Detailed description of the study
Hypertension (hypertension) is a chronic increase in systolic blood pressure of more than 140 mm Hg. Art. or diastolic blood pressure more than 90 mm Hg. The disease occurs without external causes and primary damage to other organs, such as the kidneys, which is why it was previously called “essential” hypertension
The World Health Organization estimates that 54% of strokes and 47% of cases of coronary heart disease are a direct consequence of high blood pressure, making hypertension an important risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
Blood pressure in the body is regulated by many mechanisms, including: vascular resistance to blood flow, the effect of hormones on the arteries, signals from the nervous system, and the rate of fluid filtration in the kidneys. Changes in the action of these mechanisms lead to disruption of pressure regulation. The predominant cause of hypertension is thought to be increased vascular resistance, often in combination with increased arterial stiffness.
The presence of hypertension implies a genetic predisposition. Genes have been identified whose changes (mutations) increase the risk of hypertension. They are associated with changes in the regulation of arterial wall resistance and other mechanisms, but the contribution of environmental factors is also important.
It should be taken into account that external factors such as excess salt intake, obesity, smoking and alcohol abuse are important in the occurrence of hypertension along with genetic predisposition. They ultimately determine how severe the increase in blood pressure will be.
Most people with hypertension do not show any signs of increased blood pressure, even if the levels reach dangerously high levels. Some report headaches, shortness of breath, or nosebleeds, but these symptoms are not specific to hypertension and may be related to underlying conditions.
In view of this, people whose close relatives suffer from hypertension and have suffered a heart attack or stroke need regular monitoring of blood pressure levels. Screening for genetic predisposition to hypertension can help identify causes of high blood pressure and assess the risk of hypertension among those with close relatives with the disease.
The study aims to identify mutations in genes associated with an increased risk of hypertension, such as:
- Angiotensinogen (AGT). Polymorphism: Met235Thr (M235T; Met268Thr; M268T);
- Angiotensinogen AGT: 521 C>T(Thr174Met);
- Adducin 1 alpha ADD1: G1378T;
- Angiotensin II receptor type 1 AGTR1: A1166C;
- Angiotensin II receptor type 2 AGTR2: 1675 G>A;
- CYP11B2 - Cytochrome P450 gene, family 11 B;
- G protein polypeptide 3 GNB3: C825T;
- Endothelial nitric oxide synthase type 3 NOS3: T-786C;
- Endothelial nitric oxide synthase type 3 NOS3: Glu298Asp (E298D).
Blood donation and hypertension
Donating blood is a rather serious procedure and not everyone can become a donor. There are certain criteria that allow us to determine indications and contraindications for sampling. First of all, this concerns the presence of certain diseases, especially serious ones such as HIV infection, AIDS, the presence of cancer or diseases of the cardiovascular system. For such indications, blood sampling is strictly prohibited, because otherwise you can harm not only yourself, but also the patient.
The prohibited category also includes diseases such as hypertension. It is characterized by a constant or periodic increase in blood pressure. Accordingly, if this deviation is present, it is prohibited to donate blood, with the exception of acceptable blood pressure readings and the immediate need for a donor. This is what will be discussed in this article.
Why is hypertension dangerous for donating blood?
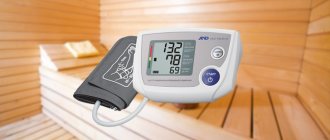
Pressure surges always cause discomfort. This can be explained by the fact that the walls of the blood vessels in our body are under a certain pressure. This is the number with which blood presses on the walls of blood vessels. For example, when measuring blood pressure, they get two-digit readings - this is 120/80. For an adult, this is the most optimal pressure at which you can feel good.
The first number shows systolic pressure, that is, the force with which blood presses on the walls of blood vessels after a heartbeat.
The second number characterizes pressure readings between heartbeats. The same can be said with confidence. That each person’s blood pressure is different, but on average in a calm state it should not exceed 140/90.
There are also three stages of hypertension, which are respectively characterized by increased pressure. In the first stage, indicators within 160/100 can be considered normal. The level may change while the patient is resting or vice versa during physical activity. As for the second stage, the indicators there are slightly higher, which in turn is characterized by other symptoms. These are numbers within 180/100, which can change during rest or exercise. With hypertension of the third stage, the highest rates can be counted. These are precisely those catastrophic numbers at which a person must keep his blood pressure under control at all times. These are limits of 200/115. The last stage is the most dangerous, since such hypertensive patients cannot not only donate blood, but also put themselves under physical activity or stress.
All stages are characterized by almost the same symptoms - headache, sleep disturbance, dizziness, heart pain, and severe vascular complications. Also for the third stage, a characteristic clinical picture is in the form of damage to the heart and brain, which can lead to a heart attack. The kidneys and fundus of the eye begin to suffer no less, and complaints arise accordingly.
Can hypertensive patients donate blood?
The loss of any amount of blood is some kind of trauma for the body. It’s just that a healthy person can tolerate it normally, but a sick person will receive a significant blow. Therefore, only a healthy person who has undergone a series of relevant tests and some other examinations should categorically donate blood.
Hypertension is a fairly serious disease, so we can say with certainty that all hypertensive patients, regardless of stage, cannot donate blood . During the examination, you will need to take a general blood test, measure your blood pressure and review your history of existing diseases. Therefore, the doctor will definitely not allow the patient to donate.
With hypertension, the body experiences constant discomfort, since high blood pressure still affects health. If you give an additional push, the person may have a heart attack, which will significantly worsen their well-being. Any doctor can tell you about this, especially for older people. In most cases, a person does not immediately notice an increase or decrease in pressure.
We often blame bad weather conditions or temperature changes. Although in fact you can measure the pressure and see that its indicators change and in some way make themselves felt. It is much worse for those people who do not feel pressure changes. This is very dangerous, because even with the highest blood pressure, you will feel satisfactory and you can continue to do either physical activity or something else that is so dangerous in such situations. Therefore, you can donate blood during pressure surges only for tests .
But do not forget that analyzes also have their limitations. If you have hypertension, it is not recommended to take blood tests more than twice a week. Even the most minimal intervention can negatively affect the well-being of hypertension.
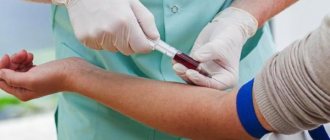
Why take a blood test for hypertension?
Such an analysis is simply irreplaceable for hypertensive patients. After all, with the help of it, doctors are able to determine the condition, disease, its main cause and the condition of the organs under great pressure. In this case, blood is taken from a vein on an empty stomach, as with all other tests. The presence of the necessary indicators is determined. This is also a wonderful opportunity to choose the right treatment for the patient.
If the test results are not very high and the pressure is also within the normal range for the first stage of hypertension, then in exceptional cases it is allowed to donate blood as a donor. In such situations, the donor is placed under strict control and pressure drops are monitored throughout the entire collection period.
If the first symptoms of an increase or deterioration in the donor’s well-being occur, the procedure is stopped. Such cases may occur when there is an urgent need for donation. For example, after severe blood loss during surgery or childbirth in a woman. Such emergency cases are more than dangerous, and finding a suitable donor is not always possible. Therefore, blood is taken under strict control.
Who else should not donate blood?
This question torments almost every person who wants to help the sick and become a donor for them. For example, come once a month and leave blood for those who really need it. But despite this, medicine has its own rules and restrictions.
You can ignore some rules for blood collection, but in no case restrictions regarding donation. People who have: AIDS, syphilis, HIV infection, tuberculosis, viral hepatitis, complete lack of hearing and speech, hypertension, congenital or acquired heart disease, malignant tumors, endocarditis, complete blindness, various lung diseases, gastric ulcer are subject to categorical restrictions. , pustular diseases of the stomach, myopia, psoriasis, trachoma and many others. Such diseases pose a danger not only to the donor, but also to the patient himself.
Together with the blood, the disease can spread to someone else, because all the smallest inflammatory bodies are present in the blood. In order to determine the presence of certain diseases, before taking blood, the donor undergoes a number of specific testing procedures. And only after this is it allowed to become a donor.
Other diseases of the cardiovascular system
There are still some problems of the heart and its entire system that do not allow donating blood. Along with hypertension, they also play a significant role, as they are quite serious and dangerous to health. You may not know about the presence of some of them, but before taking blood it is better to double-check so as not to further harm your body. These are atherosclerosis, coronary disease, heart defects and inflammatory processes, and some vascular diseases. In such cases, death can often occur, so donation is out of the question. Such a patient himself needs help and takes many medications.
There are quite a few cases in medicine where patients, not knowing their main diagnosis, decide to donate. This can result in a tragic outcome for the patient. A long time ago, medical scientist Davydovsky called such diseases uncharacteristic of the environment, since with such symptoms a person cannot adequately adapt to progressive urbanization. It is urbanization that is associated with a person’s lifestyle and is influenced by stressful situations. Ecology and some features of civilization also have a significant impact on health and well-being.
Benefits of donating blood in the absence of hypertension
We can say a lot about the fact that the development of certain diseases is influenced by a person’s image or ecology. But the main focus is the individual disposition of this or that person. But, despite many such factors, doctors say that donating blood can and should be done in the absence of such diseases.
During donation, the blood in the body itself is renewed. That is, the entire amount taken is replenished over a certain time and stimulates the work of hematopoietic cells. We can say that this is even very useful, because it is necessary to rejuvenate not only the skin, but also the cells of our body. Thus, the body receives an impetus to work more actively to replace the lost amount of plasma. Since blood can be donated not only in its entirety, but also in its individual components, this is a little better for the body. The active work of hematopoietic cells in this case is aimed directly at the production of red blood cells, leukocytes or platelets. It is these components that can be donated separately from plasma.
Women can become a donor once every two months, and men - once a month. Thus, you help not only the sick patient, but also yourself. The main thing is to help the body work immediately after the test. You can drink sweet tea with chocolate or something else delicious. Since glucose is no less important in hematopoiesis, its amount must be sufficient for the active functioning of the bone marrow. Rest a little after the procedure and you can rest assured that the procedure was successful and your blood will benefit those who need it.
The benefits of donating biomaterial
Blood donation can be carried out by people without diseases in the cardiovascular system. The body regularly independently renews the composition of this tissue and all cells, but the donation of components or whole fluid is considered a beneficial action.
Donation is allowed for men no more than 5 times a year, women can donate material no more than 3 times a year. Doctors recommend taking a break between donations of 6 months, then the liquid will be restored in composition and volume. Women are allowed to donate less blood and have regular monthly blood loss (menstruation).
The procedure has many beneficial properties. Abdominal organs such as the spleen and liver are involved in renewing tissue composition and recycling old blood cells. If you periodically undergo the donation procedure, the organs will be unloaded, and the youth of the body will also be prolonged. A person will be better prepared for blood loss, and it will be easier to endure operations and injuries. Immune cells will be renewed and activated, which will make the body more resilient.
Blood donors are less likely to suffer from cardiovascular diseases in older age. The risk of developing atherosclerosis, ischemic heart disease, arrhythmias, and thrombosis is reduced. This is due to the constant renewal of the composition of connective tissue.
There are also economic benefits from the process:
- detection of HIV and AIDS, hepatitis and other diseases during testing of material at the station;
- determination of group affiliation and Rh factor;
- receiving benefits in the form of days off from work and a small monetary reward for the procedure;
- receiving benefits for honorary donation after donating blood more than 40 times.
Donating blood if you have hypertension is not allowed by medical staff. Some scammers manipulate people's illiteracy and offer bloodletting from a vein, which is equivalent to full surrender. You can choose this treatment method after preliminary discussions with a specialist.
Who else should not donate blood?
Arterial hypertension is not the only contraindication to donating blood and its components. People with the following diseases are not allowed to donate:
- AIDS;
- HIV;
- Hepatitis;
- Tuberculosis;
- Congenital, acquired heart defects;
- Blood diseases;
- Myopia, blindness;
- Lack of speech, hearing;
- Lung diseases;
- Malignant neoplasms;
- Ulcerative, pustular lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, etc.
The following donors are also not allowed to donate blood:
- Pregnant and lactating women, within 1 year after childbirth and 1 month after the end of the breastfeeding period;
- Women during menstruation and within 5 days after their end;
- Persons who have had an acute respiratory infection (within 1 month after recovery);
- Persons with skin rashes, mucosal lesions caused by allergies or other reasons.
Using drugs at least once also becomes a contraindication. You cannot donate blood for 2 weeks after a course of antibiotic treatment, or for 1 year after surgery.
Is it possible for hypertensive patients to donate blood and what are the dangers of donating at high blood pressure?
In order to be a donor, a person must not only be an adult, his health must meet certain medical criteria, which is confirmed by the results of laboratory tests, for example, testing for AIDS and other infections, as well as the absence of certain diseases, including hypertension.
However, some hypertensive patients claim that donation only benefits their body, improving their well-being. Is this really true, is it possible to donate blood with high blood pressure, and what do cardiologists say about this?
Why you should not donate blood if you have hypertension
Donating blood requires meeting certain conditions. You will first need to undergo a body examination. It is necessary to take a test to determine the presence or absence of diseases that are transmitted through blood.
Donation has contraindications. Many people have a question: is it possible to donate blood if you have hypertension?
Previously, bloodletting was done for high blood pressure. A slight loss of blood contributed to the normalization of the condition.
Can donation improve well-being in hypertension? Does donating blood help lower blood pressure? You will find answers to your questions in this article.
Benefits of donating blood in the absence of hypertension
According to doctors, donation is good for health if there are no contraindications. The procedure promotes blood renewal, stimulating the functioning of the hematopoietic organs.
The entire amount taken is replenished in the body within a certain time. Blood can be taken in separate components:
- Cellular components (platelet-, erythrocyte-, leukocyte-containing);
- Plasma;
- Plasma components (cryosupernatant plasma, cryoprecipitate).
It will be a little more beneficial for the body. After the procedure, the work of the hematopoietic organs will be aimed at producing only red blood cells/leukocytes/platelets.
Is it possible to donate blood if you have hypertension?
Donating blood is a human right, not a direct responsibility. In our state, you are allowed to be a donor upon reaching the age of majority. Only healthy people who have been tested for HIV, hepatitis viruses, herpes and other serious diseases that are transmitted hematogenously are allowed to participate in this procedure. Donation is contraindicated in patients with hyperglycemia, a reduced amount of hemoglobin, a history of oncology, as well as those who have drug addiction, are mentally ill or suffer from cardiovascular pathologies.
Requirements for the donor, his rights and obligations
Citizens of the Republic of Belarus, as well as foreign citizens and stateless persons permanently residing in the Republic of Belarus, aged from eighteen to sixty years, who have full legal capacity, have undergone a medical examination, do not suffer from diseases and are not in conditions where in which donating blood and its components is contraindicated.
A prerequisite for performing the donor function is the prior written consent of the donor to take his blood and its components.
At what pressure can you become a donor?
People who do not have serious illnesses, weigh at least 50-60 kg, and are not addicted to alcohol and drugs can be allowed to donate.
After collection, the blood must be sent for a thorough check. Blood fluid circulates through the vessels under appropriate pressure; its level can be determined using a tonometer. Blood pressure is completely normal if it does not exceed 120/80. True, small deviations are acceptable, both smaller and larger, which is quite understandable for people of different age categories.
However, if the measuring device showed numbers of 140/90 and above, this is already an alarming situation in which a diagnosis of “hypertension” is established. As you know, this disease is characterized by 3 stages of development, and the higher it is, the more the patient’s well-being worsens.
Can hypertensive patients donate blood?
Any blood loss is a trauma for the body (to one degree or another). People in good health will survive it without any major consequences.
This is a significant stress for the body of a sick person. In this regard, only people who do not have health problems and have undergone a series of studies can become donors.
Some people have no idea about the disease. In this case, doctors will help identify hypertension. Before donating blood, you will need to undergo a medical examination, including measuring your blood pressure.
The diagnosis of hypertension is made if the readings are from 140/90. If blood pressure exceeds 145/90 or higher, donation is prohibited .
You can donate blood to hypertensive patients only for clinical studies. However, there are limitations here too. Doctors do not recommend doing such tests more often than 2 times a week.
After all, even minimal intervention has a bad effect on well-being. If you have hypertension, you need to take care of your health; high blood pressure, even without other stress, negatively affects the functions of internal organs.
Is it possible to give the material to hypertensive patients?
Donor patients with second and third degrees of hypertension (HTN) are prohibited from donating blood. Healthy people who weigh more than 60 kilograms and do not drink alcohol or other illegal drugs are allowed to donate blood. Each donor's material undergoes a thorough check after delivery.
Donating with hypertension (hypertension) is dangerous. This is explained by the fact that rapid removal of blood from the venous bed increases the load on the heart. The pressure begins to drop, and the pumping function of the heart muscle increases. In grades 2 and 3 hypertension, the vessels are changed and their elasticity is lost. Accordingly, their reaction to sudden pressure changes will also be slow.
This manipulation leads to the development of tachycardia and possible ventricular fibrillation. Defective filling of blood vessels can lead to the development of collapse and cardiogenic shock. Sometimes a patient experiences a heart attack or stroke during a transfusion. If you pump out the liquid from a finger, and not from a vein, and carry out the procedure more slowly, then the effect of reducing pressure is achieved. The strength of the heart muscle will also increase, which will prevent heart failure.
After the blood sampling procedure, healthy people’s blood pressure decreases by 8–10 units of mercury, and hypertensive patients experience a decrease in pressure by 20 units. It is important that the condition of the vessels, their elasticity, allows the fluid to be pumped out. If you have hypertension, you can take blood from your finger. Patients undergo tests in this form. The amount taken should be small so as not to cause increased cardiac activity.
Hypertensive patients should not donate blood, regardless of the stage of development of the pathology.
After two to three days, the readings on the tonometer will decrease, and the number of red blood cells and other formed elements will decrease. A state of hydremia will occur, which will positively affect the patient’s well-being. If you practice this method of pumping for hypertension, it will bring a positive effect. But full donation with the removal of 300–400 milliliters is prohibited. The effect of hypotension after blood donation is observed within 4 weeks.
What to do before and after the procedure
Persons no younger than 18 years old and no older than 60 years old, with a normal weight, which must be at least 50 kg, are allowed to donate. If a person is taking any medications, if possible, they should be stopped 3-5 days before blood sampling.
It is especially important not to take aspirin or analgin. You should give up alcoholic beverages 2 days before, and cigarettes 2 hours before.
You need to donate blood after a full night's sleep. A person should have normal health and mood. On the day of the procedure, you should exclude fried, spicy, dairy products and dishes.
You cannot eat nuts, eggs, chocolate, or drink soda. In the morning you need to have a hearty breakfast. Porridge with water and fruits (except citrus fruits and bananas) are suitable. Before donating blood, you should drink sweet tea.
To help your body recover faster after the procedure, drink plenty of water. Sweet tea (not strong) with cookies, buns, candy will be useful. You can buy children's hematogen. After donating blood, it is important to give the body a rest: you need to lie down, or better yet, sleep.
What cardiovascular pathologies do not allow donation?
In addition to hypertension, there are diseases of the cardiovascular system that prevent the possibility of being a donor.
In case of these pathologies, collection at a blood transfusion center or station is prohibited:
- atherosclerotic vascular lesions;
- heart defects;
- tendency to thrombosis;
- cardiosclerosis;
- IBS.
Along with hypertension, there are other diseases of the cardiovascular system in which donation is contraindicated
A gentle or limited sports regimen is recommended for patients. Donating blood is an above-average physical activity and often leads to an exacerbation of the underlying pathology and causes death. Before collecting the material, you need to be examined by a therapist and find out if there are any such pathologies.