September 15, 2010
How can it be easier to get through the unpleasant period immediately after quitting smoking and not start smoking again?
Not all smokers manage to give up their bad habit easily and without problems. Nicotine stimulates metabolic processes and the functioning of the nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system and cardiovascular system. Therefore, when quitting tobacco, the body, unaccustomed to independent effective activity, has difficulty adjusting to its usual mode of operation and experiences serious discomfort.
. In everyday life this is called “withdrawal”, and experts call it withdrawal syndrome. How can you get through this unpleasant period easier and not smoke again?
Strength of will
Relying only on willpower and your own endurance when trying to quit smoking is wrong. Failure in this case undermines self-confidence and makes subsequent attempts to quit smoking much more difficult. Trying to quit smoking through abstinence alone, a person is left without support, faces severe withdrawal symptoms, and increases the risk of returning to cigarettes. It is important to understand that smoking is not a bad habit that you can get rid of with willpower, but a disease. It requires special treatment: with medication support, psychotherapy, and lifestyle correction. Only with such treatment will a person be able to quit smoking forever, and not for a while.
Possible consequences
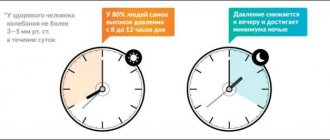
Pressure surges aggravate the condition of a person who quit smoking, preventing him from fully working, spending leisure time and enjoying life. On top of this, against the background of such a manifestation, a number of serious diseases can develop, including those fraught with death. Thus, constant pressure changes provoke occlusion of cerebral vessels, causing heart attacks and strokes. Impaired blood circulation leads to disruption of the functioning of all organs and systems, which also adversely affects the general condition of the body.
Substitution
We are talking about vapes, smoking mixtures, electronic cigarettes, tobacco heating systems and other devices. When smoking, nicotine addiction develops, and it is because of this that it is difficult to quit smoking. Nicotine affects the functioning of the central nervous system. When you try to quit smoking, withdrawal begins, which manifests itself mainly in neurological problems. Among them are difficulties in concentration, anxiety, irritability, aggression, increasing discomfort, and constant thoughts about smoking. If a person switches from regular cigarettes to devices or mixtures that replace them, in fact, he does not give up nicotine, and the addiction continues. Only the method of obtaining nicotine changes. At the same time, when using new devices, it can be more difficult to control the dosage, and they themselves are positioned as safer. Because of this, the amount of nicotine consumed may even increase, and the addiction may intensify.
Have questions? Get a free specialist consultation by phone:
+7
Gastrointestinal tract
Nicotine activates intestinal activity. During smoking, the intestines become accustomed to additional chemical stimulation and cease to function effectively on their own
.
Once nicotine is no longer regularly supplied to the body, constipation may develop for several weeks or even months. Especially if you have a penchant for it. How to cope?
Eat more foods rich in gut-boosting fiber, such as whole grains. Include fermented milk products and dried fruits in your diet, which, by the way, can curb the desire to smoke. Be sure to consult your doctor if intestinal problems persist for a long time.
Fast victory
After holding on for a couple of days, a week or a month, a person may decide that he has already coped with addiction, because the main withdrawal symptoms have already passed. This is a dangerous misconception. Under its influence, a former smoker may start smoking again: many decide to test themselves in this way or believe that one cigarette will not do any harm. In other cases, the feeling of a quick victory is dangerous due to subsequent disappointment. With nicotine addiction, withdrawal symptoms persist for three months. At this time, irritability and uncertainty may occur, a person may feel depressed, and gain weight. If dissatisfaction with these manifestations continues to accumulate, the former smoker may return to smoking simply because he does not see changes for the better.
How to eliminate or alleviate withdrawal symptoms
Let's consider a situation where a person smoked a lot and regularly. Toxic components entered his body, affecting both metabolic processes and the mental background. Nicotine and substances contained in smoke were perceived by the body as “its own”, not foreign. And when their supply suddenly stops, withdrawal syndrome is almost inevitable.
If you feel that cough, nausea, body aches, psychological disorders are getting worse all the time, more and more unpleasant sensations are being added to them, and your general health has already gone far beyond just mild or moderate severity of illness, be sure to consult a narcologist. . Without timely assistance to the body, more serious pathologies may become active.
Detoxification performed by a qualified addiction specialist is a guarantee of quick relief, reducing the risk of health problems and reducing the likelihood that you will take up a cigarette again.
Cleansing the body begins with an examination. It allows you to identify those psychological and physiological deviations that currently exist. Then adequate effective therapy is selected. Often it includes drips (intravenously), taking cardiac, sedative, psychotropic and other necessary drugs.
If the treatment is chosen correctly, then after the first session you will be able to feel relief, which will only increase.
Lifestyle
Tobacco addiction quickly becomes part of the lifestyle and begins to affect it. A person gets used to smoking after eating or immediately after waking up; he needs frequent breaks from work and smoke breaks. Smoking accompanies communication, hard work, and relaxation. It also limits opportunities for exercise and affects appetite and activity levels. Trying to quit smoking without changing your lifestyle is a common mistake: in this case, the smoker is deprived of his usual rituals, receiving nothing in return and acutely feeling the lack of a cigarette. If you start changing your lifestyle and only then move on to quitting smoking, it will be easier to get rid of nicotine addiction. There are several basic recommendations:
- change your diet. It is good if it is fractional: it is advisable to eat more often and in small portions, but at the same time try not to smoke after or before meals. The diet should be balanced and varied: this will improve your overall health and help you cope with withdrawal symptoms faster;
- bad habits. As you prepare to quit smoking, you should also limit your alcohol consumption. Alcohol can become a provoking factor: many people smoke while intoxicated, when control is weakened;
- physical activity. It is worth spending more time on the move, playing sports, being outside more often;
- sleep and rest mode. It is important to normalize it: the duration of night sleep should be at least 7-8 hours, the person should get enough rest. This will improve the functioning of the central nervous system, reducing associated symptoms during withdrawal.
It is worth changing your lifestyle in such a way as to eliminate situations that provoke a breakdown immediately after quitting smoking:
- It is undesirable to go to places or companies where people smoke;
- you need to limit your stress level, choose a “quiet” period to quit smoking: vacation, long weekends or holidays;
- It is worth changing your smoking habits in advance (for example, a cigarette immediately after waking up, with the first cup of coffee, after a meal, on the way to work, while driving).
Not just a cigarette...
Another important aspect in overcoming psychological dependence on tobacco, according to Dr. Yatsenko, is to convince yourself that smoking is not the only possible type of “quick pleasure” and make a list of things that would bring no less satisfaction. How did they answer the question “What can replace smoking one cigarette?” Facebook users at the request of Konstantin Olegovich, look at the illustrations below. Mark in it what suits you and add your own points.
Make a table: in one column - the situation in which you usually smoke, in another - the number of cigarettes you smoke, and in the third - what you could replace smoking with. For example: “Went out with colleagues for a smoke break - Two cigarettes - Drank tea with colleagues.” Imagine that two people come to you and one of them offers to go smoke. What should the other person offer to make you get carried away and forget about the cigarette? At first, these “substitutions” will not be so easy to implement, but over time, the situations in which you previously took up a cigarette will begin to be associated with something more useful.
There is no plan or it is wrong
If a person quits smoking spontaneously, without a plan, he also runs the risk of spontaneously returning to smoking. Treatment of tobacco addiction must be planned: it is important to determine motivation, adjust lifestyle, set deadlines for quitting cigarettes, decide what support measures will be used (substitution therapy, psychotherapy and others). The most common mistake in planning is trying to quit smoking by reducing the number of cigarettes. Nicotine addiction “requires” a constant increase in dose (as with any other drug). Trying to smoke less, a person only prolongs the abstinence period and intensifies it. At the same time, it perpetuates addiction, because the cigarette begins to be perceived as a “reward” for several hours of abstinence. The wrong plan can cause disappointment and breakdown if a person expects results too quickly: for example, that the craving for cigarettes will disappear in a few days or shortness of breath will disappear in a month. Positive changes are usually invisible and difficult to evaluate.
When quitting smoking, it is important to have motivation for this: to understand that quitting smoking is necessary to improve your health and reduce the risk of dangerous diseases. Nicotine addiction is almost always caused by psychological factors: people perceive smoking as part of their lifestyle, their personality, as a way to cope with stress or work more productively. In such cases, treatment with substitution methods (tablets, chewing gum, patches) must be supplemented with psychotherapy. Medical narcologists note that when quitting smoking, it is important to carefully monitor your well-being. If dizziness, nausea, insomnia, or blood pressure disorders occur, you should consult a doctor and try to quickly restore your normal state of health.
Have questions? Get a free specialist consultation by phone:
+7
Physiological symptoms of withdrawal syndrome after smoking
A quitter complains of:
- malfunction of the cardiovascular system: rapid heartbeat, changes in usual blood pressure indicators, and so on;
- deterioration of the respiratory system: rapid breathing, shortness of breath, cough and others;
- disorder of the gastrointestinal tract: feeling of nausea (even vomiting), stool disorders, loss of appetite, unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- vegetative manifestations: dizziness, loss of coordination and motor skills;
- cramps in the limbs, back and other parts of the body.
Most often, a person feels some individual symptoms. As the time spent without smoking increases, they become overgrown with other disorders. Psychological factors come into play.
Interesting fact! It has been proven that some smokers who experience withdrawal symptoms deliberately go into conflict with their loved ones. This is done so that there is a reason to smoke, supposedly against the background of stress.
What to do?
The most correct decision in this situation is to seek medical help, which in no case can be considered a manifestation of weakness or lack of will. A habit formed over years cannot disappear overnight, and without qualified help, a sharp and uncontrolled refusal of an addiction can cause even more harm than smoking itself. The doctor, having studied the patient’s medical history, will select the optimal course of treatment, including a vitamin-mineral complex, drugs to control blood pressure and, if necessary, sedatives or antidepressants.
Is there a connection between smoking and blood pressure readings?
Smoking increases blood pressure. This is especially pronounced after just smoking a cigarette.
Nicotine causes vasospasm, which slows blood flow and increases heart rate. That is why the risk of developing hypertension, and later experiencing a stroke or heart attack, is much higher for smokers.
It should also be noted that there are sudden changes in pressure from very low to dangerously high. This weakens the tone of the blood vessels, they become more fragile, so hematomas may appear on the body.