Some people sometimes have a question: how to deceive an ECG? Moreover, some want to achieve a good conclusion in order to get a job, while others, on the contrary, want to make things worse so as not to serve in the army. There are other reasons that prompt a person to deliberately deceive not only the doctor, but also the diagnostic apparatus. Naturally, if you do not follow the doctor’s recommendations for preparing for the procedure, then the results obtained can be distorted, but will this help achieve your goal? And is it possible to simulate angina pectoris, arrhythmia, RGC syndrome and other diseases on an ECG?
Indications for the procedure
The examination is carried out only with a referral from a cardiologist. A visit to the doctor can be either planned or in case of complaints about heart function.
Frequent symptoms of impaired heart function include conditions such as:
- Compressive pain in the chest, as well as in the region of the heart, which radiates to the shoulder blade;
- Rapid pulse, which causes dizziness and increased heart rate;
- Shortness of breath with minor exertion;
- Periodic fainting;
- Dry barking cough;
- Swelling of the lower extremities.
Particular attention is paid to patients who have suffered a stroke, have congenital heart abnormalities or rheumatism.
Specialists conduct an examination and give a referral to see a doctor if they find:
- extraneous noise in the work of the heart muscle;
- with low or high blood pressure;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
The following categories of citizens are subject to mandatory examinations, namely:
- Persons with congenital or acquired heart disease;
- Athletes who have a serious load on their heart function;
- Patients undergoing examination before surgery;
- Women who are pregnant.
How is an ECG performed?
The examination is carried out in the supine position. To conduct the examination, you will be asked to remove clothing above the waist and expose your lower legs. To make the procedure more comfortable, wear comfortable clothing that can be quickly removed or unbuttoned at the chest. The places where the electrodes will be attached will be treated with alcohol and a special gel will be applied. Then, ten electrodes will be attached to the arms, legs and chest using cuffs and suction cups, which monitor the rhythm of contractions of the heart muscle. All you have to do is lie quietly for a couple of minutes and wait for permission from the doctor to get up.
What is electrocardiography and the features of its implementation?
The principle of this examination method is based on recording electronic pulses of the heart that occur during myocardial contraction. The pulses that have arisen are read by the cardiograph, displaying them in the form of a graphic curve on special paper.
Order of conduct:
- Before the procedure, all jewelry should be removed;
- Expose the chest, ankles and hands;
- Lie horizontally and relax;
- Before applying the electrodes, the nurse should treat exposed skin with a cotton pad, which is moistened with water for better conductivity of the impulses.
- Afterwards, 4 electrodes of different colors are applied to the limbs in a certain sequence;
- They are fixed on the chest using suction cups. The number of the latter should be 6 pieces;
- The electrodes are connected to the device, then they are registered.
A cardiogram is necessary when detecting any heart disease; it is also prescribed during a preventive examination.
Using this examination, you can identify such disturbances in the functioning of the heart as:
- Heart rhythm disturbances, for example, tachycardia, arrhythmia, extrasystole;
- Impulse conduction disorder, for example, antiventricular block;
- Myocardial nutritional disorders, for example, heart attack, ischemia;
- Congenital or acquired diseases, for example, disorders in the structure of the fibrous ring, valves, chord;
- Myocardial thickening, for example, atrial ventricular hypertrophy.
Persons who have reached the age of 40 years old must undergo an ECG every year. This will help to identify violations in time at the initial stage.
This study is quite informative, however, despite this, to clarify the diagnosis it is necessary to perform an ultrasound of the heart.
The study is very effective and indicative, but despite this, to clarify the condition of the myocardium, it is necessary to resort to ultrasound diagnostics of the heart.
Pros of the procedure
Among the undeniable advantages are the painlessness of the procedure, safety, and the ability to obtain reliable data. In addition, another advantage is that the procedure does not take much time.
Also, the procedure has no contraindications, and due to the mobility of the device, diagnostics can be carried out outside the clinic.
Disadvantages of the procedure:
The disadvantages of the procedure include the following:
- short recording;
- inability to record heart murmurs;
- impossibility of diagnosing heart defects and various tumors;
- To obtain reliable data, the procedure should be carried out at rest or under load.
Who should not conduct
There are absolute and relative contraindications to performing ECG stress tests.
Absolute:
- the first 2 days of acute myocardial infarction;
- unstable heartbeat without prior drug treatment;
- pronounced signs of aortic stenosis;
- acute pulmonary embolism;
- acute pericarditis and myocarditis;
- dissecting aortic aneurysm, occurring in an acute form.
Relative:
- aneurysm of blood vessels or heart;
- hypertension with systolic blood pressure above 200 and diastolic blood pressure above 110 mmHg. Art.;
- tachyarrhythmia of unknown origin;
- bradyarrhythmia with pronounced symptoms;
- heart block;
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;
- severe heart rhythm problems, fainting;
- mental or physical disorders that prevent adequate physical activity;
- electrolyte disturbances;
- joint diseases;
- severe anemia;
- endocrine diseases;
- severe obesity.
Testing is not recommended in case of fever, acute thrombophlebitis, or recent stroke. However, relative contraindications are neglected if the significance of the diagnostic results outweighs the risks.
During the procedure, the patient is constantly under the supervision of a specialist. If during the examination a severe arrhythmia, sharp chest pain, increased blood pressure, dizziness, darkening of the eyes occur, or your health deteriorates significantly, the testing is stopped immediately.
What is cardiac ultrasound?
Diagnosing the heart using ultrasound is a fairly new method used in cardiology, called echocardiography. The procedure is performed using a special device - an electrocardiograph, which regenerates ultrasound, the rays of which penetrate through the chest, determining the condition of the soft tissues and the thickness of the myocardium. This technique is absolutely safe for the patient. In addition, it has high information content and reliability of the results. The procedure is necessary for:
- determination of congenital pathology in children.
- identifying any diseases in adults;
- confirmation of the diagnosis of heart attack;
- thrombosis detection;
- detecting tumors in the breast;
- monitoring the state of the myocardium.
An ultrasound of the heart must be performed in cases where a person has abnormalities in the functioning of the heart that cannot be determined using an ECG or the diagnosis needs to be confirmed.
Ultrasound can reveal:
- Hidden heart defects;
- Enlargement and compaction of the myocardium;
- Accumulation of fluid in the heart;
- Pathological changes in the contractility of the organ;
- Establishing the speed and nature of blood movement through the aortas and chambers of the organ;
The disadvantage of the procedure is the inability to detect disturbances in the passage of electrical impulses.
This diagnosis allows you to identify even minor disturbances in the functioning of the heart that cannot be determined using an ECG.
Pros of the procedure
The advantages of ECG and ultrasound are very similar. Ultrasound diagnostics is also highly informative, painless, and harmless to the patient. The procedure does not require any special preparation. Using this method, you can assess the state of heart health, as well as track genodynamics.
In addition, the advantages of the procedure also include the fact that during the procedure the specialist can listen to how the heart beats. This allows you to determine whether there are extraneous noises in the heart. And due to the echogenicity of tissues and organs, a tumor can be noticed in time.
Cons of the procedure
The disadvantages of this procedure include:
- low resolution;
- limited image clarity;
- a lot of interference.
It should be mentioned that another disadvantage is the need to perform special training when it comes to diagnosing diseases of the abdominal organs.
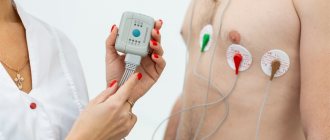
What does a halter look like?
This is a small camera that you attach to your pants belt or other item of clothing. It is connected to electrodes attached to the skin of the chest. Wearing a halter should not affect the wearer's comfort as it should behave as naturally as possible. During the 24-hour examination, the device monitors and records the patient's heartbeat. This also applies to sleep and rest time. Sometimes arrhythmia manifests itself during sleep. ECG signals are recorded from several or ten leads - 2, 3 or 12, depending on the device model.
A doctor or nurse must install the holter on the patient. Electrodes are attached in several places on the skin, after which the device is turned on and programmed. Throughout the study, the patient keeps a diary in which he writes down all his ailments and alarming changes in the body, indicating the exact time. This is to find out what is actually causing your heart problems.
So which study is better: ECG or ultrasound of the heart?
Ultrasound and ECG are two diagnostic methods that are used in cardiology to diagnose problems in the functioning of the heart muscle. Based on the results, the specialist assesses the degree of damage to the organ and selects the most appropriate treatment method.
The data obtained from both studies have equally high information content, but the results of the ultrasound examination provide a more meaningful picture. That is why, before conducting any examination, you should visit a cardiologist, who, based on the patient’s complaints, will be able to determine the most appropriate examination method. In most cases, an ECG is considered the primary procedure, because it allows you to get a general picture of the condition of the heart muscle. If the cardiologist does not like the resulting picture, then he can prescribe a more accurate procedure, namely an ultrasound.
Both methods are independent of each other and it is not possible to determine which one is better, because both of them must be completed periodically if there are complaints about the work of the body. Thus, timely detection of heart disease will help to avoid more serious consequences.
How can x-rays be dangerous?
X-rays are electromagnetic waves in the range between ultraviolet and gamma radiation.
Accordingly, an X-ray machine is a source of ionizing radiation, a serious overdose of which leads to the destruction of the integrity of DNA and RNA chains. They are not always restored, because the ability of the DNA molecule to withstand the negative effects of ionizing radiation is limited. Therefore, the annual effective dose approved by SanPin is determined based on the rapid restoration of DNA and RNA molecules, as well as the amount of radiation at which the damage will be insignificant.
Possible consequences of abuse of the procedure:
- cancer of any system or organ;
- radiation sickness;
- mutations;
- genetic changes, etc.
The consequences can be unpleasant and even scary, but all this becomes possible only with huge overdoses of ionizing radiation, which is simply impossible to obtain in modern digital X-ray machines. Especially if you are undergoing examination on the recommendation of a doctor.
The average annual dose of natural radiation is 2.4 mSv per person, and 1 hour on an airplane costs 0.003 mSv.
Now, for a better understanding, let’s look at the radiation doses that a patient receives during radiography:
- chest x-ray - 0.03 mSv;
- mammography - 0.05 mSv;
- intraoral radiography - 0.02 mSv;
- cervical spine - 0.03 mSv;
- fluorography - 0.03 mSv;
- X-ray of the skull - 0.04 mSv;
- X-ray of the intestines - 0.02 mSv.
It is obvious that X-ray examinations using modern digital devices are completely safe
and do not provide significant radiation exposure to the human body. This increases the chances of detecting a serious disease at an early stage and prescribing the most effective treatment.