According to statistics, the number of diabetics is increasing every year. Recently, 9.6 million patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) have been registered in Russia.
According to doctors, the disease occurs because people lead an incorrect lifestyle. They have become less active, eat poorly, and often experience stress. The diet consists mainly of simple carbohydrates, due to which weight and sugar concentration steadily increase.
If elevated glucose levels are suspected, the doctor will prescribe a test for diabetes mellitus. There are different types of diagnostics that allow us to identify the type of disease, possible complications and the general condition of the patient.
Types of diabetes
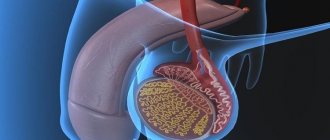
Diabetes mellitus is an endocrinological pathology, which is characterized by a violation of the metabolism of carbohydrates and water in the body. Due to autoimmune damage, the functionality of the ß-cells of the autoimmune gland is impaired. Diabetes is divided into 2 types: insulin-dependent (type 1 diabetes) and non-insulin-dependent (type 2 diabetes). In addition, there is gestational (during pregnancy) and neonatal (in the first six months of life).
Doctors distinguish diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2
Type 1 diabetes develops in childhood. ß-cells located in the tail of the pancreas stop producing insulin (a hormone that regulates carbohydrate metabolism). To prevent sudden surges in sugar, insulin solution should be administered on time and regularly. This type of diabetes was diagnosed in 10% of all patients.
The most common form of endocrine pathology is type 2 diabetes. Most often it is detected in overweight people with a genetic predisposition to diabetes. This means that the risk group includes people whose relatives have diabetes. Type 2 disease most often affects people over 40 years of age. The disease is usually mild, so the patient can regulate sugar levels. To do this, you should eat right and perform a special set of exercises.
Gestational diabetes occurs due to hormonal imbalance. Most often, the disease goes away on its own after the pregnancy ends safely. However, a woman with this diagnosis should be constantly examined by a doctor to prevent the development of type 2 diabetes and other dangerous complications.
Neonatal diabetes is a disease that occurs due to a genetic disorder. As a result, the pancreas cannot produce insulin normally.
To detect the disease, a test for diabetes is performed.
Evaluation of treatment effectiveness
The effectiveness of the prescribed treatment must be monitored and, if necessary, the treatment program adjusted. In addition, it is important to identify emerging complications at an early stage. To do this, patients are recommended to check glycated hemoglobin every three months, microalbuminuria (MAU) every six months, and undergo a clinical examination once a year.
Patients with diabetes mellitus of the first group are registered with an endocrinologist, and patients with T2DM, after selecting appropriate therapy in the absence of severe cardiovascular diseases, are observed by a therapist or general practitioner. If the patient's condition worsens, the therapist can re-refer him to an endocrinologist to adjust the therapy. If the complications that arise lead to a person’s loss of ability to work, he is assigned a disability, but this is done on the basis of the conclusion of a medical and social examination.
Tests to detect diabetes symptoms
People with diabetes have a lot of symptoms, but first you should pay attention to extreme thirst and frequent bladder emptying. These signs indicate that the kidneys are working at a high rate. This happens because the concentration of sugar increases and the kidneys try to remove excess sugar from the body. This process requires large volumes of fluid, which the kidneys take from body tissues. As a result, the patient is constantly thirsty and goes to the toilet more often.
Unquenchable thirst and frequent urination are characteristic symptoms of diabetes.
Diabetes mellitus is characterized by other symptoms:
- xerostomia (dry mouth);
- constant feeling of hunger;
- headache, vertigo (dizziness) with diabetes or prediabetic condition;
- tingling or numbness in the legs;
- increased nervous excitability;
- chronic fatigue;
- rapid weight loss;
- increased blood pressure;
- the appearance of wounds or ulcers that heal slowly;
- dry skin, itching;
- sexual disorders in men (due to increased glucose levels, testosterone decreases);
- menstrual irregularities.
With the development of diabetes, the blood vessels of the brain are severely affected. Cells cannot absorb glucose without the participation of insulin, and as a result, they starve. For this reason, the patient has trouble concentrating, has a headache, and constantly feels tired.
If you notice at least a few symptoms of diabetes, then go to an endocrinologist. After all, complications of diabetes can be life-threatening, so there is no need to hesitate. In addition, there is hidden (latent) diabetes mellitus, so it is recommended to test 2-3 times a year.
What happens in the body of a diabetic?
In diabetes, the secretion of the hormone by pancreatic cells is disrupted (type 1) or its absorption becomes difficult (type 2). For this reason, the blood sugar level increases. This phenomenon is called hyperglycemia, which is chronic in diabetics. A short-term increase in sugar - nutritional hyperglycemia - occurs when a person has eaten. Eating food increases glucose levels due to the carbohydrate content and, accordingly, activates the production of insulin. Insulin is responsible for delivering amino acids, glucose and fats into cells, thereby maintaining blood glucose levels at a safe level. A normal level is considered to be around 80–100 mg/deciliter.
If the pancreas is healthy, sugar levels decrease after a while. Its excess under the influence of insulin is deposited in the muscles and liver in the form of glycogen.
In patients with diabetes, this physiological process is disrupted. Chronically elevated blood sugar has a negative impact on the functioning of all body systems. If this condition is not compensated for by taking medications and diet, irreversible pathological changes occur. In severe cases, they can be fatal.
How to detect diabetes complications early
If diagnosis and treatment are not timely, the likelihood of severe complications of diabetes increases. Factors that provoke the development of the disease include a passive lifestyle, poor diet, lack of blood sugar control and violation of doctor’s recommendations regarding drug therapy. During treatment, patients must strictly follow all rules in order to normalize glucose levels.
Diabetes has dangerous complications
If the recommendations of the endocrinologist are violated in diabetics, the likelihood of the following complications increases:
- Diabetic coma is a dangerous condition that requires immediate medical attention, as the patient’s risk of death increases.
- Diabetic retinopathy is a vision disorder associated with damage to the blood vessels of the retina of the eyeball.
- Diabetic damage to the glomeruli and tubules of the kidneys, as well as the blood vessels that feed them.
- Hypoglycemia is a pathological condition in which blood sugar drops sharply.
- Severely weakened immunity, as a result of which the likelihood of contracting infections of viral origin increases.
- Angiopathy is a disease in which blood vessels become thin and damaged.
- Encephalopathy is a non-inflammatory lesion of the brain due to impaired microcirculation, death of nerve cells and brain hypoxia.
In addition, diabetes is often complicated by arterial hypertension, heart and vascular diseases, and diabetic foot syndrome.
There are different ways to detect diabetes
Diagnostic methods for diabetes
If you notice symptoms of diabetes, it is first recommended to visit an endocrinologist who will take an anamnesis and prescribe tests.
To identify the disease, it is necessary to undergo one or more tests:
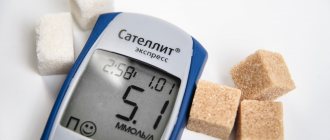
- Detection of glucose concentration in blood serum. This is an effective study, the results of which are considered the most truthful. The analysis is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. The normal amount of sugar ranges from 3.3 to 5.5 mmol/l. If the indicator is elevated, this indicates that the sugar concentration is high. It is recommended to remain calm before the test, as any stress can trigger the release of glucose into the blood.
- Glucose tolerance test (glucose tolerance test). This study allows you to identify any disorders of glucose metabolism in the body. The analysis is carried out in the morning, the last meal should have taken place at least 10 hours ago. A few days before the test, a diabetic should avoid intense physical activity, give up alcohol, cigarettes and medications that increase glucose levels. The patient drinks a solution with glucose (75g), and after 2 hours a test is performed. If the results are above 7.8 mmol/l, then glucose metabolism in the body is impaired. Indicators that exceed 11 mmol/l indicate the development of diabetes mellitus.
- Urine test for sugar. If a person is healthy, then there should not be glucose in urine. In diabetes, the sugar level rises so much that it penetrates the filtration barrier of the renal corpuscle. A urine test is performed as part of a comprehensive diagnosis of diabetes.
- Urine test for acetone. Often endocrine pathology is complicated by ketoacidosis caused by metabolic disorders. According to the results of the study, acetone bodies will be observed in the patient’s urine, which indicates a serious complication of diabetes.
Only after complete research and clarification of the diagnosis will the patient receive a prescription for treatment from the doctor. It is important to strictly adhere to its recommendations in order to prevent complications or stop the development of existing ones.
Why measure your sugar level?
Self-monitoring of glucose will allow you to:
- determine the effectiveness of medications at night, after meals and between meals;
- calculate the optimal dose of insulin and dosage of medications;
- adjust nutrition and physical activity;
- assess the dynamics of the disease;
- ensure driving safety;
- prevent the development of diabetic crisis, hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
It should be noted that self-monitoring cannot replace laboratory diagnostics. Therefore, you should visit the clinic every month for a blood test.
Online test and glucometer
You can determine the “sweet disease” at home. There are special online tests for this purpose. To pass them, you need to enter the request “take an online test for diabetes.” After opening the site, you will need to answer questions: age, body mass index, glucose level, genetic predisposition to the disease, etc. After passing the test, you will receive a result indicating the likelihood of developing the disease. It is recommended that you print out the test with answers and take it with you to the doctor before professional diagnosis. This is necessary, since the results of online tests are quite questionable and require additional research.
You can monitor your sugar levels using a glucometer
A glucometer is a device for measuring blood sugar levels. Using this device, you can quickly and accurately determine your glucose concentration. Normal fasting blood sugar levels range from 70 to 130 mg/dL. Often the device comes with test strips and scarifiers (a knife for making scratches).
Instructions for using a glucometer to detect diabetes:
- Before the examination, thoroughly clean your hands with antibacterial soap.
- Massage your finger and wipe with an antiseptic solution at the puncture site.
- Use a scarifier to pierce the side of the fingertip.
- Wipe off the first drop of blood, squeeze the second onto a strip and place it in the glucometer.
- The results will appear on the device monitor.
The A1C kit allows you to accurately determine the concentration of glucose in the body. This technique is recommended to be used for 3 months, after which the patient receives an average value.
Test strips
To detect the concentration of sugar in urine, the analysis is carried out with special test strips. However, this diagnostic method raises doubts among most doctors. The strip can only detect high levels of sugar in urine. Normally, the glucose concentration ranges from 0 to 0.02%. If after passing the test the amount of sugar is high, then it is recommended to undergo additional tests. Thus, test strips are used as part of a comprehensive diagnosis of diabetes.
Test strips help detect high concentrations of glucose in urine
Many patients are interested in the question of how many strips diabetics should take. According to the order of the Ministry of Health, it is planned to provide patients with test strips in the amount of 730 pieces per year for type 1 diabetics and 180 pieces for type 2 diabetes.
Based on all of the above, tests to detect diabetes mellitus are an excellent opportunity to diagnose the disease and begin treatment. The most effective method for diagnosing diabetes at home is a glucometer with test strips. If you detect an increased concentration of sugar, you should consult a doctor who will clarify the diagnosis and prescribe proper treatment.
Is it possible to determine at home that a person has diabetes?
Only an endocrinologist can make such a diagnosis after the necessary laboratory tests. However, there are signs that may indicate chronic excess glucose in the blood and the need to seek medical help. Here are the main symptoms that diabetics experience:
- Severe fatigue persists even after sleep, with reduced loads.
- Body weight begins to increase or decrease sharply. In type 1 diabetes, it decreases, although the person has a good appetite and a plentiful diet. With type 2 diabetes, you constantly want to eat, so the person consumes more calories and body weight increases.
- Excess blood sugar leads to dry mouth and unpleasant odor.
- Some patients experience such phenomena as dizziness, headache, and darkening of the eyes.
- Men may experience decreased libido. Up to a third of young and middle-aged patients report signs of erectile dysfunction.
- Itching in the vagina, frequent thrush, burning sensation when urinating - this is how diabetes manifests itself in women. High sugar levels increase the risk of yeast infection. Candida is a yeast-like fungus that uses sugar as a nutrient medium that is optimal for their growth and reproduction.
- On the part of the nervous system, diabetes can manifest itself not only as lethargy, but also as excessive irritability, anxiety, tearfulness and decreased academic performance in children.
- Diabetics are constantly thirsty, which is also caused by hyperglycemia. This condition is accompanied by frequent urination and increased load on the kidneys.
The absence of alarming symptoms does not negate the need to monitor your diet and periodically take glucose tests. At first, the disease may be asymptomatic, so the person is unaware of the danger and leads a normal lifestyle. Up to 50% of cases of diabetes remain undiagnosed! The disease is discovered during medical examinations or after the patient urgently calls an ambulance due to problems with well-being due to the development of complications.
In addition, many of the above signs are symptoms of diabetes and a number of other diseases.