Today, many people have begun to refuse to eat meat, citing the fact that it contains a lot of cholesterol and other harmful components.
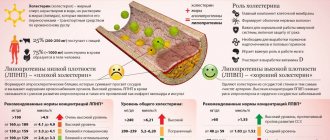
Cholesterol is a biologically active substance belonging to the group of polyhydric alcohols, which is necessary for the full functioning of the body. Its deficiency leads to insufficient production of hormones by the endocrine glands, deterioration of the emotional background, and changes in the structure of cell membranes. High levels of cholesterol in the blood inevitably lead to the development of such a dangerous disease as atherosclerosis.
To maintain normal plasma cholesterol concentrations, you need to exclude sausages and smoked meats . But you don’t have to go to extremes and completely give up meat. It is enough just to study the information which meat has more cholesterol, and which has a small amount.
The effect of cholesterol on the body
Cholesterol is the main element of fat metabolism, the synthesis of which occurs to a greater extent in the liver (about 80%) and partially comes with food (20%).
A sufficient amount of cholesterol is necessary for the production of bile acids, proper metabolism, the synthesis of vitamin D and steroid hormones (minerals and glucocorticoids).
Cholesterol is the content of the myelin sheath of nerves and contributes to the proper transmission of nerve impulses. Cholesterol is also part of the structure of cellular structures and is responsible for their elasticity and permeability.
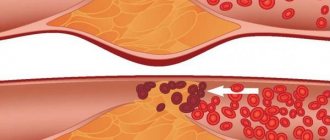
An increase in cholesterol concentration leads to the development of atherosclerotic vascular damage and the formation of the following diseases:
- Coronary heart disease and hypertension (threat of acute myocardial infarction).
- Ischemia of cerebral vessels (threat of hemorrhagic/ischemic stroke).
- Ischemia of the kidneys and intestines (possible thrombosis of intestinal vessels, development of chronic renal failure).
- Vascular ischemia of the lower extremities (risk of developing trophic ulcers, gangrene of the legs).
The recommended daily requirement for cholesterol is about 250 - 300 mg, necessary for the general functioning of the body, regardless of the person’s age and gender.
Where is the most cholesterol?
Cholesterol and health
Cholesterol is an essential component of our body. It is more correctly called cholesterol (chemical name), which is a substance from the family of lipophilic alcohols. The vast majority of it is synthesized in liver cells and only about 20% enters our body with food.
It is a very important component of all tissues; therefore, when the amount fluctuates in the body, pathological processes begin to occur, for example, with a decrease, there is a risk of developing oncological processes, and with an excess, the formation of fatty plaques in the arteries and veins is provoked.
The body needs cholesterol because:
- is an obligatory component of the cytoplasmic membranes of all mammals;
- Without it, the synthesis of steroid hormones, bile acids and vitamin D will be impossible.
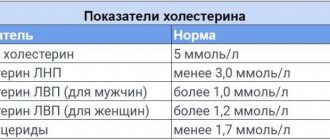
The normal concentration in the blood is from 3.4 to 5.2 mmol per liter, which is necessary for the full functioning of the body. According to data released by scientists belonging to the American Heart Association, in order not to develop negative processes in the bloodstream, daily cholesterol intake should not exceed 300 mg.
Benefits of eating meat
Meat dishes are part of the daily nutritious diet of most people, are combined with various foods and have the following beneficial qualities:
- Meat contains all the amino acids necessary for the body, which are absent in proteins of plant origin, are not produced by the liver and are important for the biosynthesis of its own proteins. Proteins form the basis of cells, are a storehouse of energy, play the role of neurotransmitters (participate in the transmission of nerve impulses), and regulate the function of vitamins and minerals.
- Meat is a donor of L-carnitine and coenzyme Q 10, substances necessary for the normal functioning of the heart muscle.
- Meat contains vitamins B6 and B12, which are essential for the functioning of the central and peripheral nervous system, hematopoietic organs and which are donors of methyl groups (antioxidants responsible for the body’s response to stress, involved in tissue detoxification and having an anti-inflammatory effect).
- Creatine contained in meat is needed for energy metabolism in muscle and nerve cells. Also, creatine slows down the accumulation of lipofuscin pigment - a marker of aging and wear and tear of the body, has a positive effect on mental abilities and inhibits the progression of Parkinson's disease.
- Heme iron (found in “dark” meat) is very well absorbed by the body and is necessary for people suffering from anemia.
- Meat includes multiple trace elements: potassium, calcium, zinc, magnesium, manganese.
What are the benefits of eating meat?
Harm
Vegetarianism is becoming popular at the moment.
This direction completely excludes the consumption of meat, not only for ethical and religious reasons, but also based on the medical disadvantages of consuming this product:
- Meat products contain a high concentration of cholesterol , which is directly proportional to the part and type of meat and culinary processing.
- Meat is difficult to process and lingers in the gastrointestinal tract for a long time due to lack of fiber. That is why, after eating meat dishes, there is heaviness and discomfort in the abdominal area.
- Meat from animals raised under conditions of accelerated growth contains thyroid and sex hormones, which will disrupt the human hormonal balance and negatively affect health.
- Eating meat products is contraindicated for gout due to their high protein content.
What are the benefits of meat?
You can often hear heated discussions about whether you should eat meat or not. Among the majority of opinions, two are in the lead: first, you need to eat, second, there is nothing good from eating it.
Since the article is devoted to a different topic, we will not take either side, but will only indicate how this product is useful:
- Meat is a valuable source of protein, which is the dominant organic compound in the body, consisting of nonessential and essential amino acids. The latter come exclusively from food since they are not synthesized in our body. Thus, by eating meat products, we replenish the protein reserves of which we are composed. Therefore, it is important to eat animal products for children, athletes, pregnant and lactating women, people who have suffered fractures or other serious somatic diseases;
- Meat contains a fairly high set of micro- and macroelements necessary for the body:
- iron is needed for hematopoiesis and increasing hemoglobin levels;
- calcium is needed for bone and dental tissue;
- potassium is involved in intercellular transport processes;
- zinc takes part in providing protective systems;
- manganese and magnesium stimulate the faster occurrence of many biochemical reactions;
- vitamins A, B and D stimulate the immune system, renewal of epithelial tissues, improve vision, nervous activity, and hematopoiesis.
Chemical composition
The main part of meat is muscle tissue, which contains:
- Water 70 -75% . The amount of water depends on the age and fatness of the animal.
- Proteins 18 – 20% . Complete proteins (myosin, albumin, globulin, myogen) and incomplete (elastin, collagen).
- Fats 3 – 5% , of which saturated, “harmful” fats are about 45 – 50%.
- Carbohydrates 0.025 – 0.05% . The main carbohydrate in meat is glycogen, which affects the stage of meat ripening.
- Nitrogenous substances 1.5 - 1.7% stimulate appetite and provide meat and meat broths with a specific pleasant taste and aroma.
- Minerals 0.8 – 1.5% (iron, potassium, sodium, phosphorus salts).
The main part of meat is muscle tissue
Pork
The amount of cholesterol per 100 grams of pork is 100 mg. Pork is the most popular and frequently consumed type of meat. Pork is consumed in the form of freshly prepared dishes, canned food and smoked products, and cooked on the grill.
Energy value of the product (per 100 grams):
- Amount of protein 27 grams;
- Amount of fat 13 grams;
- Amount of carbohydrates 0 grams;
- Calorie content 250 kcal.
To reduce cholesterol consumption with pork, it is recommended:
- Choose leaner meat, remove excess fat and tendons.
- When preparing meat, give preference to boiling, stewing, baking, or steaming.
- The daily rate of meat consumption is no more than 200 - 250 grams.
- People with hypercholesterolemia are recommended to eat pork no more than 4 times a month.
Content of cholesterol and saturated fatty acids in different parts of pork (per 100 grams of product).
| Pork product | Amount of cholesterol, mg | Amount of EFAs, mg |
| Brisket | 80 | 6 |
| Brain | 2200 | 3 |
| Liver | 140 | 3 |
| Kidneys | 310 | 2 |
| Lungs | 1000 | 4 |
| Language | 55 | 2 |
Pork
Beef
It is known that beef has much less cholesterol than pork. High-quality beef is red in color and has a fibrous, marbled structure.
Nutritional value of the product (per 100 grams):
- Proteins 19 grams;
- Fat 18 grams;
- Carbohydrates 0 grams;
- Calorie content 155 kcal.
To reduce the amount of cholesterol consumed, you should follow the same rules when cooking pork. It is necessary to take into account that when consuming “old” meat (dark red in color and hard when pressed), digestibility and digestion become more difficult.
Individuals with high levels of cholesterol in the blood are not recommended to consume beef by-products; do not exceed the daily intake of 250-300 grams (we are talking about beef fillet).
Table of cholesterol and saturated fatty acids content in beef (per 100 grams of product).
| Beef product | Amount of cholesterol, mg | Amount of EFAs, mg |
| Fillet | 62 | 1 |
| Brain | 3000 | 2 |
| Liver | 300-400 | 2 |
| Kidneys | 320 | 1 |
| Language | 90 | 3 |
Beef
Veal
Veal is the meat of a young calf, which differs from beef in its tenderness, dietary quality and the fact that it has less fat.
This type of meat is special because it has exceptional extractive substances that increase the concentration of gastric juice and improve the digestion process.
Therefore, veal is recommended for people with a low concentration of gastric juice, or for hypoacid gastritis/stomach ulcers. Veal broths are recommended for use in cases of severe illness and for elderly people.
Veal dishes are an excellent source of protein, vitamins and minerals for pregnant women, nursing mothers and children.
Tender steamed veal cutlets or boiled meat are an excellent choice for the first feeding of a baby (from 6-7 months).
Energy value of the product (per 100 grams):
- Proteins 24 grams;
- Fat 8 grams;
- Carbohydrates 0 grams;
- Calorie content 140 kcal.
Veal
Mutton
By lamb meat we mean the meat of bulls or sheep. Fresh lamb meat is tender and soft, red in color. The meat of an old animal is dark in color, tough, and has an unpleasant aftertaste.
Lamb differs from other types of meat in the presence of lecithin, a phospholipid complex, a building material at the cellular level that strengthens the nervous system and liver.
Nutritional value (per 100 grams):
- Proteins 26 grams;
- Fat 21 grams;
- Carbohydrates 0 grams;
- Calorie content 285 kcal.
The cholesterol content in lamb is 95 mg per 100 grams.
Mutton
horsemeat
Horse meat has a spicy taste and is in demand among nomadic peoples. Most often, the meat of young foals (no more than 1-2 years old) is used. Despite its unusual nature, horse meat is an excellent nutritious, hypoallergenic and dietary meat.
Horsemeat, unlike other types of meat, contains many organic compounds that help improve digestion and establish intestinal microflora.
Energy value:
- Proteins 29 grams;
- Fat 8 grams;
- Carbohydrates 0 grams;
- Calorie content 170 kcal per 100 grams of product.
Amount of cholesterol: 70 mg per 100 grams of product.
horsemeat
Rabbit meat
Rabbit meat is soft and tender and is almost completely absorbed by the body. Rabbit meat is the most hypoallergenic and dietary type of meat.
Also, rabbit meat is distinguished by a high content of arachidonic acid, an antioxidant that stabilizes the cells of our body, has a positive effect on blood vessels, and reduces the level of lipids in the blood.
Nutritional value (per 100 grams of meat):
- Protein 33 grams;
- Fat 4 grams;
- Carbohydrates 0 grams;
- Calorie content 165kcal.
Rabbit
Chicken
Chicken is one of the dietary types of poultry meat and contains the largest amount of protein. The least nutritious is the brisket, the fattest is the thighs with skin.
Due to the high concentration of essential oils and nitrogenous substances, chicken broth has a rich and specific pleasant aroma.
Chicken contains a large amount of B vitamins (B1, B6, B12), necessary for the normal functioning of the nervous system, as well as vitamin A, which improves visual acuity.
Chicken meat is distinguished by the presence of vitamin F - linoleic acid, which belongs to the omega-6 family of polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Linoleic acid regulates the concentration of cholesterol and sugar in the blood, has anti-inflammatory and regenerating abilities.
Nutritional value of chicken meat (per 100 grams):
- Proteins 23 grams;
- Fat 17 grams;
- Carbohydrates 0 grams;
- Calorie content 235 kcal.
People with high cholesterol levels should avoid eating chicken by-products and separate the skin from the meaty part when cooking.
Table of cholesterol and EFA content in chicken (per 100 grams of product).
| Product | Amount of cholesterol, mg | Amount of EFAs, mg |
| White chicken meat without skin | 81 | 0.5 |
| Dark meat chicken without skin | 91 | 1 |
| Chicken heart | 165 | 1.5 |
| Chicken liver | 500 | 1 |
Chicken
Turkey meat
Turkey is the most dietary and popular type of meat. The absorption of turkey by the body exceeds 95%. An excellent choice of poultry for people suffering from hypercholesterolemia and excess body weight.
In terms of phosphorus content, turkey is equal to fish, and therefore is recommended for people suffering from diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
The high potassium content provides protection to the cardiovascular system.
Turkey contains equal amounts of Omega-3 and Omega-6 polyunsaturated acids, which normalize fat levels, blood pressure, and have an anti-carcinogenic effect.
Energy value of turkey (per 100 grams):
- Proteins 22 grams;
- Fat 4 grams;
- Carbohydrates 0 grams;
- Calorie content 190 kcal.
Turkey
Duck meat
Duck meat is rich in protein, all the vitamins and microelements that are also found in other types of poultry. But compared to chicken and turkey, duck meat is much higher in calories and fat. Therefore, its use is not recommended for persons with elevated lipid levels.
Duck meat is more recommended for people with increased physical activity and energy expenditure during the day, as it adds strength and leaves a feeling of fullness for a long time.
The nutritional value:
- Proteins 20 grams;
- Fat 7 grams;
- Carbohydrates 0 grams;
- Calorie content 180 kcal.
Duck
Goose meat
Eating goose meat is less common than chicken or turkey meat. Due to the fact that geese are active birds, their meat has few blood vessels and this explains its toughness, which not every person will like.
Goose meat does not have the same chemical composition as other types of poultry meat, and even surpasses them in the amount of amino acids.
Energy value (per 100 grams):
- Protein 23 grams;
- Fat 24 grams;
- Carbohydrates 0 grams;
- Calorie content 165 kcal.
Goose
Quail meat
Quail meat is considered a delicacy and is distinguished by its dietary, taste and beneficial properties. The contained magnesium, cobalt, and sulfur have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the central nervous system and improve cognitive functions.
Low energy value and a small amount of fat allow us to call this product dietary and containing a low amount of cholesterol.
Therefore, quail meat is recommended to be consumed in the diet of people with diseases of the cardiovascular system, diabetes and obesity.
Nutritional value (per 100 grams of quail meat):
- Proteins 26 grams;
- Fat 12 grams;
- Carbohydrates 0 grams;
- Calorie content 80 kcal.
Quail
Oils and nuts: which ones to choose?
Butter and margarine contain the same amount of fat (up to 81 g per 100 g), but these fats differ in their composition. Butter contains a lot of saturated fatty acids (about 63%) and about 4% of so-called trans fatty acids (partially hydrogenated vegetable fats). Trans fatty acids are recognized as harmful to health.
Compared to butter, all types of margarines contain lower amounts of saturated fatty acids, and margarines labeled “high in polyunsaturated acids” contain a large amount of trans fatty acids, which, along with saturated fats, cannot be recommended in the diet of patients with hypercholesterolemia.
Olive oil is an ideal product from the point of view of the concept of the so-called Mediterranean diet and low cholesterol nutrition. Olive oil is absorbed by the body by 98%, while sunflower oil is only 65%.
Olive oil has been used by humans for thousands of years and is considered one of the oldest foods. Like wine, olive oil comes in different flavors, colors and aroma as it is grown in different climates and soils and harvested in different ways.
Olive oil is divided into several grades based on flavor and acidity. Extra Virgin Olive Oil is produced from selected quality olives. It has excellent taste and aroma and does not require cleaning. The acidity of this oil is no more than 1%.
“Virgin Olive Oil” is also an excellent product that does not require purification. It has a high standard of taste and aroma, and its acidity is no more than 2%.
“Olive oil” is an oil that initially has a high percentage of acidity. It is processed (refined) and flavored with “super natural” olive oil. Its acidity is no more than 1.5%.
Olive oil can serve as a salad dressing, a marinade for meat and fish, it is resistant to high temperatures and is widely used for frying and baking.
Nuts are a very healthy and nutritious product. Nuts contain a large amount of calories, vegetable protein and unsaturated fatty acids. Recent evidence suggests that eating certain types of nuts (such as walnuts) leads to a modest reduction in cholesterol by up to 12%.
Brazil nuts are an excellent source of selenium. Selenium is an important trace element that is involved in oxidative processes, normal thyroid function and the production of the sex hormone testosterone, and also ensures normal sperm motility. Three whole Brazil nuts (10 g) provide the daily dose of selenium - 153 mcg (daily value for men - 75 mcg, for women - 60 mcg).
Cholesterol content in meat (table)
In order to be sure and know how much cholesterol is contained in what types of meat, below is a table of comparative data on the amount of cholesterol.
It should be noted that the indicated concentration of cholesterol contained in the meat fillet is without skin and fat.
| Name of meat type | Amount of cholesterol, mg (per 100 grams) |
| Pork | 80 |
| Beef | 62 |
| Veal | 90 |
| Mutton | 95 |
| horsemeat | 70 |
| Rabbit meat | 120 |
| Chicken breast | 50 |
| Turkey meat | 42 |
| Duck meat | 84 |
| Goose meat | 90 |
| Quail meat | 85 |
The leaders in low cholesterol levels, as indicated in the table, are chicken breast and turkey meat.
But we must not forget that the type of culinary processing and combination with other food products significantly influence the value of this indicator.
The leaders in low cholesterol levels, as indicated in the table, are chicken breast
Diagnosis of pathologies
In order to periodically observe a picture reflecting how much cholesterol is in the blood, you need to regularly consult a specialist and periodically take blood tests. If the maximum permissible norm is exceeded, you should limit yourself to most foods containing large amounts of fat and include foods containing low amounts of cholesterol in your diet.
It also happens the other way around: the amount of cholesterol in the blood does not exceed the standard value and is far behind it; in this state of affairs, the level of the substance must be increased to ensure normal body function. But nevertheless, this should be done gradually, with extreme caution, so that the indicator is not exceeded again.
In any case, it is much easier to just monitor your health and eat right.
How to choose the right meat?
In order for eating meat to bring benefits, and not vice versa - to harm the body, you need to comply with certain criteria when purchasing meat:
- The meat should be a bright color. A dull color indicates that the meat is of poor quality and not fresh.
- When pressed, a notch forms in fresh meat and quickly disappears; in spoiled meat, the notch does not disappear and liquid accumulates in it.
- Fresh meat when cut has a thin crust of a pink-red color (pork), a whitish-pink tint (veal), or a brown-red tint (lamb).
- During a visual inspection, you need to pay attention to the presence of helminth eggs; they look like millet and can crunch when cutting meat.
- Unhealthy shine and stickiness also indicate spoiled meat.
- If the cut meat has a greenish or bluish tint, you should not buy such meat.
When should you not use it?
There are no absolute contraindications to eating meat, but there are some diseases for which eating meat is undesirable:
- Gout. Due to the high content of purines, the excretion of which is difficult with gout, eating meat is not recommended, as it can provoke another attack of the disease.
- Chronic renal failure. Due to the high protein content in meat, it is not consumed for chronic kidney diseases, because their filtration capacity is reduced.
Cholesterol content in different types of meat
Harm from meat products
But there are also ardent opponents of eating meat in any form. They call it alien to the human gastrointestinal tract, and in addition to the moral aspect of eating living beings, they note the biological “difficulties” of digesting this product.
Indeed, meat contains little fiber. These important dietary fibers regulate the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and stimulate the movement of the food bolus through the intestines. Due to their lack, meat is difficult to digest, and the body spends a lot of energy on this process. Hence the heaviness in the stomach familiar to many, which occurs after a hearty feast and excessive consumption of meat food.
Another feature of the chemical composition of meat is the high content of refractory fats and cholesterol. How many “bad” lipids are contained in a product depends not only on its type, but also on the conditions of keeping and feeding the livestock. The harmful properties of meat are also significantly enhanced by modern processing methods - the use of hormones to enhance the growth of livestock and poultry, the addition of pesticides and nitrates to feed, and the use of dyes to give meat a “beautiful” color.