The use of magnetic resonance imaging in medical practice has expanded diagnostic capabilities. The method allows you to study in detail the soft tissue structures of the body. MRI of the heart provides layer-by-layer images that evaluate the condition of all anatomical elements of the object in question. Using tomography, it is possible to detect changes in the myocardium in the early stages of development, when treatment is most effective. Contrast enhancement with gadolinium-based drugs is relevant when studying the functional parameters of an organ, in the diagnosis of inflammatory, oncological and vascular pathologies.
A specialist examines MRI images of the heart
Anatomy of the heart
Acting as a pump, the organ ensures continuity of blood circulation and oxygen supply to tissues. The heart is located in the chest, between the spine, diaphragm and lungs, slightly shifted to the left relative to the central axis of the body. The walls consist of three layers (endocardium, myocardium, epicardium). On the outside is a serous membrane called the pericardium.
The structure of the muscle tissue of the heart contains atypical cells that produce electrical impulses. The conduction system distributes the latter, maintaining rhythmic contractions of the organ.
Schematic representation of the structure of the human heart
There are four cavities in the structure of the heart. On the left and right are the atria and ventricles of the same name. One half of the organ receives venous blood, the other - arterial.
The central solid septum provides isolation of the heart chambers. This is necessary to prevent mixing of venous and arterial blood. The atria are connected to the ventricles. The mitral (left) and tricuspid (right) valves work synchronously, ensuring unidirectional movement of blood from the lower cavities to the upper ones.
The structure of the heart contains coronary vessels - the aorta, pulmonary trunk and arteries, inferior and superior vena cava. The direction of blood flow (the organ pumps 7-10 thousand liters per day) is provided by semilunar valves.
Unusual Facts About the Heart
- The heart rate in a fetus is several times higher than in an adult, and is approximately 140 beats/min, while after 10 weeks the volume of circulating blood is equal to 60 l/day.
- In an adult, the heart rate is approximately 72 times/day, so over the course of approximately 65 years, more than 2 million heartbeats are detected.
- The total length of all blood vessels is more than 120 million meters, which allows you to circle the Earth three times along the equator.
- Blood vessels also pass through adipose tissue, and with obesity, the heart has to pump blood through vessels more than 8 thousand kilometers long.
- One cycle of blood supply lasts approximately 23 seconds and is approximately the same time it takes a person to run 200 meters.
- In one cubic milliliter of blood, there are about 5.5 million red blood cells, which are also called red blood cells. It takes 120 days to fully update them.
- Heart disease is the most common cause of human death. It has been proven that cardiovascular diseases have claimed more lives than all the wars in the entire history of mankind.
Video 10 unknown facts about the human heart. I Vam Science
4.80 avg. rating ( 94 % score) – 5 votes – ratings
What diseases does cardiac MRI show?
During magnetic resonance imaging, up to 1500 images are obtained. The width of the cuts starts from 1 mm. The scans assess the size, shape and condition of all structures of the heart. Changes in the intensity of the MR signal reveal characteristic signs of pathology. Functional tests provide information about the nuances of blood circulation and contractility of the organ.
What does an MRI of the heart show? From the scans you can determine:
- congenital defects (atrial septal defect, etc.);
- aortic diseases (aneurysms, stenosis, coarctation, thrombosis);
- cardiomyopathy of ischemic and other nature;
- inflammation of the heart muscle and serous membrane;
- myocardial infarction;
- tumors, etc.
The study is prescribed to collect additional information about the organ, for the purpose of diagnosing pathologies, to monitor changes during the progression of chronic diseases. Based on the results of cardiac MRI, the timing and specifics of surgical interventions are planned, and the effectiveness of therapy is assessed. The procedure has prognostic value after myocardial infarction, as it provides information about tissue viability, scar localization and the impact of the latter on the functioning of the organ.
MRI image of the heart
Diseases
Cardiovascular diseases are the most common cause of death in the world. Of these, more than three-quarters are the result of coronary artery disease and stroke. Risk factors include:
- smoking;
- overweight, sedentary lifestyle;
- high cholesterol;
- high blood pressure and others.
Cardiovascular disease often has no symptoms but can cause chest pain and difficulty breathing.
Preparing for cardiac MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging does not require special organizational measures on the eve of scanning. Before a cardiac MRI, there is no need to follow a diet, stop or take any medications.
Women of reproductive age should make sure that there is no pregnancy (the procedure is contraindicated in the early stages). The best option is to take a blood test for hCG or undergo a urine test. After week 13, native (without contrast enhancement) cardiac tomography can be performed.
Persons with metal implants (endoprosthesis, vascular clips, pins, etc.) will need to obtain a document on the compatibility of the product with a magnetic field. A passport or an extract from the medical institution where the structure was installed will do. After vascular stenting, MRI can be performed no earlier than six months later. The time of the operation must be confirmed with the appropriate certificate. The presence of a pacemaker, defibrillator or other electronic device is an absolute contraindication to MR scanning of any anatomical area. Devices may stop working under the influence of the magnetic field of the tomograph.
It’s worth organizing a light snack 40-45 minutes before leaving the house. Yogurt, a small sandwich or fruit, or an egg will do. This measure will allow you to avoid the manifestation of vegetative reactions (nausea, vomiting, dizziness, etc.) to the drug.
Women supporting lactation can undergo MRI. But you need to purchase formula for the baby in advance or stock up on expressed breast milk for 2-3 times. Natural feeding can be resumed 6-12 hours after contrast administration.
Children undergo MRI if they remain motionless during the scan. If the child is not able to lie for 20-30 minutes in one position, tomography is performed under anesthesia in a hospital setting or an alternative method is found.
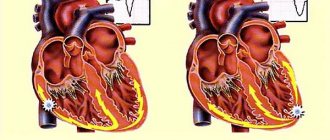
Human cardiac cycle
Human cardiac cycle
In a state of physical and psycho-emotional calm, the heart contracts in the range of 70-80 cycles per minute . One cycle occurs in 0.8 seconds, of which:
- It takes 0.1 seconds for the atria to contract
- 0.3 fractions of a second are spent on the ventricles
- 0.4 remains for the relaxation period
The frequency of the cycle is determined by the heart rhythm: the area of the heart muscle where impulses occur that control the frequency of contractions.
The work of the heart goes through two main phases:
- Ventricular contraction or systole . Venous blood pushes through the pulmonary artery into the vessels of the lungs. There it is saturated with oxygen and then, enriched, it is collected in the left atrium.
- Pause or diastole . The period of relaxation of the heart muscle. At this time, the pockets of the left atrium are filled with blood, then it passes into the left ventricle and, pushed through the valve, goes to the aorta, scattering throughout the body. The blood continues its movement, collecting in the right atrium and then flowing into the right ventricle.
Rhythmic, stable alternation of the phases of calm and contraction is ensured by the appearance and conduction of an electrical nerve impulse through a special system of conducting cells. The impulse originates in the superior sinus node, located in the right atrium. Next, it enters the atrioventricular node and passes along the fibers to the muscles of both ventricles, causing them to contract.
How is a cardiac MRI done?
MRI scan at heart level
The procedure is carried out by prior appointment. You will need to fill out forms at the clinic. You should bring with you an identification card, a doctor's prescription (if you have one) and other medical documentation that may be useful for analyzing the results (previous images, ultrasound, etc.).
The scanning procedure takes place in 3 stages:
- 1. Preparatory. In the locker room, you need to remove jewelry, accessories (hairpins, belt, glasses), clothes with metal fittings, and leave electronic devices and gadgets (they may break down). In the diagnostic room, you should lie down on the tomograph platform. For safety purposes, the patient's body is secured with soft straps. It is important to immediately take a comfortable position, since you cannot move during the scanning process. When planning contrast contrast, a catheter is installed in a vein and the device is connected to an injection syringe for automatic drug delivery.
- 2. Active stage. The radiologist goes into a nearby office, where he monitors the procedure and operates the equipment. You can communicate with a specialist at any time via a two-way communication system. After the command not to move, you need to relax, breathe freely, and remain calm. If necessary, the doctor will ask you to hold your breath for a few seconds. A heart scan in native mode lasts about 20 minutes.
- 3. Contrasting. They are not always performed, but only when indicated. On command, an amplifier is injected into the patient’s bloodstream using a syringe-injector, then a second scan is performed. How exactly it is necessary to do an MRI of the heart (with or without contrast) is usually indicated by a cardiologist. If a serious pathology is suspected, a radiologist may recommend enhancement.
Upon completion of the study, dress and take away personal belongings. You can wait for the results at the clinic or, if you go on personal business, return to the center later. Preparing a report takes from 15 minutes to several hours. In complex cases, decoding images takes longer. If necessary, the results are sent by e-mail (the address should be indicated when filling out the forms).
MRI of the heart shows enlarged chambers and inflammatory fibrotic changes in the septum
Position of the human heart: types, size
Position of the human heart
The size or size of the heart, its position in the human sternum depends on many factors:
- Floor
- Age
- Physiological indications
- Hereditary predisposition
Based on the location of the organ in the human body, there are three types:
- Oblique position . The most common type. The angle of inclination of the placement relative to the cardiac axis is about 45° .
- Horizontal . The silhouette of the heart on x-ray shows a nearly recumbent position. The angle of inclination relative to the axis shows from 35° .
- Vertical arrangement . The silhouette of the heart shows an almost standing position. Tilt angle from 50° to 56°.
Representatives of the brachymorphic type of body structure, with a wide chest and a high position of the diaphragm, have a horizontal heart. People of the dolichomorphic type with a long, narrow chest often have a vertical arrangement of the organ. Consequently, even focusing on the body shape and appearance of the chest, we can talk about the position of the heart organ. A person's gender also affects the position and size of the heart. In women, the heart is more often located horizontally.
The size of the heart muscle directly depends on a person’s age, gender, body weight and height. Its value is influenced by external factors - working conditions, place of residence. The heart increases along with body weight, height, and muscle development. The latter indirectly affects the fact that women's heart muscle is smaller than men's.
Interpretation of photo MRI images of the heart
The scans are black and white images of the anatomical area. The device takes pictures at intervals from 1 to 10 mm (depending on the equipment). Detailed and clear images are obtained using high-field tomographs with a power of 1.5 Tesla or more.
Image interpretation requires knowledge of anatomy and MR semiotics of pathologies. Heart functions are described in the form of indices and indicators that should be studied by a cardiologist. Depending on what the MRI of the heart shows, a conclusion is drawn up. The scanning protocol describes the main parameters of the organ and notes signs of pathological changes. Finally, the information is summarized. When presenting the results to the patient, the radiologist can briefly explain the situation. For more detailed information, please contact your doctor.
Scanning the cardiovascular system requires special equipment capabilities and is therefore not carried out in all diagnostic centers. Whether MRI of the heart and blood vessels is performed in a particular institution, you need to find out in advance. At the Magnit DC, scanning of this organ is not carried out. Any questions you may have can be clarified by phone.
Appearance of the fetal heart
The appearance of the heart depends a lot on the period of human development. For example, at the very beginning of fetal development, the heart looks like a tube, which in principle resembles a blood vessel. During the development of the embryo, the walls of such a formation thicken, as muscle fibers begin to actively form, which later become part of the structure of the myocardium. At the same time, the fetal heart has the opportunity to contract.
The first contractile activity of the heart tube is observed on the 22nd day after conception. At first it is weak, but gradually the strength of the contractions increases and after a couple of days blood begins to circulate through the blood vessels of the embryo. Thus, on the 28th day from the beginning of development, the fetus has a primitive blood supply system.
Correct formation of the heart during fetal development allows one to avoid many congenital diseases of this organ. That is why it is extremely important in the first months of pregnancy to avoid various nervous shocks, physical stress, the harmful effects of alcohol, smoking, medications, and infections, which often lead to various heart pathologies.