Osteocalcin is a protein and hormone produced by osteoblasts, the cells that create bone tissue. It is released by osteoblast cells during bone formation and partially enters the blood. Osteocalcin is considered the most informative marker for assessing bone formation. It binds calcium in bones, participates in the formation of bone tissue and its regeneration.
As a hormone in the blood, osteocalcin is capable of:
- Increase insulin production by the pancreas (, )
- Change blood glucose levels ()
- Stimulate testosterone ()
- Improve brain function ()
general characteristics
The main non-collagenous protein of bone and dental tissue. Synthesized by osteoblasts and odontoblasts, it reflects the metabolic activity of bone tissue osteoblasts. The synthesis of osteocalcin is directly influenced by calcitonin and parathyroid hormone. The synthesis process depends on vitamin K, C and is regulated by vitamin D3. Part of the synthesized osteocalcin that is not included in the bone matrix is excreted by the kidneys, so its level in the blood depends on the functional state of the kidneys. The level of osteocalcin in the blood can vary depending on the nature of metabolic disorders in the bone and is subject to large daily fluctuations. It is most advisable to determine osteocalcin simultaneously with b-Cross Laps, deoxypyridinoline, in order to determine the rate of bone metabolism (high or low), which will make it possible to select a drug for pathogenetic treatment.
What increases osteocalcin
Vitamin K
Vitamin K is necessary for the activation of osteocalcin in the body . A lack of vitamin K leads to a lack of osteocalcin in the bones. Vitamin K deficiency is also associated with low bone mineral density and an increased risk of fractures. ()
A placebo-controlled study in 40 healthy young men found that vitamin K supplementation increased osteocalcin levels only after taking it for 4 weeks. This has improved the body's use of insulin (by reducing insulin resistance) and maintaining healthy glucose levels. These results are consistent with other clinical studies of vitamin K supplementation in young men and older women and men. ()
An analysis of blood samples from 896 people found that most people do not get enough vitamin K from their diet, but vitamin K can be obtained as a supplement. The best type of vitamin K to take is vitamin K2, specifically the MK-7 form.()
However, people who take certain types of blood thinning medications (anticoagulants), such as warfarin, should be careful. There is a significant risk that some of these medications will become less effective if vitamin K2 in the form of MK-7 is taken at the same time. Therefore, this combination is not recommended.
VITAMIN K2 ACTIVATES OSTEOCALCIN
Exercise stress
Osteocalcin levels are higher in people who are more physically active .() An association between physical activity and higher osteocalcin levels was found in a study of 54 adolescents.()
One hour of exercise per day, 3 times per week for 12 weeks, increased osteocalcin levels and increased bone mineral density in 29 women with osteoporosis (age range: 71-78 years).
A study of 11 middle-aged men found that osteocalcin levels increased and remained at that level for several hours after a short period of high-intensity exercise (4 sets of 4 minutes of near-maximal exercise cycling). This same type of training also resulted in an increase in insulin sensitivity .()
There is also evidence that longer periods of less intense exercise may increase osteocalcin levels. A study of 31 middle-aged people found a significant increase in osteocalcin levels after cycling for an hour, 3-4 days a week.()
Another study of 39 obese but otherwise healthy young adults showed that an 8-week exercise program with 4 bouts per week increased blood levels of osteocalcin and leptin.
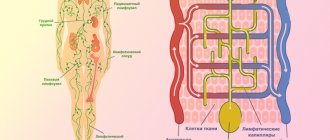
DIAGRAM OF THE RELATIONSHIP OF BONE CELLS OF OSTEOCLASTS AND B-CELLS OF THE PANCREAS WITH THE HELP OF INSULIN AND OSTEOCALCIN
Losing weight and restricting calories
In a study of 107 older adults, osteocalcin increased in the blood with the transition to a calorie-restricted . () In another study of 49 obese men, osteocalcin values increased after weight loss. ()
However, in a weight loss study of 71 postmenopausal women, no association was found between weight loss and changes in osteocalcin levels. Finally, in 178 obese people, increased blood levels of osteocalcin were associated with decreased body fat. However, after losing weight, osteocalcin levels did decrease.()
Vitamin D
Vitamin D directly stimulates the production of osteocalcin .(I) In a study of 76 obese menopausal women aged 51-63 years, vitamin D supplementation combined with a low-calorie diet resulted in increased osteocalcin levels and some improvement in insulin sensitivity.()
Zinc and manganese
Zinc supplementation increased osteocalcin levels in 22 short adolescents. However, these supplements did not change height itself when observed over 6-12 months.()
Manganese supplementation has also been shown to increase blood osteocalcin, bone mineral density, and bone formation in a mouse model.()
Olive oil
A 12-month study of postmenopausal women with reduced bone mass but no diagnosis of osteoporosis found that taking olive leaf extract resulted in increased blood levels of osteocalcin and increased bone density in the spine. ()
Consistent consumption of olive oil as part of the Mediterranean diet increases osteocalcin levels. This conclusion was reached in a study of 42 older men at high risk of heart disease.()
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation increased osteocalcin levels in rats. But this study requires certain additional evidence from further research.()
Ellagic acid
Ellagic acid is found in many fruits and vegetables, such as pecans, walnuts, pomegranates, raspberries, strawberries and cranberries. This substance works as an antioxidant that prevents cell damage. Ellagic acid promotes an increase in osteocalcin in rats after tooth extraction.()
Milk thistle
The main beneficial substance in milk thistle is silymarin . It promotes the growth of osteocalcin, helps bone healing, and increases bone density in mice with bone fractures.()
Icariin
Icariin is a flavonoid from the Korean Horny Goat Weed plant. A long-term 24-month study suggests that icariin may help prevent bone loss in postmenopausal women. Icariin maintains osteocalcin levels and prevents bone loss.()
Insulin therapy
Type 1 diabetes can cause changes in the skeleton, especially when glucose levels are poorly controlled. Some studies have shown that insulin treatment increases osteocalcin content, which leads to improved bone structure and bone flexibility in people with existing diagnosis of type 1 diabetes.()
Alendronate
Alendronate is a drug used to treat osteoporosis and Paget's disease. Use of alendronate in low doses is associated with increased osteocalcin and improved bone turnover.()
Teriparatide
Teriparatide is a parathyroid hormone used to treat osteoporosis. In a study of elderly women with rheumatoid arthritis, long-term treatment (48 weeks) with teriparatide increased osteocalcin levels in the blood.()
Since people with rheumatoid arthritis have a higher risk of osteoporosis , treatment with teriparatide may be beneficial.()
The information on this site has not been evaluated by any medical organization. We do not seek to diagnose or treat any disease. The information on the site is provided for educational purposes only. You should consult your physician before acting on information from this site, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, taking medications, or have any medical condition.
Rate this article
Average 4.9 Total votes (8)
Indications for use
1. As an addition to the diagnosis of diseases associated with increased bone turnover: Paget's disease, osteomalacia, osteoporosis, osteosarcoma, metastatic prostate or breast cancer with osteoblastic bone formation, primary hyperparathyroidism, renal osteodystrophy. 2. Monitoring and evaluation of the effectiveness of antiresorptive therapy (including hormone replacement therapy, use of bisphosphonates). 3. In pediatrics, an additional test for diagnosing rickets.
Increased calcium in the blood - what could it be?
Theoretically, there are three most likely clinical problems that could cause elevated blood calcium levels. All possible reasons for calcium levels in the blood being higher than normal are quite serious.
The first cause of high blood calcium
is primary hyperparathyroidism, a disease accompanied by the appearance of a tumor in one or more parathyroid glands (it would be more correct to say “parathyroid glands,” but the term “parathyroid glands” is very widely used). The main task of the parathyroid glands in the body is to maintain normal blood calcium levels. The cells of the parathyroid glands “know how” to sense the concentration of calcium in the blood plasma and, in accordance with the level of calcium, produce parathyroid hormone. The main effect of parathyroid hormone is to increase the level of calcium in the blood (by destroying bone tissue and releasing calcium from it into the blood, as well as by enhancing the absorption of calcium from primary urine in the kidneys and enhancing its absorption from the intestines). When a tumor occurs in the parathyroid gland, its cells stop sensing the concentration of calcium in the blood - it “seems” to them that there is no calcium in the blood, or that it is low. Tumor cells begin to uncontrollably produce parathyroid hormone, which sharply increases the breakdown of bone tissue and the release of calcium from it into the blood. As a result, in the laboratory we determine increased blood calcium and at the same time high levels of parathyroid hormone. Most often, such changes are also accompanied by a decrease in the level of phosphorus in the blood and an increase in the level of calcium in the urine. The danger of the disease lies in a decrease in bone density with a tendency to fractures, bone deformation, and decreased growth. An increased level of calcium in the blood leads to the deposition of calcium salts in the walls of blood vessels and heart valves, which reduces their elasticity and increases the tendency to thrombosis, which means the risk of strokes and myocardial infarction.
The second possible cause of elevated calcium
– this is the breakdown of bone tissue due to the occurrence of metastases of a malignant tumor in it. Metastases have a so-called lytic effect, i.e. destroy bone tissue and release calcium salts from it, which enter the blood and lead to increased calcium levels in the blood. In this case, calcium in the blood is increased, but at the same time the level of parathyroid hormone is within the normal range or at the lower limit of normal.
The third possible cause of high calcium levels in the blood
– development of neuroendocrine tumors that produce so-called PTH-like peptides. These tumors are most often located in the lungs, although their location can be very variable. The size of such tumors is usually small - from 4-5 mm to 1-2 cm. They “know how” to produce chains of amino acids, the sequence of which coincides with the active end of parathyroid hormone. Such peptides (they are called PTH-like because they are very similar in action to parathyroid hormone) cause a situation where calcium in the blood is elevated, but laboratory analyzers do not show an increase in parathyroid hormone levels in this case, since PTH-like peptides do not completely copy the parathyroid hormone molecule.
Interpretation:
- Primary and secondary hyperparathyroidism, Paget's disease, secondary osteosarcoma, healing period of bone fractures, renal osteodystrophy, chronic renal failure, tumors and bone metastases, diffuse toxic goiter, rapid growth in adolescents
- Hypercortisolism (Itsenko-Cushing disease and syndrome), therapy with glucocorticoid hormones, hypoparathyroidism, primary biliary cirrhosis, pregnancy, somatotropin deficiency, rickets in young children
Sample result (PDF)