heartbeat. Let's consider both approaches.
Home listening methods
- Stethoscope. It can be used at 18 - 20 weeks, when the heart works quite strongly and clearly. Place the device on your stomach and listen. If you don't hear any knocking sounds, don't worry - move the stethoscope over your stomach. You can buy the device at a medical equipment store or pharmacy.
- Heart monitor. If you are worried about your child's development, purchase this device. It is relatively cheap, but will save you from unnecessary worries between consultations with a gynecologist. At any moment you can listen to the baby's heartbeat and calm down. But it is advisable to buy it only from the fifth month of pregnancy - before that, a portable cardiac monitor for home use simply will not hear heart rhythms.
- Mobile app. This method is suitable for later dates. Various applications have been developed: some are paid and some are freely available. Some even allow you to record the sound of your heart beating so you can play it back for family or friends. To listen to your heart rhythm, you just need to place the smartphone microphone on your stomach.
When choosing devices for home use, ask your doctor which model he or she recommends. The result of “listening” depends on the quality of the device, so choose devices from trusted manufacturers.
Medical methods for measuring heart rate
- Fetal Doppler. This method is used at the 12th week of pregnancy, although it can also be heard at the 9th - 10th week. Using sound waves, the device amplifies the sounds of your heartbeat. The procedure is simple: a woman lies down on a couch, the doctor runs a sensor over her stomach, and the beating of a nascent heart can be heard in the office.
- Ultrasound. Ultrasound is performed at the very beginning of pregnancy. Already at the 8th week, during the examination, you can hear how the baby’s heart works. Please note that the study is prescribed so early if there are risks or it is necessary to exclude an ectopic pregnancy.
- Stethoscope and fetoscope. These devices are not as powerful as ultrasound or Doppler. Therefore, they are used from the second trimester. Tones are assessed - clear or dull. In the first case, everything is fine with the fetus, in the second, developmental delay or hypoxia is possible.
- CTG. Cardiotocography is used to listen to the heart from the 30th week.
Modern medicine has reliable methods for assessing a baby’s heart rate and timely detecting developmental problems.
Why listen to the fetal heartbeat?
- To confirm the fact of pregnancy. When first contacting a doctor about a possible pregnancy, a woman is sent for an ultrasound. Usually at this stage you can already hear the heart of the unborn baby beating. If it is absent while there is a fertilized egg in the uterus, this is not a reason to worry. As a rule, a heartbeat can be heard after a week. But if it never appears, and the egg is deformed, this is a sign of a frozen pregnancy, which means its termination is required.
- To assess the general condition of the unborn child. Diseases, physical or emotional stress of the mother, the oxygen content in the air that the woman breathes at the moment, the activity or resting phase of the fetus - all this affects the heartbeat, and its changes are short-term. A high fetal heart rate that persists for a long time is a sign of chronic placental insufficiency, that is, a violation of the blood supply to the fetus. A drop in heart rate below normal also indicates a deterioration in the condition of the unborn child. Treatment will depend on the stage of pregnancy. In some cases, emergency delivery is necessary.
- To monitor the condition of the child and record parameters during childbirth. Monitoring is necessary due to the fact that the baby goes through serious trials during birth (compression, lack of oxygen). Most often, the heart and blood vessels cope with the load, but sometimes situations arise that require urgent medical attention (placental abruption, the umbilical cord is pinched). In order not to miss signs of acute fetal hypoxia, the heartbeat is measured during all contractions.
Is it possible to determine the sex of a child by heartbeat?
It is impossible to give a definite answer to this question. Some obstetricians deny the reliability of the method, others use it in practice.
Previously, when there were no ultrasound and other hardware research methods, obstetricians determined the sex of the unborn child by heartbeat. And this method was considered reliable. And now you can find doctors who accurately determine gender using this method.
Of course, hardware methods are more reliable. Therefore, the reliability of the method of determining sex by heart rate can be estimated at 50%.
Truth or Myth
American scientists have found that calculating gender based on heartbeat has a right to exist. The Americans received the following indicators: a boy was identified in 90% of cases, a girl in 70%.
However, studies conducted after this refuted the fact of the relationship between gender and heart rate (HR). Medical professionals consider this test to be uninformative, although the percentage of matches is quite high.
- Gender of baby based on heartbeat at 12 weeks. Determining sex by fetal heartbeat
In any case, checking the result obtained using this method with reality is easy and absolutely harmless. Following the reviews of many women, the information received quite often coincides with reality. Below watch a video on the interesting topic of myths.
How to find out a child's heartbeat from a gynecologist
The doctor uses a stethoscope device. It allows you to listen to the first heartbeats at 18 - 20 weeks of pregnancy. A stethoscope is placed on a woman's stomach.
The work of the heart is heard as double beats. The obstetrician evaluates it according to the following characteristics:
- beats per minute;
- key;
- rhythm;
- point of best audibility.
Based on these characteristics, the doctor first of all evaluates the condition and development of the organ. But he can also guess the sex of the unborn child, since the heart of children of different sexes works differently.
Changes in fetal activity
Changes in fetal activity may be associated with external influences. For example, if a pregnant woman lies on her back for a long time, then the enlarged uterus compresses a large vessel - the inferior vena cava, and the flow of blood to the fetus is disrupted, which immediately causes its violent reaction - active movements. The same changes in the baby's activity can occur in any other uncomfortable position of the mother - if she leans forward, squeezing her stomach, or sits with her legs crossed, the child, with her activity, forces the mother to change her position. A similar situation arises if the baby himself squeezes or presses the loops of the umbilical cord, limiting the flow of blood through it. He begins to move more actively, changes his position and relieves pressure on the umbilical cord. However, in some cases, an increase or, conversely, a decrease in fetal movements can be a sign of a serious pathology.
If after 28 weeks of pregnancy the baby does not make itself known for 3-4 hours, perhaps he is just sleeping. In this case, the expectant mother needs to eat something sweet and lie on her left side for half an hour. If these simple manipulations do not lead to results, you should repeat them again after 2-3 hours. If this time the baby does not make itself known, this is a reason to consult a doctor. Rare and weak movements may also indicate unwellness of the fetus, most often a lack of oxygen for the baby, that is, fetal hypoxia.
How to determine the sex of a child by heartbeat
Obstetricians who practice this method of determining gender use several methods.
By beat frequency
It is generally accepted that a female fetus's heart beats faster than a male fetus's. If the heart beats up to 140 times, there is a high probability of having a son, and more often a daughter. This method is used during pregnancy until the end of the second half.
By rhythm
Boys are in the lead on this basis - their heart beats more clearly and rhythmically. Moreover, it works in unison with the mother’s pulse. But in girls, the heart does not work so orderly: it can slow down, speed up, and does not work so clearly.
By sounds
The sound of the heart depends on the position of the baby. If the sound is better heard on the left, expect a son, and if on the right, wait for a daughter.
By tone
Babies have muted tones, boys have clear tones. Only obstetricians with extensive experience can determine the sex of a child by the heartbeat - namely, the tone - with great reliability.
On the possibility of influencing the gender of the unborn child
I always explain to my patients and their relatives that they cannot in any way influence the gender of the unborn baby. It is widely known that the sex of a child is determined at the moment of conception. However, at the very beginning of development, girls and boys look the same, despite the fact that some have XX chromosomes and others XY. Sex differences begin to form only from the tenth week of pregnancy.
Although we have already established that the fetal heart rate is not a reliable indicator of determining the sex of the child, there are methods that can accurately tell whether you are expecting a boy or a girl.
Heart rate norms by week
Various factors influence the functioning of the heart - the phase of fetal activity and the duration of pregnancy, for example. Using the heart rate, the gynecologist evaluates the development of the organ and the overall health of the fetus.
Here are the fetal heart rate norms by week of pregnancy:
- from the 4th to the 6th week - from 80 to 85 beats per minute;
- in the 6th week - from 100 to 135;
- in the 7th week - from 115 to 130;
- in the 8th week - up to 170;
- from 9th to 10th - from 170 to 190;
- from the 11th to the birth - an average of 150 beats with a possible slight fluctuation in one direction or another (from 140 to 160 beats is the norm).
From the 2nd trimester, the pulse stabilizes and ranges from 140 to 160 beats. Any deviations from this indicator indicate a problem: if the pulse is rapid, the fetus experiences oxygen starvation, and if it is slow, it suffers from hypoxia.
In this case, the gynecologist refers the patient for additional examinations and, if necessary, corrects the condition.
At what time does fetal movement begin?
The future baby begins to make its first movements early - already at 7-8 weeks of pregnancy . It is at this time that the first muscles and rudiments of the nervous system of the fetus are formed. Naturally, at this time the movements of the embryo are still very primitive - these are muscle contractions in response to nerve impulses.
about 10 weeks of pregnancy, the fetus begins to move more actively in the uterus, and, encountering an obstacle on its way (the walls of the uterus), change the trajectory of movements. However, the baby is still very small and the impacts on the wall of the uterus are very weak; the expectant mother cannot yet feel them. At 11-12 weeks of intrauterine life, the little man already knows how to clench his fists, grimace, wince; by 16 weeks of pregnancy he begins to react to loud, sharp sounds with increased motor activity, at 17 weeks the first facial expressions appear, and at 18 weeks he covers his face with his hands and plays. with the umbilical cord, squeezes and unclenches the fingers.
Gradually, with increasing gestational age, movements become more coordinated and more like conscious ones. As the baby grows up, the pregnant woman begins to feel his movements.
When does fetal movement begin during the first and subsequent pregnancies?
It is generally accepted that during the first pregnancy, the expectant mother feels the first movements of the fetus at 20 weeks of pregnancy, and for repeated pregnancies - at 18 weeks. This is not entirely true. A mother who is expecting her first child, indeed, most often begins to feel fetal movements a little later than a multiparous woman. This is due to the fact that “experienced” mothers know how the baby’s movements feel at first and what they should feel. Some primigravidas perceive the first movements of the fetus as increased intestinal motility, “gas”. Many women describe the first movements of the fetus as a feeling of fluid transfusion in the stomach, “butterflies fluttering” or “fish swimming”.
The first movements are usually rare and irregular. The time of the first sensations of fetal movements naturally depends on the individual sensitivity of the woman. Some expectant mothers feel the first movements already at 15-16 weeks, and some only after 20. Slender women, as a rule, begin to feel movements earlier than plump ones. Women who lead an active lifestyle and work a lot usually feel fetal movements later.
By 20 weeks, due to the formation of the spinal cord and brain, as well as the accumulation of a certain amount of muscle mass in the fetus, movements become more regular and noticeable.
From 24 weeks of pregnancy, the movements of the fetus already resemble the movements of a newborn - the expectant mother feels how the fetus changes position, moves its arms and legs. The motor activity of the fetus increases gradually and its peak occurs in the period from the 24th to the 32nd week of pregnancy. At this time, the activity of the baby’s movements becomes one of the indicators of his normal development. After 24 weeks, the baby begins to “communicate” with his mother through movements, respond to the sounds of voices, music, and the mother’s emotional state. As the gestation period increases beyond 32 weeks, the motor activity of the fetus gradually decreases due to the fact that the baby grows up and simply does not have enough space for active movements. This becomes especially noticeable at the time of childbirth. By the end of the third trimester of pregnancy, the number of fetal movements may decrease slightly, but their intensity and strength remain the same or increase.
Reliability of the measurement method
The method is time-tested. But still, some gynecologists criticize the tactic of determining the sex of a child by heartbeat. From the point of view of modern obstetrics and gynecology, the functioning of the cardiovascular system depends on many factors. And they affect the reliability of the results. These are the factors:
- Term. In different trimesters, the heart works with different frequencies, rhythms and tonality. This is due to the formation of the autonomic nervous system. For example, after conception and until the 2nd trimester, the heart beats evenly and rhythmically, regardless of gender. Then the heart rate changes: in boys it increases to 150, in girls up to 140 beats;
- Activity phase. If the baby is awake, the heart works faster, if he sleeps, it is calmer and slower;
- Mom's condition. If a woman is worried or under stress, the baby’s heart can work faster, and vice versa. The woman’s physical condition and her posture while listening to the fetal heart rate are affected.
The frequency and rhythm of heart contractions are influenced by the location of the fetus, the peculiarities of the development of the cardiovascular system, and the tone of the uterus. Many modern gynecologists believe that it is impossible to take into account all these factors when determining the sex of a child by heartbeat.
The method of determining the sex of a child by heartbeat is also criticized by parents for whom it did not work.
Amniocentesis and chorionic villus biopsy
These methods are also used primarily to diagnose diseases, but in the process of performing them you can find out the sex of the child. During amniocentesis, a puncture of the uterus is performed to remove a small amount of amniotic fluid for analysis. This fluid contains cells that are studied for genetic abnormalities. Despite the fairly high safety of the procedure, based on data from international obstetric organizations, in my practice I never perform amniocentesis in the absence of direct indications, since there is always a risk of bleeding or infection. This procedure is most often performed after the fifteenth week.
Chorionic villus biopsy is also an invasive procedure, meaning it requires a puncture. During this test, a small amount of placental tissue is removed. It can be performed earlier than amniocentesis, from the eleventh to the fourteenth week. We only perform this procedure on women with a high risk of genetic abnormalities.
Who will be born: modern ways to find out
There are 2 reliable ways to find out who will be born in a family.
The first is ultrasound. Already at the second screening, that is, from the 12th week, you can get an answer. But errors are also possible - the method guarantees the correct result in 97% of cases.
The second method is amniocentesis. This invasive technique is carried out according to strict indications and not to find out who will be born to a couple, but to diagnose certain diseases in the baby. And sex determination is only an additional option of amniocentesis. But this is currently the only method that gives a 100% correct result.
Cell-free DNA
In recent years this method has become widely used. Despite the presence of a barrier in the form of the placenta, little fetal genetic material or DNA enters the mother's blood. This analysis can be carried out early, starting from the ninth week. The main goal of this study is to identify hereditary anomalies and in the process of performing it, based on the set of chromosomes, it usually becomes clear what sex the fetus is. I cannot recommend this method for routine determination of the sex of the fetus due to its complexity, high cost and high percentage of false results. This test is most often performed on women who are at increased risk for genetic diseases (such as Down syndrome).
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
The main medical indications for DNA testing are:
- the risk of developing hereditary diseases associated with the X chromosome - hemophilia, Klinefelter syndrome;
- identifying likely genetic conditions.
Even if there are no medical indications, such an analysis can be done at the personal request of the parents. The procedure is painless and absolutely safe for mother and baby. DNA testing will show an accurate result and will allow you to avoid such serious and dangerous manipulations as amniotic fluid sampling or chorionic tissue analysis.