Myocardial infarction
– an extremely dangerous and severe manifestation of coronary heart disease. Myocardial infarction is the death (necrosis) of a section of the heart muscle caused by a critically dangerous deterioration of blood supply in the coronary arteries. Experts note that myocardial infarction most often affects the male half of the population. If previously the conventional age of patients with myocardial infarction was 55-60 years, today cases of such pathology in young people are increasingly being recorded. The risk of death from myocardial infarction is very high. A patient with myocardial infarction requires urgent hospitalization in the intensive care unit. The life of the victim will depend on how quickly he receives the necessary treatment.
Main causes of myocardial infarction
There is a risk group - a population whose likelihood of developing myocardial infarction is higher than the rest of the population. It includes:
- men over 50 years old.
- hypertensive patients.
- smokers and alcohol abusers.
- overweight.
- persons leading a sedentary lifestyle.
- persons who have previously had a heart attack.
The main cause of myocardial infarction
It is considered to be a narrowing of the lumen of the coronary arteries caused by atherosclerotic changes. Increased blood clotting leads to the formation of blood clots that disrupt blood circulation in the heart muscle. The tissues of a vital organ suffer from a lack of nutrients. Myocardial infarction can be triggered by severe emotional and physical stress, the presence of coronary heart disease or angina, as well as diabetes, obesity, addiction to alcoholic beverages and smoking.
Clinical case
A patient was admitted to the hospital with severe chest pain that lasted for three days. Taking analgesics and Nitroglycerin did not bring relief. Previously, a diagnosis of angina pectoris FC II was made. A week before the attack, I experienced severe stress, and my condition worsened. The cardiogram revealed a large-focal infarction localized in the anterior wall, acute stage. In the blood - increased myoglobin and troponin.
After a month of hospitalization, the patient was discharged for treatment on an outpatient basis. An ECG showed scarring in the affected area, and blood counts returned to normal.
Stages of the disease and main signs of myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction goes through several stages in its development. The duration and severity of each depends on the size of the lesion, the condition of the blood vessels, concomitant diseases and complications, as well as the correctness of the chosen treatment tactics. There are acute, subacute periods, periods of scarring and post-infarction periods. Many patients noted that the acute period was preceded by some signs of unstable heart function - angina pectoris, arrhythmia.
Acute period
can last up to 10 days. This is the most difficult time for the patient, when all sorts of complications arise and the likelihood of death is quite high. A characteristic clinical picture of the acute period of myocardial infarction is severe pain in the chest area radiating to the left shoulder, collarbone, neck, ear, and shoulder blades. The sensations of spasm can be different - cutting, stabbing, pressing, burning. This condition during myocardial infarction lasts from thirty minutes to several hours. An attack during myocardial infarction occurs in waves. The pain may increase or decrease. It is impossible to stop them with nitroglycerin. At the same time, during myocardial infarction, the patient experiences severe weakness, a feeling of lack of air, and anxiety. Pallor of the skin, cyanosis (acrocyanosis) of the nasolabial triangle, arrhythmia, and profuse sticky sweat are also noted. Possible increase in blood pressure.
Subacute period of myocardial infarction
characterized by the disappearance of pain. Their preservation indicates the addition of pericarditis (inflammation of the outer lining of the heart). Necrotic processes in the area of inflammation can cause fever with a rise in body temperature. The patient is concerned about persistent low blood pressure.
Scarring period
in case of myocardial infarction, it is characterized by gradual healing of the affected area through the formation of scars. The duration of the process ranges from several weeks to several months. The patient's condition improves significantly. Painful symptoms disappear.
Post-infarction period
– time for recovery and return to normal life. It is recommended to avoid moving heavy objects on your own, give up alcohol and smoking, follow a diet, monitor your body weight, monitor your pulse and blood pressure, and avoid prolonged exposure to the sun.
It is important to know that there are atypical forms of myocardial infarction, in which the signs of a life-threatening condition are not always obvious. They make diagnosis and timely provision of medical care difficult. Among the most common:
Sign up for a test for myocardial infarction
Make an appointment
Expert advice
When the first signs of a heart attack appear, measures should be taken immediately.
I advise you to immediately call an ambulance, and while the doctor is on the way, provide the patient with complete rest, sit him down or put him in a position that will alleviate the condition as much as possible. Give Corvalol, Nitroglycerin, Aspirin, ventilate the room. The most dangerous period is the most acute period, which is usually manifested by very severe pain, shortness of breath, and rhythm disturbances. The patient’s life depends on the speed and correctness of the actions of the person nearby. When calling a doctor, it is best to describe the symptoms so that a specialized team can arrive to take an ECG, give oxygen, and administer medications to limit the area of necrosis.
Complications of myocardial infarction
In the first hours of myocardial infarction, various complications may arise that aggravate the patient's condition. This is the appearance of an aortic aneurysm, myocardial rupture, cardiogenic shock, cessation of cardiac activity (asystole), pulmonary edema. The consequences of a heart attack can accompany the patient for life. These are heart rhythm disturbances, cardiosclerosis and other problems associated with disruption of the cardiovascular system. Experts do not guarantee absolute recovery after a heart attack and recommend following all the instructions of a cardiologist in order to avoid a relapse. The next attack threatens the appearance of a new area of necrosis. It is almost impossible to compensate for such consequences for the heart.
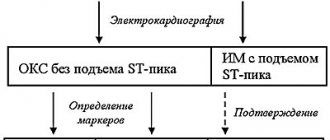
ECG predictors of reperfusion
Pathogenetic therapy for AMI has the goal of restoring blood flow in the affected artery. Lack of restoration of blood flow (reperfusion) is the most powerful predictor of the development of LV systolic dysfunction and the risk of death after AMI. In the absence of reperfusion, 30-day mortality can reach 15% [14]. In turn, the resolution of ST segment elevation is an indicator of improved short-term (30-day) and long-term (one-year) prognosis [5]. Assessing ST segment resolution is also useful for deciding on further management of the patient.
Failure to resolve the ST segment within the first 90-120 minutes after thrombolytic administration should be a reason to consider angioplasty. A specific marker of reperfusion that has occurred is considered to be a reduction in ST segment elevation by more than 50-70% in the lead with maximum elevation, which is associated with the most favorable further prognosis. At the same time, a number of authors propose a criterion of 50% reduction in ST segment elevation after 60 minutes of reperfusion therapy as a predictor of a good prognosis in individuals with AMI [13]. Considering that the maximum effect from subsequent angioplasty after thrombolysis is achieved no later than 6-8 hours from the onset of AMI [14], reducing the time for assessing reperfusion has good reason.
Other ECG markers of reperfusion include T wave inversion within four hours of AMI onset. T wave inversion, which occurs within the first hours of reperfusion therapy, is a highly specific sign of restoration of blood flow. T wave inversion, which develops after more than four hours, is associated with natural ECG dynamics during AMI and does not indicate restoration of blood flow. Accelerated idioventricular rhythm 60-120 beats/min, late, paired, ventricular extrasystoles are also a highly specific marker of reperfusion. These rhythms are considered not dangerous and, as a rule, do not require antiarrhythmic therapy. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation can also be associated with reperfusion, but are rare and more often a consequence of persistent coronary occlusion.
Diagnosis and treatment of myocardial infarction
In addition to the clinical picture of myocardial infarction and taking a detailed medical history, a number of additional studies are used to confirm such a serious diagnosis:
If you suspect a heart attack, you must call an ambulance for urgent hospitalization in the cardiac intensive care unit. A patient with myocardial infarction is prescribed strict bed rest, rest and dietary nutrition with the exception of foods that excite the nervous and cardiovascular systems. Therapy is aimed at relieving pain, eliminating arrhythmias and heart failure, restoring normal blood circulation and combating the formation of blood clots. For this purpose, analgesics, neuroleptics, antiarrhythmic drugs, and thrombolytics are used. The list of medications is individual for each patient. It corresponds to the extent of the current disease, the general well-being of the patient and the presence of associated complications. In addition to medications, according to special instructions, surgical treatment methods are used - bypass surgery, excision of an aortic aneurysm, implantation of pacemakers (a device that sets the correct heart rhythm).
Cost of consultation for myocardial infarction?
| Name of service | Price, rub.) |
| Initial appointment with a cardiologist | 2000 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a cardiologist | 1500 rub. |
| Primary appointment with a general practitioner | 2000 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a general practitioner | 1500 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment (drawing up an individual treatment regimen) | 1500 - 3000 rub. |
All our services and prices
Prevention of myocardial infarction
Despite all the efforts of modern medicine, mortality from heart attacks will continue to remain quite high. To reduce the likelihood of this pathology occurring, you need to know how to prevent the disease. Expert recommendations:
Sign up for a test for myocardial infarction
Make an appointment
First aid
In order to promptly independently determine the possible development of the pathology in question, it is very important to pay attention to:
- intensity and nature of pain. a heart attack is characterized by squeezing, pressing, burning sensations;
- localization of pain. location of pain in the left side of the body, just behind the sternum, in the area of the shoulders, shoulder blades;
- irradiation of pain to the arm, side, neck.
But in order to really help a patient with an angina attack, the first thing that is very important to do is, of course, to call a medical team. The sooner doctors have the opportunity to begin their work, the greater the patient’s chances of surviving and avoiding the sad complications of the primary problem.
The first pre-medical treatment or simply assistance to the patient should be as follows:
- It is important for the patient to take a comfortable body position; he can be laid down or seated comfortably, allowed to lean back on the pillow;
- unbutton tight clothes;
- provide air flow, open windows;
- You can give the patient one tablet of nitroglycerin or aspirin.
Further actions should be carried out by the resuscitation team. Unfortunately, it is extremely difficult to teach people without medical education to perform chest compressions and artificial respiration, which may also be urgently needed by patients in such situations.