Description
Non-stenotic atherosclerosis - what is it? Generally speaking, these are the consequences of an incorrect lifestyle. Plaques form on the surface of blood vessels, which is caused by excessive levels of “bad” cholesterol in the blood. Pathological processes do not concern the walls of blood vessels, but their openings.
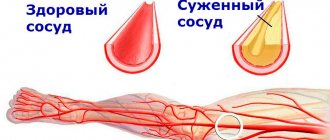
Plaques, which are blood clots, are deposits of lipid tissue. With atherosclerosis, they grow inside the vessels, which impedes normal blood flow. In the non-stenotic form of the disease, they do not slow down the blood flow.
Cholesterol problems often arise in youth and remain asymptomatic for years. Symptoms begin to be actively expressed upon reaching 50 years of age. Changes in the walls of blood vessels affect various internal organs, including large, vital ones.
It is a mistake to believe that non-stenotic atherosclerosis, like other forms of the disease, affects only the elderly.
Symptoms
- A sharp weakening or disappearance of the pulse in the groin, popliteal fossa or foot
- Pain in the muscles of the lower leg (more often) and thigh, which regularly occurs when walking and goes away after a short rest (stop) - intermittent claudication
- Constant or periodic pain in the foot, requiring a forced position with the limb lowered down
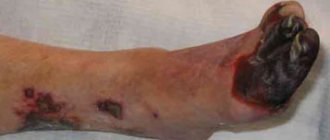
- Coldness, paleness of the foot; in severe cases – the appearance of pronounced cyanosis (cyanosis), marbled spotted color and/or trophic disorders in the form of necrosis (tissue death)
The most striking symptom is the appearance of pain when walking, which forces the person to stop or slow down their walking speed. Most often, in the initial stages, the patient feels increased fatigue of the lower leg muscles, mainly along the back surface, then a pronounced sensation of painful compression appears. In some cases, similar sensations may occur in the thigh muscles and buttocks. As the disease progresses, walking speed decreases and the distance walked shortens. In addition, young men often experience a decrease in potency. All these symptoms are a reason to contact a vascular surgeon.
Kinds
Any arteries or vessels can be affected. The lesions described below have the most pronounced symptoms. Each species has its own characteristics, most often several of them develop simultaneously. Damage to the blood vessels of the brachiocephalic arteries, aorta, and lower extremities is considered especially common.
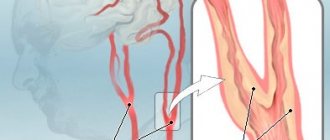
Brachiocephalic arteries
For the body to be viable, it is necessary to ensure uninterrupted blood flow to the brain. The following main ways are involved:
- through the carotid artery;
- left subclavian artery;
- brachiocephalic trunk.
The brachiocephalic artery is one of the branches of the aorta through which blood flow reaches the brain. Due to its parameters and accessibility, cholesterol plaques often form in it, affecting the walls of blood vessels. The main symptoms of non-stenotic atherosclerosis of the extracranial brachiocephalic arteries are:
- frequent tinnitus;
- dizziness;
- migraine attacks;
- fainting state;
- numbness of the limbs;
- prostration.
Symptoms of damage to parts of the bts also include hair loss, brittle nails, deterioration of the skin, and changes in gait. Many people view these problems as cosmetic, delaying treatment.
Non-stenotic atherosclerosis bca is considered one of the most dangerous forms of atherosclerosis. Damage to the extracranial vessels that supply blood to the brain and neck causes a lot of discomfort, worsening the quality of life. However, given that this often manifests itself in older people, such symptoms are attributed to age and left unattended. Non-stenotic atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries may also involve damage to the carotid arteries.
The larger the plaque becomes, the stronger the disruption of the blood flow system, given the proximity of the arteries to the brain, this condition is life-threatening
Aorta
The aorta is the largest blood vessel. Often, those parts of the aorta that are located in the chest and/or peritoneum are susceptible to non-stenotic atherosclerosis of the aorta. The danger lies in the non-obviousness of the symptoms; even if the plaques have affected every centimeter of the aorta, the person may not feel it.
The main signs of aortic plaque damage include:
- painful sensations in the chest, peritoneum;
- frequent headaches;
- causeless coughing attacks;
- hoarseness, hoarseness.
Arteries of the lower extremities
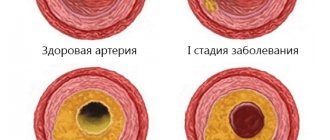
Painful sensations appear in the hips, lower back, buttocks, and the pain syndrome is especially pronounced in the calf muscles. The development of the disease occurs in several stages, most patients detect it in the second or third:
- First. Pain in the lower extremities is felt only after intense physical activity. Many people ignore it, chalking it up to fatigue or poor fitness.
- Second. Painful sensations occur even after minor exertion. Short walking and doing household chores are accompanied by severe discomfort.
- Third. Due to pain, any load on the legs is limited. A person cannot stand for a long time, the maximum possible distance to move is no more than 50 m.
- Fourth. Wounds appear on the limbs, developing into gangrene. This happens due to a deficiency of nutrients, vital microelements to the feet.
Other types of disease
Non-stenotic atherosclerosis can also affect other elastic arteries in the body, although this is less common. In addition to the sections of the brachiocephalic arteries, aorta and lower extremities, plaques can form on:
- main arteries;
- pulmonary;
- subclavian;
- carotid;
- extracranial.
The disruption of the arteries occurs gradually, first the plaques affect the large ones, then the smaller ones. The deposition of cholesterol plaques can occur chaotically, therefore, when at least some of them appear on one type of artery, there is immediately a risk of their formation on others - the entire cardiovascular system may suffer.
Classification of forms of the disease
(Reference: narrowing of the arteries - stenosis, complete blockage - occlusion)
- stenosis and occlusion of the internal carotid artery,
- stenosis and occlusion of the common carotid artery,
- stenosis and occlusion of the vertebral artery,
- stenosis and occlusion of the subclavian artery.
Narrowing of these arteries that supply blood to the brain leads to chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency (CCI) or stroke (cerebral infarction).
KhNMK
- a state of constant lack of blood in the brain, continuous oxygen starvation of brain tissue, forcing brain cells to be in constant tension of all intracellular systems and intercellular connections, which leads to disruption of the normal functioning of both brain cells and the organ as a whole.
The main classification of chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency (CHF), used in Russia (according to A.V. Pokrovsky), contains 4 degrees:
- I degree
- asymptomatic course or absence of signs of cerebral ischemia against the background of proven, clinically significant cerebral vascular damage; - II degree
- transient ischemic attack (TIA) - the occurrence of focal neurological deficit with complete regression of neurological symptoms within up to 1 hour; transient cerebrovascular accidents (TCI) - the occurrence of focal neurological deficit with complete regression of neurological symptoms within up to 24 hours; - III degree
- the so-called chronic course of SMN, i.e. the presence of cerebral neurological symptoms or chronic vertebrobasilar insufficiency without a history of focal deficiency or its consequences. In neurological systematizations, this degree corresponds to the term “dyscirculatory encephalopathy”; - IV degree
- previous, completed or complete stroke, i.e. the existence of focal neurological symptoms for more than 24 hours, regardless of the degree of regression of the neurological deficit (from complete to no regression).
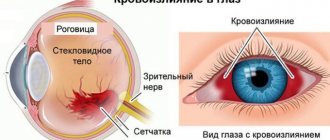
Dry statistics cannot fully reflect the tragedy of the situation when a cerebral infarction occurs - a stroke... But stroke ranks second in the structure of overall mortality of the population, second only to cardiac pathology. 35% of patients who have had a stroke die within the first month, and approximately 50% of patients die within a year, i.e. every second. Think about these numbers: stroke affects about 6 million people in the world every year, and in Russia - more than 450,000, i.e. Every 1.5 minutes, one of the Russians suffers a stroke for the first time. In St. Petersburg, 12 thousand cases of stroke are registered annually.
Causes
The main reason for clogging of arteries due to the formation of cholesterol plaques in the inner lining is a violation of lipid metabolism in the body. Often the person himself is to blame for this condition; it arises due to an incorrect lifestyle. The most common provocateurs of nonstenosing atherosclerosis are:
- obesity;
- smoking, alcohol abuse, drug use;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hypertension (high blood pressure);
- improper diet with excessive amounts of animal fats;
- genetic predisposition;
- constant stress.
Usually, the formation of plaques in the arteries occurs when several factors appear simultaneously. For example, hypertension in people over 45 years of age occurs in every second person. If a person has bad habits and does not play sports, the likelihood of developing non-stenotic atherosclerosis increases significantly.
Some people don't understand how bad habits relate to arterial health. The thing is that under the influence of alcohol, nicotine, and other negative factors, the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels decreases, which makes them a favorable basis for the appearance of plaques.
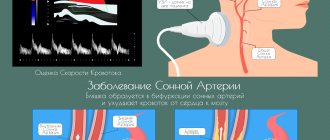
Diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries in the clinic on the Yauza
The development of atherosclerosis can be detected using instrumental studies of the brachiocephalic arteries. At the medical center on Yauza, you can undergo several diagnostic procedures to accurately determine the presence and characteristics of the disease. To identify pathology, the following are used:
- triplex scanning;
- angiography with contrast;
- multislice tomography.
The hospital does not have outdated equipment. All studies are carried out on modern high-precision devices used in leading clinics in the world.
Diagnostics
A cardiologist treats vascular pathologies. However, patients with non-stenotic atherosclerosis rarely go to the hospital with suspicion. As a rule, problems are identified during a blood test, after which the patient is sent for a detailed examination.
Damage to the BC and other types of arteries can be detected using diagnostic methods such as:
- Doppler ultrasound;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- CT scan of the brain and heart;
- donating blood for various indicators.
Doppler ultrasound allows you to assess the general condition of the walls of blood vessels, determine the speed of blood flow - the result allows you to confirm or refute the suspicion of non-stenotic atherosclerosis
Diagnostic results allow you to establish a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. It is impossible to identify cholesterol plaques on your own.
Treatment
Only comprehensive treatment will be effective, which includes diet therapy, giving up bad habits, and the use of medications. Thanks to this, it will be possible not only to normalize the level of cholesterol in the blood, but also to improve the general condition of the patient, preventing relapse. Therapy includes:
- Taking statins. This is the main group of drugs that allows you to normalize the amount of lipids in plasma. They block the production of “bad cholesterol”, accelerating the production of “good” cholesterol.
- Other medications. These include anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, and medications that improve brain function. Also, the choice of medications depends on the cause of atherosclerosis. If it develops against the background of hypertension, medications are prescribed to normalize blood pressure.
- Lifestyle. A complete cessation of bad habits, normalization of sleep and rest patterns, and moderate exercise are required. A diet is also prescribed that involves excluding animal fats from the diet.
In advanced cases, surgery may be necessary. It is used if medication does not bring results or the patient goes to the hospital too late. After diagnosis, endovascular surgery is prescribed - stenting of the affected vessel. If the plaque is large and the artery is almost completely blocked, it may be necessary to remove part of it, and a prosthesis is installed in this place.
Diet therapy
Usually the diet is prescribed for life. Any form of atherosclerosis is endogenous and completely depends on the diet and lifestyle of the patient. The table below shows permitted and prohibited products.
| Allowed | Prohibited |
| Lean meats – chicken, turkey, beef | Fatty meats, lard |
| Fish | Trans fats (margarine, spread) |
| Fresh fruits, vegetables | Sausages, frankfurters, other smoked meats |
| Sea kale | Mayonnaise, all fatty sauces |
| Bran, cereals | Fast food |
| Low-fat dairy products, cheeses | Fatty dairy products, cheeses |
| Chicory, herbal teas | Baking, flour |
Fast food is considered one of the most harmful foods that provokes high cholesterol, it is especially important to give it up for life
Prevention
Preventive measures must be observed by everyone, especially those who have a genetic predisposition to atherosclerosis. They are also important in preventing relapse after successful recovery. The basic rules of prevention include:
- rejection of bad habits;
- choosing a suitable sport taking into account age and health status;
- maintaining normal weight;
- avoiding overeating;
- limiting stress;
- limiting the addition of salt to the diet;
- adherence to the principles of proper nutrition.
Also, an important preventive measure is to consult a doctor in a timely manner if you suspect any health problems.
Thus, non-stenotic atherosclerosis is a serious problem associated with the formation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of the arteries. The sooner it can be diagnosed, the greater the consequences can be avoided. Treatment requires complex therapy: medication, diet therapy, and lifestyle changes.
It is important to know!
- 70% of all strokes “live” in the carotid arteries.
- If you or your relatives have experienced symptoms of CNM, stroke, TIA, do not risk your life and consult a cardiovascular surgeon and doctors at the Department of X-ray Endovascular Diagnostics and Treatment - your family needs you!!!
- Stroke can and should be prevented.
- Atherosclerotic plaques do not dissolve!!!
- The benefit of surgery is always greater than the risk associated with it.