The change of seasons brings pleasant variety to our lives. After sweltering summer days , the coolness is pleasant; the monotonous green of the leaves is replaced by a riot of colors. But when the leaves fall and the temperature is no longer comfortable, many feel like their battery is dead. A person is overcome by apathy and constant drowsiness . I want to eat a lot, my body requires sweets, fatty foods, fried foods, and not getting up from the couch. But no one canceled their studies or work. Constant absent-mindedness and weakness have a bad effect on work results and prevent you from studying well, making a career, or running a business. Some take vitamins or go to the doctor and get examined. It is useful to monitor your health and undergo an annual medical examination, but autumn drowsiness, if there are no other unpleasant symptoms, should not be a cause for concern. This is a natural reaction of the body to cold weather and reduced daylight hours .
Physiological reasons
When weakness is constant and you want to sleep, you need to look for why this happens in your daily habits. Sometimes a person himself becomes the cause of this condition.
Physiological causes of drowsiness:
- Lack of sleep - sleep deficit cannot be made up over the weekend, this is a myth. If you fail to sleep 7–9 hours, fatigue and weakness become constant companions.
- Night or daily mode of operation - wakefulness and sleep do not coincide with circadian rhythms, hence the poor quality of rest and constant fatigue.
- Poor sleep hygiene - sleeping in a bright, stuffy or noisy room, which is especially important in the summer, gadgets and food less than 2 hours before bedtime.
- Sedentary lifestyle - Scientists have discovered a connection between lack of physical activity and drowsiness.
- Physical fatigue - too active sports activities exhaust the body, it does not have time to recover.
- Alcohol – The body has a hard time processing alcohol, especially at night. Therefore, you should not drink “to sleep soundly.”
- Smoking creates a deficiency of oxygen in the blood, which causes the brain to function worse and fatigue.
- An abundance of simple carbohydrates in the diet often causes blood sugar levels to jump, and when they drop, you feel tired.
Those who have chronic pain in any part of the body may also feel tired due to poor sleep. It is difficult to call this reason physiological, but in this case, drowsiness is not a consequence of unknown pathologies in the body, but a consequence of existing ones.
Read also: Pain in the back of the head
Which doctor should I contact about weakness?
If weakness is the main complaint, then it is best to consult a general practitioner (general practitioner or family doctor).
If you have stomach problems due to weakness, you can consult a gastroenterologist.
If weakness is accompanied by pain or discomfort in the heart area, you should consult a cardiologist.
Be prepared for the fact that you may be referred for consultation to doctors of such specialties as a hematologist, oncologist, neurologist, endocrinologist, or psychotherapist.
Possible diseases
When a person is weak and constantly wants to sleep, this is due to poor quality rest or processes that occur inside the body. In some cases, the cause is damage to the nervous system.
Diseases that cause weakness and drowsiness:
- Apnea or snoring is the cessation of breathing during sleep followed by noisy inhalation. Because of this, little oxygen enters the body, the quality of sleep and well-being in the morning suffer.
- Deviated nasal septum - a person has difficulty breathing, including during sleep, he inhales little oxygen, which makes it difficult for the brain to function and leads to fatigue.
- Chronic runny nose - the supply of air, and therefore oxygen, decreases. The brain works worse, the patient feels unwell.
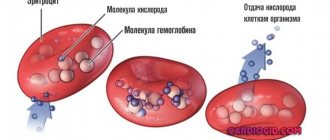
- Anemia, including iron deficiency - the brain does not have enough oxygen, since red blood cells do not tolerate it well.
- Hypovitaminosis B, D and C - these vitamins affect the state of the nervous system, and ascorbic acid is responsible for the condition of blood vessels.
- Hypothyroidism - a lack of thyroid hormones leads to fatigue, drowsiness, and apathy.
These are the most common causes of drowsiness, but not all. Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis after a comprehensive examination.
Why is autumn drowsiness dangerous?
Drowsiness and weakness occur due to the approach of winter , but it can be the first sign of dangerous diseases: diabetes, heart failure, atherosclerosis, anemia, oncology. If there are other symptoms (increased sweating, palpitations, dry mouth, constantly thirsty, loss of appetite, weight loss, etc.), discuss the reasons for lethargy with your doctor.
Unless you have an underlying medical condition, drowsiness can also be life-threatening. Difficulty concentrating can be deadly for drivers and pedestrians, and for people who operate complex machinery and equipment. Absent-mindedness is not life-threatening, but it can create big problems for a student, accountant, or store clerk.
Diagnostics
If you constantly want to sleep and feel weak, you should first look for the reasons yourself.
Checklist for self-control:
- How long do you sleep?
- What are the sleeping conditions: light, noise, fresh air?
- Is there dinner, gadgets or TV 2 hours before bed?
- Is there physical activity? If so, isn't there a lot of it?
- How many simple carbohydrates are in your diet?
- Are there any bad habits?
If there is something wrong with the conditions, you need to correct it and observe for 2-3 weeks. If there is no improvement, consult a therapist.
List of examinations:
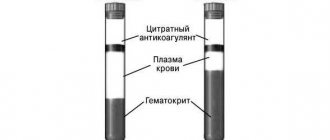
- general blood analysis;
- analysis of the level of vitamins B, D and C;
- analysis of free T3 and T4 content, TSH.
You need to go to your therapist with the test results. He will evaluate them, select therapy or refer them to a specialist for further examination and clarification of the diagnosis.
Dear patients! Remember that only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, determine the causes and nature of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. You can make an appointment with our specialists or call a doctor at home by calling 8-(4822)-33-00-33
Be healthy and happy!
When should you see a doctor if you feel weak?
If weakness does not go away within a few days or, moreover, lasts more than two weeks, you should definitely consult a doctor.
You should not hesitate to consult a doctor if weakness is accompanied by symptoms such as:
- dyspnea;
- cough;
- fever, chills, increased temperature;
- stomach upset;
- sudden weight loss;
- mood changes, apathy, depression.
Vitamin deficiency
It is known that asthenia can be caused by a deficiency of certain vitamins and microelements, in particular vitamin D. Low levels of this vital nutrient in the blood can have a negative impact on performance and quality of life in general7. The results of clinical studies indicate that a decrease in the level of sunshine vitamin in the blood of women less than 29 ng/ml is associated with significantly more frequent complaints of increased fatigue compared with a level of more than 30 ng/ml8.
Many biochemical processes occurring in the body every day are accompanied by fluid loss, which is important to compensate. Research shows that even small amounts of fluid loss can lead to decreased energy levels, decreased concentration, and increased fatigue9.
Physical inactivity and stress
One of the most common causes of increased fatigue among middle-aged and elderly people is low physical activity8. According to research, people with low activity levels have insufficient strength and endurance, which limits their ability to exercise. However, as you start training, fatigue decreases. Moreover, the effectiveness of training is manifested even with minimal loads11.
Another scourge of our time is chronic stress. It has been proven that they are associated with increased fatigue and asthenia12.
References
- Hagemans MLC et al. Impact of late-onset Pompe disease on participation in daily life activities: Evaluation of the Rotterdam Handicap Scale // Neuromuscul. Discord. Elsevier, 2007. Vol. 17, No. 7. P. 537–543.
- Pizova N.V. Fatigue, asthenia and chronic fatigue. What it is? // Cons. medicum. 2012. T. 14, No. 2.
- Shakirova I.N., Dyukova G.M. Asthenia is an interdisciplinary problem // Difficult patient. 2012. T. 10, no. 5. pp. 14–16.
- Chen MK The epidemiology of self-perceived fatigue among adults // Prev. Med. (Baltim). Academic Press, 1986. Vol. 15, No. 1. P. 74–81.
- Westerterp KR Diet induced thermogenesis. // Nutr. Metab. (Lond). BioMed Central, 2004. Vol. 1, No. 1. P. 5.
- Blomstrand E. A Role for Branched-Chain Amino Acids in Reducing Central Fatigue // J. Nutr. 2006. Vol. 136, No. 2. P. 544S–547S.
- Johnson K., Sattari M. Vitamin D deficiency and fatigue: an unusual presentation // Springerplus. 2015. Vol. 4, No. 1. P. 584.
- Ecemis GC, Atmaca A. Quality of life is impaired not only in vitamin D deficient but also in vitamin D-insufficient pre-menopausal women. // J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2013. Vol. 36, No. 8. P. 622–627.
- Ganio MS et al. Mild dehydration impairs cognitive performance and mood of men // Br. J. Nutr. 2011. Vol. 106, No. 10. P. 1535–1543.
- Hartzler BM Fatigue on the flight deck: The consequences of sleep loss and the benefits of napping // Accid. Anal. Prev. 2014. Vol. 62. P. 309–318.
- de Vries JD et al. Exercise as an Intervention to Reduce Study-Related Fatigue among University Students: A Two-Arm Parallel Randomized Controlled Trial // PLoS One / ed. Fisher G. 2021. Vol. 11, No. 3. P. e0152137.
- Doerr JM et al. Reciprocal relationship between acute stress and acute fatigue in everyday life in a sample of university students // Biol. Psychol. 2015. Vol. 110. P. 42–49.
GZEA.PD.18.09.0435n
CNS lesions
Any brain damage caused by infection, trauma, postoperative complications or systemic diseases can lead to the development of drowsiness. Associated symptoms:
- headache;
- fatigue;
- lethargy;
- violation of attention and active orientation;
- change in facial expressions.
Drowsiness develops as you fall into a coma. Patients in a state of partial unconsciousness complain of headache, nausea, dizziness, aggravated by bright light and loud sounds.
Drowsiness also occurs when poisoned by poisons that affect the central nervous system. As a result of exposure to endogenous or exogenous toxins, depression of the central nervous system occurs. The person complains of weakness, headache, lethargy, and blurred vision. In some cases, drowsiness is replaced by bouts of excitement, after which severe fatigue sets in. The listed symptoms are alarming and indicate the need for emergency medical care.
Treatment of fatigue and its causes
To eliminate weakness, drowsiness, and constant fatigue, it is necessary to treat the disease that provokes them. If this is osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, the resulting vertebral artery syndrome or other disorders, treatment is selected by a neurologist. But in any case, it is always developed strictly on an individual basis, taking into account the nature of the existing pathological changes, the degree of their severity and the individual characteristics of the patient.
In the absence of critical changes, patients are prescribed conservative therapy. It is always comprehensive and aimed at:
- increasing the intensity of recovery processes in the intervertebral discs;
- improving the quality of blood circulation;
- relief of inflammatory processes;
- normalization of nerve conduction;
- restoration of normal anatomy of the spinal column;
- improvement of general condition by eliminating the symptoms of the disease (symptomatic therapy).
Thus, treatment is simultaneously carried out aimed at eliminating the underlying disease and improving the patient’s quality of life. Therefore, it is always comprehensive and includes:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- exercise therapy;
- manual therapy.
In addition, when spinal pathologies are detected, it is important to adjust your lifestyle and bring it as close to healthy as possible. First of all, the level of physical activity requires a review: it is important to avoid prolonged stay in a static position, especially with a bowed head, as this contributes to the progression of degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs. Therefore, all patients with cervical osteochondrosis, and especially office workers, need to make it a rule to take breaks from work at least every hour and spend them actively.
But during exacerbation of the disease, bed rest and limitation of physical activity are indicated.
It is also recommended to review your diet. Eliminating processed foods, fast food and other harmful products from it will have a positive effect on the condition of blood vessels and will allow you to lose weight. This will reduce the risk of developing vertebral artery syndrome and rapid progression of the underlying disease.
Also, if you experience increased fatigue, it is important to:
- normalize work and rest schedules;
- review your work schedule and workload distribution in order to allocate the most productive hours for solving important tasks;
- use complex vitamin preparations, and also increase the amount of fresh fruits, vegetables and berries in the daily diet.
Often a change of environment and a short vacation have a positive effect on the psycho-emotional state.
Drug therapy
For diseases of the spine, the use of a complex of drugs is indicated, which can be prescribed in different dosage forms depending on the severity of its course. These may include:
- NSAIDs – used to relieve pain and inflammation;
- muscle relaxants - indicated to eliminate muscle spasms, which helps reduce pain and limitations in mobility;
- corticosteroids – used to relieve severe inflammatory processes and are prescribed exclusively in short courses;
- chondroprotectors - used to activate the processes of regeneration of intervertebral discs, but are most effective only in the initial stages of development of degenerative-dystrophic changes;
- B vitamins – indicated to improve nerve conduction;
- vascular drugs - prescribed to improve blood circulation;
- Vitamin D – is used to improve the condition of bone tissue and the processes of higher nervous activity.
In case of severe pain that makes a person unable to work, novocaine or lidocaine blockades can be performed. They allow you to almost immediately eliminate painful neck pain, but do not affect the causes of their occurrence. But such procedures are carried out exclusively in medical institutions.
To solve the problem of increased fatigue and decreased performance, especially mental, patients may additionally be prescribed a set of medications to normalize sleep, restore normal levels of mental and physical activity, and generally improve overall well-being. This:
- nootropics;
- neurometabolic drugs;
- herbal preparations;
- anxiolytics.
Taking such medications is absolutely safe and is not accompanied by the risk of side effects, provided they are selected correctly. They are prescribed in courses of varying durations and quickly allow you to:
- increase memory, attention;
- increase your waking time;
- increase resistance to stress and the negative influence of external factors;
- reduce symptoms of weakness and lethargy;
- eliminate anxiety, irritability, apathy.
Therefore, drugs from these groups are included in the treatment regimen for almost any disease and pathology of the spine, in particular in cases where patients complain of increased fatigue and decreased performance.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed outside the period of exacerbation and exclusively in combination with other treatment methods. Most often, for increased fatigue caused by diseases of the spine, the following courses are indicated:
- electrophoresis with the introduction of drugs;
- ultrasound therapy;
- traction therapy;
- detensor therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- UHF.
Exercise therapy
Therapeutic exercise is one of the most important elements of treatment, acting directly on pathologically altered tissues. Thanks to it, it is possible to normalize muscle tone, in particular, to strengthen muscles that have weakened as a result of leading a sedentary lifestyle. This is important because a strong muscle corset is the basis for a healthy spine. Therefore, exercise therapy helps stop the progression of pathological changes in the intervertebral discs, and, in addition, activates blood flow and increases the intensity of metabolic processes. This has a positive effect on the condition of all anatomical structures and helps eliminate weakness.
But for each patient, the load and nature of the exercises are selected individually, taking into account the characteristics of the existing disease, the patient’s age, his level of physical fitness and other factors. But exercise therapy should always be performed in a calm environment without haste or sudden movements. At the same time, their regularity is extremely important. Therefore, in order to achieve maximum results, it is necessary to engage in physical therapy daily.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy sessions are one of the mandatory components of the treatment of diseases of the cervical spine. They can be carried out outside the period of their exacerbation and allow one to obtain a pronounced therapeutic effect, as well as improve the general condition and get rid of increased fatigue. But it is important to trust only qualified specialists to carry out manual therapy, since the cervical spine is easily injured. Therefore, errors in the technique of performing various techniques can lead to a deterioration in well-being.
Properly conducted manual therapy sessions allow you to:
- restore the normal position of the vertebrae as completely as possible and thereby reduce the load on the intervertebral discs, release the pinched spinal roots, normalize the position of the vertebral arteries and the length of the spinal canal;
- activate blood circulation, which has a positive effect on the course of regeneration processes;
- eliminate weakness and increased fatigue by normalizing blood supply to the brain and cerebrospinal fluid circulation;
- improve the functioning of internal organs that have undergone changes as a result of disturbances in their innervation due to compression of the nerve roots;
- increase the body's overall resistance to negative external influences.
Thus, fatigue and decreased performance may indicate not only professional burnout, but also be a sign of the development of disorders in the functioning of the body. Most often, spinal diseases and in particular osteochondrosis manifest themselves in this way. However, if you immediately pay attention to such changes in well-being and contact a neurologist, treatment will be as easy and quick as possible, and the condition will progressively improve. But even in more advanced cases, you can achieve a significant improvement in well-being and restoration of normal performance. The main thing is not to ignore the problem, but to seek qualified medical help.
0 0 votes
Article rating
Symptoms
The main symptom of chronic fatigue syndrome is - as you might guess - the presence of chronic severe fatigue over a long period of time. Typically, this condition appears after a viral infection or prolonged stress. Since the development of the syndrome is often associated with a viral infection, other specific symptoms are usually noted at the onset of the disease:
- fever,
- a sore throat,
- lymphadenopathy with enlargement and tenderness of the axillary and cervical lymph nodes (other localizations are less common),
- sweating at night,
- pain in muscles and joints.
In most patients, the symptoms of chronic fatigue syndrome, having begun during the period of a flu-like illness, decrease somewhat after 1–2 weeks, but recovery does not occur. In some cases, the disease develops a long time after the first attack.
There is no specific laboratory diagnostic test that can show whether a person has chronic fatigue syndrome, so the diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture. The doctor pays attention to the following symptoms, which should be observed for at least 6 months:
Basic
Fatigue during the last 6 months (constant or periodically increasing, or suddenly occurring, not going away after sleep or rest), limitation of motor activity and a decrease in performance by more than 50% in the absence of other causes or diseases that can cause chronic fatigue.
Additional
- increased body temperature,
- pain and sore throat,
- soreness and slight (up to 2 cm) enlargement of the lymph nodes, most often the cervical and axillary ones,
- generalized muscle weakness, muscle pain,
- joint pain without visual changes in the joints,
- headaches, unusual, new to the patient,
- rapid physical fatigue, long-term (more than 24 hours) general weakness after physical activity previously tolerated by a person normally,
- sleep disorders (insomnia or, conversely, drowsiness),
- neuropsychiatric disorders (photophobia, depression, memory loss, increased irritability, decreased ability to concentrate),
- rapid development (within hours or days) of the entire symptom complex.
The diagnosis of chronic fatigue syndrome is established when the main symptom and at least six additional symptoms are present. In this case, at least two additional symptoms must be objective, that is, those that can be determined by a doctor (from the first three on the list).
The following conditions may also occur with chronic fatigue syndrome:
- dizziness,
- increased anxiety,
- chest pain,
- weight loss,
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract,
- allergic reactions,
- increased sensitivity to medications, alcohol, strong odors,
- increased sweating.
Brain contusion
With a brain injury, negative symptoms increase gradually, so the patient’s general well-being does not always correspond to the severity of the injuries received. Drowsiness and apathy may be the only signs indicating a pathological condition. As swelling increases, tissue compression increases, intracranial pressure increases, which causes symptoms such as headache, nausea, and vomiting. Urgent care should be called if the patient is sleeping after the injury without taking sedatives.