Do the lungs recover after COVID-19? Yes. But you need to not miss the rehabilitation period and take the doctor’s recommendations seriously.
The new coronavirus infection caused by SARS-CoV-2 has not been well studied, but it is clear that it causes harm to all human organs and tissues. The virus enters the body through the mucous membranes of the nose, eyes, and pharynx. The first symptoms appear on days 2-14. Usually this is a fever above 37.5 degrees Celsius, a runny nose, loss of smell, dry cough, loose stools, weakness and headache. On days 6–10 from the onset of the first symptoms, shortness of breath, chest pain, and increased cough may begin to bother you. These are alarming symptoms that indicate lung damage and require additional examination: computed tomography of the lungs, measurement of blood oxygen saturation (saturation).
Lungs after COVID-19
Entering the human body through the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, SARS-CoV-2 causes a powerful inflammatory reaction. Immune cells are activated and a colossal amount of inflammatory substances (inflammatory cytokines) are produced. The intensity of this reaction is most likely determined genetically. It is the intensity of the inflammatory reaction that determines the severity of damage to the lung tissue according to research data. In the lung tissue, damage during COVID-19 is caused both by damage to the alveoli themselves (in which gas exchange occurs and the blood is saturated with oxygen from the air) by our own immune cells and by damage to the pulmonary vessels that encircle the alveoli. The extent of lung damage can be determined using CT (computed tomography).
Table 1. Lung damage due to COVID-19
| № | Percentage of lung tissue damage | Manifestations | Hospitalization |
| 1. | 15 | Part of the lung is affected. Slight difficulty breathing. | Not shown. |
| 2. | 25 | Half of one lung is affected. There is difficulty breathing, but the person copes with the situation. | Treatment at home is possible. |
| 3. | 50 | One lung is turned off from breathing. Shortness of breath is noticeable. Active treatment is required. | The decision about hospitalization is made by the doctor. |
| 4. | 75 | Only half of one lung breathes. Severe respiratory failure. | Shown. |
Lungs may lose elasticity after COVID-19. The affected areas of lung tissue are replaced by connective (scar) tissue, and fibrosis occurs. Due to fibrotic changes in the lungs, the gas exchange function of the lung tissue suffers. There is no longer any inflammation, but respiratory failure remains. If measures are not taken during the disease itself, pathological changes in the lungs can remain for life. The person will be disturbed by:
- shortness of breath, worsening with physical activity;
- frequent dizziness;
- dry cough;
- chest pain;
- increasing weakness;
- decreased performance.
Sometimes the weakness is so severe that the ability to self-care is lost. To avoid these serious complications, it is necessary to carry out restorative measures - rehabilitation.
Principles of pulmonary rehabilitation after COVID-19
Rehabilitation begins 20–25 days after the onset of the disease, sometimes while still in the hospital. As soon as the acute process is over, the body temperature has returned to normal, an examination is carried out. It is clarified whether there is dysfunction of the kidneys, heart, blood vessels, or other organs. The lung recovery program after COVID-19 is developed individually. Taken into account:
- the severity of the coronavirus infection;
- the nature of viral pneumonia, the degree of lung damage;
- floor;
- weight;
- age;
- associated diseases.
The duration of rehabilitation is from 2 weeks to a year. It can go continuously or in courses of 10–14 days with breaks of 5–7 days. With minimal changes, breathing exercises, physical therapy, inhalations, massage, and physiotherapy are prescribed. Regime and nutrition play an important role.
What causes high blood cholesterol
The main reasons for the accumulation of lipids in blood vessels:
- Endocrinological problems, hormonal imbalances.
- Metabolic disorder.
- The constant presence of fatty components in the menu, as well as products with a low content of mineral and vitamin complexes.
- Smoking, alcohol abuse.
- Frequent exposure to stress, depression.
- Infectious processes in the liver and kidneys.
- Lack of physical activity.
- Genetic predisposition to cholesterol accumulation.
- Elderly age.
If at least one of the listed factors is present, it is necessary to resort to folk remedies to clean blood vessels and free them from plaques.
General recommendations for lung rehabilitation after COVID-19
- Maintaining a daily routine, getting a full eight hours of sleep
- Moderate physical activity (10,000 steps per day - walks in the park, forest in dry and warm weather). On a cold, windy or rainy day, it is better to stay home. For a walk, dress according to the weather; shoes should be comfortable.
- Breathing exercises
- Daily wet cleaning and ventilation of the room.
- Refusal to visit the bathhouse or sauna. You should not take hot baths.
- Prohibition on drinking alcohol and smoking.
What results can be achieved
Herbal medicine is a gentle way to get rid of atherosclerosis and more serious pathologies. Using herbs you can achieve impressive results:
- improvement of general well-being;
- increased performance;
- normalization of lipid metabolism, cholesterol levels;
- normalization of pressure;
- improving quality of life.
It is necessary to start herbal treatment at an early stage or for the purpose of prevention. Herbal medicine is not able to remove existing plaques from blood vessels. This can only be done surgically. Medicinal herbs can prevent the formation of new plaques and inhibit the growth of old plaques.
Nutrition for lung recovery after COVID-19
It is recommended to eat nutritious meals 5-6 times a day, in small portions.
Table 2. Required nutritional components
| № | Component | Product examples |
| 1. | Easily digestible protein | Chicken, turkey, young beef, cottage cheese, eggs. |
| 2. | Healthy fats | Sea fish, nuts, vegetable oils. |
| 3. | Alimentary fiber | Cereals, fresh vegetables and fruits. |
| 4. | Slow carbohydrates | Cereals, vegetables. |
| 5. | Probiotics | Fermented milk drinks, sauerkraut. |
| 6. | Iron | Parsley, beef liver, buckwheat. |
You need to drink 1.5–2 liters of water per day. Regular drinking water, fruit drinks, unsweetened compotes, and rosehip decoction are suitable.
Prohibited: “fast” carbohydrates - cakes, sweets, buns, fatty, hot, spicy foods, deli meats.
Breathing exercises for lung recovery after COVID-19
Breathing exercises stimulate blood circulation, train the respiratory muscles, increase the elasticity of the lung tissue, and improve bronchial drainage. You need to perform gymnastics in a clean, ventilated room. Start with 30 seconds, gradually increase to a quarter of an hour. Overwork should be avoided. If you feel dizzy, take a break.
Preparatory exercises
- While lying on your back, inhale slowly for 3–4 seconds, then exhale the same slowly for 5–6 seconds.
- Diaphragmatic breathing, when the stomach “inflates” as you inhale.
- Slowly inhale air, slowly exhale through a straw into a glass of water, and relax. Repeat 2-3 times, gradually increase to 10 times.
Initial exercises
- Sit on a chair, press your back against the back of the chair, lower your arms down. As you inhale, gently raise your arms forward and then up. As you exhale, return to the starting position.
- The same exercise, only raise your arms up to the sides.
- Stand up, put your fingers on your shoulders. As you inhale, slowly spread your arms to the sides. Exhaling through your mouth, return to the starting position.
Basic exercises
Gymnastics by A. N. Strelnikova has proven itself well. It is difficult to master it on your own. It is necessary that the movements be shown by a person who knows the technique. Instead of this breathing exercise, your doctor may recommend another one.
When to clean vessels
You need to clear cholesterol from your blood vessels when:
- According to instrumental methods, atherosclerotic plaques were detected or
- when there is already a violation of internal organs, against the background of which a high atherogenic index is detected (according to lipid profile). These are: cholesterol above 6.19 mmol/l;
- LDL – more than 4.12 mmol/l;
- HDL: below 1.04 for men, below 1.29 mmol/l for women.
In the following cases, it is necessary to do everything possible to prevent the deposition of cholesterol on the walls of blood vessels:
- men over 40 years old;
- women over 55 years old;
- if you have bad habits;
- if a person eats a lot of smoked, fried, salty food, meat;
- if relatives have atherosclerosis, ischemic or hypertension;
- suffering from diabetes mellitus;
- those who note the presence of excess weight;
- those who have suffered a complication of streptococcal infections such as rheumatism;
- if at least once there was numbness of one limb or half of the body, which did not follow their compression, but arose “by itself”;
- if at least once there was a visual impairment in one eye, which then went away;
- when there was an attack of sudden general weakness;
- if there is causeless pain in the navel area, accompanied by flatulence and constipation;
- when memory deteriorates, and the desire to rest causes less and less mental stress;
- if it becomes more and more difficult to walk, your legs hurt with less and less load;
- when there is chest or cardiac pain that is not relieved by nitroglycerin;
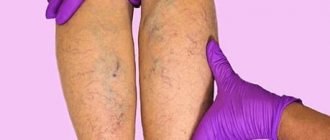
- if the hair on your legs falls out, and your legs themselves turn pale and freeze;
- if any ulcers, redness, or swelling begin to appear on the lower extremities.
Exercise to treat lungs after COVID-19
Exercise therapy strengthens muscles weakened by disease, stimulates blood circulation, and normalizes the nervous system. Gymnastics are performed after breathing training, at a slow pace. You need to place a chair nearby and hold the back of it with your hand to control your balance. The first part of each exercise is performed while inhaling, the second – while exhaling.
Sample list of exercises
- Rise on your toes, stand on your full foot.
- Bend your leg at the knee, lifting it up and lowering it. Then - the second leg.
- Take your leg back and return it to its place. Same with the second leg.
- Circular movements of the shoulders forward, then back.
- Take your right hand back, return to the starting position, then your left.
- Place your hands on your belt. Turn your torso to the right, then to the left.
- Lean forward 20–30 degrees, straighten up.
- Bend to the right, straighten up, then to the left.
Contraindications
You cannot clean vessels using traditional methods if you have:
- inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- epilepsy;
- stomach or duodenal ulcer;
- kidney diseases.
Prohibitions also include pregnancy and breastfeeding.
If there is a risk of cholesterol accumulation in the vessels, you can reduce it with the help of folk remedies. It is advisable to first carry out a complete cleansing of the body from toxic substances and toxins. Otherwise, the effectiveness of the procedures will be low.
Physiotherapy after coronavirus
Table 3. Popular physiotherapeutic procedures
| № | Name | Action |
| 1. | SMT therapy | Sinusoidal modulated currents eliminate bronchospasms and improve drainage. |
| 2. | Laser therapy | Improves blood circulation, has a resolving and anti-inflammatory effect. |
| 3. | Polychromatic polarized light | Accelerates the resorption of infiltrate, improves bronchial patency. |
| 4. | Magnetotherapy | Eliminates inflammation, swelling, pain. |
| 5. | Ultrasound therapy | Removes phlegm, prevents the development of fibrosis. |
Fibrosis – as a consequence for the lungs after COVID-19
Signs of pulmonary fibrosis on CT (computed tomography) indicate that part of the lung tissue is replaced by scar tissue. Fibrosis does not develop in a few days. This usually takes up to 6 months. Fortunately, fatal pulmonary fibrosis leading to severe respiratory failure is not common, and for most people who survive coronavirus infection, the remaining changes in the lungs will not affect their health. In most cases, a control study shows a clear positive trend. Signs of fibrosis decrease or disappear. Normal lung tissue is restored.
Therefore, it is so important to consult a doctor in time and begin proper treatment for COVID-19, which will help avoid serious complications and reduce the recovery time after lung damage from SARS-CoV-2.
Once fibrosis has truly formed, it is irreversible. In this case, doctors try to create optimal conditions for the functioning of the remaining lung tissue. This can often be done, since the compensatory capabilities of the respiratory system are great. But simple methods are not enough for this. It is necessary to involve serious therapy, including medications and respiratory support.
Medicinal cleansing
To clean blood vessels and get rid of cholesterol, folk recipes are used as part of complex therapy. But the drugs must be prescribed by a doctor; independent use is strictly prohibited.
Typically, the following medications are used:
- Cholestyramine, cholestid - indicated for binding bile acids in the intestine.
- Atromid, Gevilan - reduce the production of fats.
- Medicines containing nicotinic acid prevent the production of cholesterol.
- A group of statins - inhibit lipid synthesis. These include Lovastatin, Rosuvastatin, Atorvastatin, Simvastatin.
- Fibrates – reduce the concentration of harmful deposits and thin the blood. These include Lipostabil, Traykor, Clofibrat.
It is necessary to undergo a diagnosis before using pharmacological agents.
Publications by doctors from the Family Doctor clinic on the topic “How to overcome post-Covid syndrome”
- Restoring the sense of smell after coronavirus
- Restoring memory after suffering from coronavirus
- Overcoming mental disorders during post-Covid syndrome
- Loss of smell due to COVID-19 - advice from an otolaryngologist
- Post-Covid screening - examination after a new coronavirus infection
- How to return digestion to normal after coronavirus?
- Recommendations from a cardiologist after suffering from COVID-19
- Coronavirus turned out to be “vindictive” - what is important to know
- We are experiencing COVID. How the coronavirus pandemic affects mental functioning
- Melatonin and COVID-19 - a cure for Trump
- Post-Covid syndrome: program for diagnosis and regression of post-Covid symptoms. How to Manage Long-Term Long COVID Symptoms
What are cholesterol plaques
Each human organ receives nutrition from vessels, of which there is a huge and extensive network in the body. Blood flowing through the vessels is not a solution, but a suspension, when a suspension of cells, called formed elements, floats in the liquid. The liquid part of the blood does not at all resemble water, which is explained by the molecules dissolved in it, mainly of a protein nature. But various products of fat metabolism also “float” in the blood, in particular cholesterol, triglycerides, and lipoproteins.
According to the laws of physics, blood moves through the vessels in such a way that it is practically free of cells, and most of the formed elements “go” along the edges, representing a kind of “quick response department”: in response to damage to the vessels, platelets immediately descend from here, “closing” gap.
The liquid part of the blood also comes into contact with the vascular walls. As we remember, the products of fat metabolism are dissolved in it. There are several different ones, cholesterol is only one of the components. This system is structured as follows: normally, “bad” fats are in balance with their antagonists, “good” fats (“good” cholesterol). When this balance is disturbed - either the number of “bad” ones increases, or the volume of “good” ones decreases - fatty tubercles - plaques - begin to be deposited on the walls of arterial vessels. The risk of depositing such plaques is judged by the ratio of good fats (they are called “high-density lipoproteins” - HDL) and the sum of low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL). This can be done using a blood test from a vein, called a lipid profile.
Such a plaque is dangerous in the following ways:
- It can come off and, having passed with the blood flow to a vessel of “suitable” diameter, clogs it, thereby depriving the area feeding from there of some kind of nutritional organ. The smaller the vessel, the smaller the area that dies, the less the functioning of this organ and the body as a whole is disrupted (there is “duplication” within the tissue of each organ, thanks to which each “piece” receives nutrition from several small-diameter vessels at once).
- The blood is forced to bypass the plaque, as a result of which, instead of a uniform flow in the vessel, “vortices” are created when part of the blood flowing near the wall covered with the plaque has to return back. Turbulence in the blood flow impairs the nutrition of the blood supply to the organ. Here the relationship is the same as in the point above: the larger the diameter of the artery damaged by the plaque, the more the organ suffers.
- If the composition of the blood does not change, and the amount of HDL and enzymes that should “break off” the plaque does not increase, the body tries to limit it. To do this, he sends immune cells to the site of plaque deposition, whose task is to “bite off” pieces of the plaque and digest them. But the cells are unable to do this: instead of digesting, the immune cells are damaged by cholesterol and fats, and remain “lying” around the cholesterol. Then the body decides to cover this formation with connective tissue, and the plaque increases in size even more, now worsening the blood supply to the organ not only due to turbulence, but due to a decrease in the lumen of the vessel.
- Covering with connective tissue is good for the plaque and bad for the vessel. Now, if something damages the plaque, it will “call” platelets to itself, which will form a blood clot on its surface. This phenomenon, firstly, will further reduce the diameter of the vessel, and secondly, it will increase the risk (especially in vessels with “active” blood flow) of a blood clot breaking off and blocking a smaller vessel.
- A long-existing plaque becomes covered with calcium salts. Such a wall formation is already stable and will not come off without intervention. But it tends to grow and reduce the lumen of the vessel.
The rate of plaque formation is affected by:
- consumption of animal fats;
- smoking;
- diabetes;
- excess weight;
- physical inactivity;
- high blood pressure;
- binge eating;
- eating large amounts of simple carbohydrates with food.
The localization of plaque deposition is unpredictable: it can be either the arteries supplying the brain or the arteries of the kidneys, limbs or other organs. Depending on this, they can cause:
- ischemic stroke;
- angina pectoris;
- myocardial infarction;
- intestinal gangrene;
- aortic aneurysm;
- discirculatory encephalopathy, which is manifested by memory deterioration, headaches, decreased ability to analyze what is happening;
- deterioration of blood supply to a larger or smaller area of the limb, up to its gangrene;
- if the plaque blocks the aorta in the area where large vessels originate from it to each of the lower extremities, both legs will suffer only from ischemia or gangrene.