Surgeon
Bohyan
Tigran Surenovich
Experience 36 years
Surgeon of the highest category, Doctor of Medical Sciences, member of the International Association of Surgeons, Gastroenterologists and Oncologists
Make an appointment
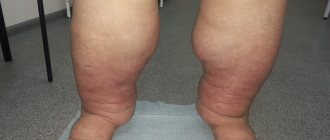
Lymphostasis is one of the pathologies of the lymphatic system associated with impaired circulation of lymph and its retention in the body. The pathology is accompanied by tissue compaction, persistent swelling and thickening of the limb, impaired mobility, the appearance of characteristic ulcers on the skin and darkening of the skin.
Causes
Violation of lymph outflow and its accumulation in the extremities is often a consequence of:
- violations of the excretory function of the kidneys;
- cardiac or chronic venous insufficiency;
- postthrombophlenic syndrome;
- damage and obstruction of lymphatic vessels;
- fistulas in the structure of arteries and veins;
- compression of lymph flows by tumors, inflamed tissues, infiltrates;
- defect of the lymphatic system, etc.
The exact cause of the disease can only be determined by studying the patient’s medical history and identifying the underlying disease that caused disturbances in lymph flow.
Types of lymphostasis
Depending on the cause of the development of lymphodema, there are:
- primary, or congenital form;
- secondary, or acquired form of the disease.
Congenital pathology develops against the background of disturbances in the formation of the lymphatic system during intrauterine development. In rare cases, a hereditary factor may influence lymph flow disturbances. Cases of primary lymphostasis account for about 6% of the total number of patients with this disease.
The acquired form of lymphodema occurs under the influence of unfavorable external factors. The first symptoms often make themselves felt in childhood and adolescence, and later intensify during pregnancy and lactation, which is due to hormonal changes in the body during puberty and gestation. A sharp progression of lymphostasis is possible after pregnancy or severe injury.
Symptoms
A number of characteristic signs indicate the development of the disease:
- severe swelling of the limb, which develops in the evening and subsides in the morning;
- increased swelling during physical activity, prolonged limitation of arm mobility, etc.;
- the constant nature of edematous phenomena;
- a noticeable mark that remains on the skin after pressing on the swollen area of tissue;
- the skin at the site of lymph stagnation becomes stretched and thickened, which is accompanied by severe pain.
In more severe cases requiring immediate intervention from specialists, patients experience:
- irreversible disorders of lymph flow;
- signs of benign cystic and fibrous formations in tissues;
- limb dysfunction;
- loss of hand contours;
- the appearance of contractures due to limited movement;
- signs of trophic ulcers, eczema and erysipelas;
- symptoms of tissue sepsis.
How does the lymphatic system work?
There are many lymphatic capillaries in all human organs and tissues.
They are closed at one end and unite into larger lymphatic vessels. As blood flows through small arteries, some of its liquid part, plasma, leaks into the tissues. Tissue fluid is partially absorbed into small veins and partially into lymphatic capillaries. Thus, it does not accumulate in tissues. All lymphatic vessels empty into lymph nodes. Here the lymph is filtered and cleared of foreign agents. Lymphocytes, the cells of the immune system, are formed in the lymph nodes. Usually many small afferent vessels flow into the lymph node, and only 1-2 efferent vessels exit.
Lymphatic vessels unite into larger ones and form two main ducts: the thoracic and right lymphatic. They flow into the right and left subclavian veins, respectively. Thus, the lymphatic system cleanses tissue fluid and returns it to the bloodstream.
Possible complications
In the absence of timely medical care, the patient may develop:
- severe pain caused by compression of nerve endings;
- deep skin damage with multiple trophic ulcers and inflammatory processes;
- deep vein thrombosis;
- depression;
- compaction of lymphatic vessels.
Features of care for lymphedema at the Ilyinsky Hospital
We use an intermittent pneumatic compression device. The device is programmed and performs compression in a special sequence. This allows lymph to be evacuated in one direction.
In the Ilyinsky hospital, in case of resistant lymphedema, interventional treatment methods are also used. One of them is thoracic sympathetic blockade at the level of Th-3 (third thoracic vertebra) under X-ray control. It is the thoracic section of the sympathetic system that is responsible for the vascular tone of the limb, and blockade of the nerve plexus allows the outflow collaterals to open. Thanks to this procedure, we have good results in cases of difficult-to-resolve lymphostasis. This is essentially one small injection. The procedure is safe and easily tolerated.
We avoid the use of physical therapy treatments such as laser and electrical stimulation due to insufficient evidence of their effectiveness for lymphedema.
We also help restore and control balance in various pain syndromes and in the event of peripheral neuropathies.
In case of increased fatigue, we evaluate the factors that can lead to this condition and teach the technique of “conserving / conserving daily energy”.
For patients undergoing surgical treatment at the Ilyinskaya Hospital, rehabilitation doctors evaluate hand function before surgery. Physical therapy exercises begin on the first day after surgery with easy restoration of the angles of movement of the limb. We recommend such passive exercises under the supervision of a physical therapist during the first week after surgery. Then, in the second week, or when the drainage is removed, patients can begin active movements on their own. This phase lasts 6 to 8 weeks until shoulder function is fully restored. At the same time, you can massage the scar (with the help of a massage therapist or after receiving instructions for self-massage). Between 4 and 6 postoperative weeks, you can do light weight exercises.
If you develop signs of lymphedema, it is very important to take proper skin care to reduce the extent of lymph node dissection, avoid trauma, weight gain, vaccinations, insect bites, and venous access to the involved limb. And immediately resolve the issue of antibiotic therapy in case of signs of infection.
Stages of the disease
Clinical manifestations of arm lymphostasis depend on the stage and type of pathology:
- temporary reversible lymphostasis often occurs after surgery in the chest or upper extremities, and easily resolves when wearing a compression sleeve;
- subacute lymphostasis is characterized by pain and severe tissue swelling, subject to correction using a compression sleeve;
- Chronic lymphostasis has a long course and is difficult to treat.
Based on the characteristic signs of lymphostasis, you can easily determine the stage of development of the pathology:
- Stage I is called spontaneously reversible. The swelling is noticeable, increases in the evening and goes away in the morning; when pressing on the skin, a dimple forms.
- Stage II – spontaneously irreversible. The skin at the site of swelling becomes denser, and when pressure is applied to the skin, the hole does not remain. The skin is tense and sensitive, and pain is noted.
- Stage III is irreversible. Due to the stretching and proliferation of connective tissue, the skin becomes covered with scars, cystic formations and papillomas. The limb becomes deformed and becomes almost immobile. The stage of elephantiasis begins, named after the characteristic shape of swollen limbs that lose their original shape.
Complex Decongestive Therapy (CDT)
Treatment of lymphedema in our clinic is carried out in accordance with European standards using the Complex Decongestive Therapy (CDT) method. The treatment is a course of 10 procedures, performed every day or every other day, and consists of SEVERAL stages:
- Manual lymphatic drainage massage is a therapeutic procedure, the technique of which is fundamentally different from classical massage and requires certain professional skills. Therefore, it is carried out by specially trained medical staff of our center. After the massage, a sleeve is put on for pneumocompression.
- Pneumocompression. Hardware lymphatic drainage is carried out in the absence of contraindications - as a rule, between manual massage sessions, and always under the supervision of the attending physician. This procedure helps to increase the tone of the lymphatic channel, activate the passage of intercellular fluid and reduce swelling. Usually prescribed daily or every other day.
- Banding is one of the important components of the complex treatment of lymphedema; it is carried out after sessions of manual and hardware lymphatic drainage. It maintains the effect of the procedures performed, improves lymphatic drainage, and promotes softening of altered tissues. Bandaging prevents swelling from increasing, for which special low-stretch bandages are applied to the arm.
- Compression sleeve. After treatment, it is recommended to wear compression stockings to prevent recurrence of lymphedema. For this purpose, special flat-knit compression sleeves are used, which have high density and wear resistance. This knitwear practically does not stretch and holds its shape well, which prevents swelling from reoccurring. The compression sleeve is selected based on individual measurements and ordered in Germany.
For 20 years, the partner of the Phlebology Center clinic has been the German company medi, which is famous for its pedantic attitude to the quality of its products.
German companies are considered the world leaders in the production of compression knitwear. For 20 years, the partner of the Phlebology Center clinic has been the medi company, which is famous for its pedantic attitude to the quality of its products.
Diagnostics
It is possible to establish a preliminary diagnosis already at the first examination of the patient and by studying the anamnesis. The specialist’s assumptions can be confirmed by:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvis to clarify the condition of the kidneys and excretory system;
- Ultrasound of the veins of the upper extremities;
- Chest X-ray;
- Lymphography using an X-ray machine;
- Lymphoscintography;
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging.
The conclusion about the stage and type of the disease is made based on the comprehensive results of all the listed examinations.
Literature
- Yudin V.A.. Savkin I.D. Treatment of lymphedema of the extremities [Electronic resource] // Journal “Russian Medical and Biological Bulletin named after. Academician I.P. Pavlova, 2015.
- Larinsky N., Byalovsky Yu., Ivanov A. Magnetic therapy with a running field in the complex treatment of postmastectomy lymphedema of the upper extremities [Electronic resource] // Doctor Magazine, 2021.
- Yarema I.V., Aliev M.M., Sipratov V.I. Chronic lymphovenous insufficiency of the lower extremities and lymphoscintigraphy [Electronic resource] // Medical scientific and practical portal “Attending Doctor”, 1999.
Treatment
The main goal of the treatment course is to restore lymph flow and eliminate the consequences of lymph stagnation. Therefore, priority is given to mechanical impact on the limb with severe pathology. Gives a good effect:
- physiotherapy;
- lymphatic drainage massage;
- hardware pneumocompression;
- therapeutic exercises for lymphostasis of the hands;
- wearing special jersey;
- Exercise therapy and swimming to restore arm mobility;
- local treatment of ulcers and skin lesions.
As an auxiliary measure, the patient is recommended to limit salt in the diet.
If the measures taken are ineffective, a decision may be made on surgical treatment of lymphostasis of the upper extremities, during which artificial lymph outflow pathways are created and connective tissue formations are removed.
Preventive measures
Patients will be able to prevent the development and accelerate treatment of lymphostasis of the upper extremities by:
- regular physical activity, special exercises for lymphostasis of the hands;
- lymphatic drainage self-massage skills;
- giving up alcohol and smoking;
- reviewing the diet to reduce the amount of dishes high in fat and salt;
- avoidance of tight clothing and jewelry that pinches the hands;
- compliance with safety precautions to prevent overheating or skin burns;
- treating wounds and ulcers on the hands to prevent infection;
- weight control.
Additional recommendation: during sleep, it is better to place the limb on a pillow in an elevated position.
Choosing the right compression sleeve will help you cope with the disease at the initial stage. It is advisable to give preference to products from a well-known manufacturer, which guarantees the quality and safety of the ordered product.
Prevention
Preventive measures play an important role. Among them we note:
- Avoiding heavy physical activity;
- Proper balanced nutrition;
- Active lifestyle, swimming, performing special exercises;
- Avoiding overheating;
- Extremity skin care;
It is also important to promptly contact a specialist regarding the use of compression hosiery if symptoms of pathology occur.
The Onco.Rehab Integrative Oncology Clinic tells you that a lot in avoiding the disease depends on you.