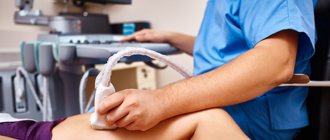
To examine blood flow in vessels, a non-invasive research method such as Doppler ultrasound (USD) and duplex scanning (DS) is used.
Doppler ultrasound is used to assess blood flow in vessels. The ultrasonic waves of the sensor are reflected from red blood cells and provide a complete picture of the condition of the vessels, based on the speed of blood flow and pressure.
The following studies are carried out at the Euromedsi Clinic using Doppler ultrasound:
- Ultrasound Dopplerography of uteroplacental blood flow
- Ultrasound examination of the mammary glands with Doppler examination
- Ultrasound Dopplerography of the vessels of the spermatic cord
- Ultrasound examination of the scrotal organs with Dopplerography
- Doppler ultrasound of the arteries of the upper and lower extremities
You can get detailed advice and make an appointment with a doctor at the Euromedsi Clinic by calling +7 (499) 754 58 08 or leaving a request on our website.
Types Ultrasound diagnostic method (sonography) allows you to study blood flow in any organ of the human body. Ultrasound waves help obtain information about veins and arteries: the condition of the walls, configuration, blood circulation speed and other parameters. Ultrasound is an indispensable research method, widely used in pediatrics and obstetrics, which indicates that it has no contraindications. Ultrasound of the vascular system is based on a principle named after the physicist Christian Doppler. The Doppler effect is based on the ability of programs to analyze echolocation signals reflected from moving red blood cells. The sonologist draws conclusions based on the speed and direction of blood flow and analyzes the completeness of blood circulation in the tissues of the organs being examined. Ultrasound equipment for conducting one or another type of ultrasound is adjusted to the desired mode.
Contraindications to vascular MRI
- The presence of implanted devices and devices of a medical nature - pacemakers, metal joint prostheses, hemostatic clips, vasodilating stents, Ilizarov devices, inner ear implants, metal pins, staples, plates.
- Metal teeth, crowns, braces, metal-containing orthodontic devices.
- Pregnancy - first trimester. On later lines, angiography with contrast is not done, since the effect of the drugs used on the fetus and embryo has not been sufficiently studied. Since gadolinium is not absorbed into breast milk, contrast-enhanced MR angiography is completely safe during breastfeeding.
- Contrast examination is contraindicated in cases of severe damage to the kidneys and liver, for which the additional burden that occurs during drug excretion is undesirable.
- The presence of metal fragments in the body.
- Tattoos made with pigment containing metal.
- Permanent piercing.
Relative contraindications are:
- the patient’s inability to remain motionless for a long time;
- severe psychological illnesses accompanied by excitability;
- claustrophobia - fear of closed spaces;
- early childhood.
Most patients with relative contraindications can be examined under light general anesthesia.
USDG
Ultrasound Dopplerography (Doppler ultrasound) of the veins and arteries of the lower extremities is a vascular research technology that gives quick and accurate results. Detects problems with the vascular system without x-rays or injections, so it has no contraindications.
Doppler ultrasound is based on the Doppler effect and the repulsion of ultrasound waves from blood cells in motion. The test is used to measure the volume of blood flowing through arteries and veins, assessing the speed of blood movement, and helps detect blood flow abnormalities in arteries and blood vessels.
Unlike ultrasound machines, which produce waves at equal intervals of time and receive the signal back, Doppler produces waves at one speed and receives them at another.
The difference between the fluctuations helps to analyze the movement of blood through the vessels, including its speed.
Doppler sonography is a safe and painless procedure that does not require complex preparation. The effectiveness of the study depends on the professionalism of the doctor and the quality of the device, therefore, ultrasound examination of the lower extremities should be performed in certified medical centers. When you contact EVERMEDIC, you can be sure that the test results will be accurate.
Preparation for the procedure
When preparing for angiography without contrast, no special measures are required. Before the procedure, you need to remove jewelry, glasses, and metal-containing removable dentures. Angiography is performed in clothing that does not have metal elements.
Five to seven days before a study using a contrast agent, alcohol should be avoided. MRI diagnostics with the administration of drugs is done strictly on an empty stomach, so as not to provoke nausea and vomiting. Before this, an allergy test for the administered drug is indicated.
Ultrasound of cardiac vessels
Using Doppler sonography, congenital and acquired pathologies of the heart and its vessels are detected. With ultrasound, information is obtained about the speed of blood flow, the condition of medium- and large-caliber vessels, and the myocardium. Detected pathologies:
- heart failure;
- myocarditis;
- expansion of the heart chambers;
- increase in myocardial volume;
- valve stenosis;
- pericarditis;
- signs of arterial hypertension;
- aneurysms;
- septal defects.
Cardiac ultrasound with Doppler sonography is prescribed for people with complaints of heart pain (constant, periodic), dizziness, rapid heartbeat, and shortness of breath. Doppler ultrasound is also indicated for people with changes in the ECG and heart murmurs.
Important!
The study can be carried out for preventive purposes to prevent strokes and heart attacks.
Carrying out the procedure
When conducting an examination without contrast, the patient lies down on a table, which will subsequently slide inside the tomograph. Since the device is quite noisy, the patient’s ears are protected with headphones or earplugs.
During the procedure, the duration of which depends on the examination area, the technician will take pictures and transmit data to the screen. After treatment with a special program, the doctor will see the state of the blood flow on the monitor.
MR angiography can be:
- general, in which the doctor receives information about the patient’s entire circulatory system. It is prescribed, if necessary, to check the entire body, for example, those suffering from diabetic angiopathy;
- selective - used when you need to examine blood flow in a specific area, such as the abdominal cavity or extremities. The vascular network of one basin, forming a common “branch,” is also being studied. For example, to assess the blood supply to the brain, MR angiography is performed in the carotid and vertebrobasilar areas formed by the carotid and vertebral arteries. For varicose veins, the basin of the great saphenous vein is examined;
- superselective, in which a specific vessel is tested. Diagnostics is prescribed if stenosis, wall damage or the presence of a blood clot is suspected.
During an examination with contrast, a special substance containing gadolinium salts is injected in a stream or drop. The rest of the technique is no different from MR angiography without contrast, but the resulting image will be brighter.
How are the results assessed?
The interpretation of the results of ultrasound examination of the veins is given in the table below:
| Parameter | Explanation |
| Arterial wall thickness | The standard value is 0.9 mm. Deviation within 0.2 mm is permissible in the direction of increase and decrease |
| Diameter of the spinal arteries | Normally exceeds 2 cm (over the entire length) |
| Speed of blood flow through the veins of the spine | Standard indicator – 0.3 m/s |
| Vein lumen | A healthy person has free |
| Pathological venous branches | Normally absent |
| Turbulence | Present only in the area where veins branch |
| Signs of vascular compression (compression effect) | In the absence of pathologies there are no |
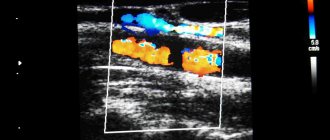
The basic method of recording the results of Doppler studies of blood vessels is a Dopplerogram. It is a picture of frequency shifts, which consists of an envelope curve and a spectrogram. These components are assessed comprehensively or separately.
How does the patient feel?
MR angiography performed without contrast is not accompanied by pain or discomfort. When using the substance, the patient may feel hot flashes, dizziness, lightheadedness, nausea, and the urge to vomit. However, in most cases, the discomfort quickly disappears.
If the person being examined becomes ill, he can press a special button, which is given to his hands, and the specialist will stop the examination. After a gadolinium procedure, you need to drink more fluids to remove the substance from the body.
How is the study of veins and arteries performed?
The procedure is practically no different from ultrasound:
- The patient frees the examination area (legs) from clothing. There is no need to remove glasses, contact lenses, dentures or hearing aids.
- Before the procedure, you will be asked to lie on an examination table or couch.
- The doctor applies a special gel to a portable device called a transducer that sends high-frequency sound waves into the arteries or veins being examined.
- The doctor moves the sensor over the patient's skin, examining different areas.
- Information is displayed on a computer monitor when the sensor is pressed against the skin and moved along the legs. The sensor sends sound waves through the dermis and other body tissues into the blood vessels. Sound waves are reflected from the vessels and send information to a computer for processing and recording. The computer creates diagrams that show the flow of blood through arteries and veins.
When examining arteries and veins, the specialist will pay attention to problem areas. First of all, areas with inflammation, pain, and hyperthermia are examined.
The procedure lasts about an hour. After an ultrasound scan of the veins and arteries of the lower extremities, the patient can return to normal activities.
What does vascular MRI show?
The patient receives diagnostic results on the day of treatment in the form of a series of images and recordings on magnetic media. Based on their data, a medical description is compiled. MR angiography shows the location and structure of the circulatory network, and also identifies pathologies.
- Aneurysms are sac-like protrusions that can rupture, causing hemorrhages and bleeding. Such lesions located in the brain are especially dangerous. Rupture of large aneurysms can be fatal.
- Pathological anastomosis - areas of connection between arteries and veins, in which part of the arterial blood is directly discharged into the vein, without reaching the organs and tissues. Such pathologies cause circulatory disorders - ischemia - and overload the veins. Pathological anastomoses in the brain are especially dangerous, leading to memory impairment, headaches, tinnitus, increased intracranial pressure and blindness.
- Stenosis (narrowing) caused by congenital anomalies, atherosclerosis, blood clots. Reducing the lumen impairs blood circulation in the organs. Stenoses lead to heart attacks, strokes, trophic ulcers and gangrene.
- Thrombosis – complete or partial blocking of the lumen by a thrombus (blood clot). Blood clots interfere with blood supply and can break off, leading to pulmonary embolism. This complication often ends in death.
- Atherosclerotic changes - vessels affected by atherosclerosis lose their elasticity, and plaques are deposited on their walls, obstructing blood flow. This leads to deterioration of blood supply, heart attacks and strokes.
- Occlusion - blockage. Patients experience acute tissue ischemia, leading to tissue death, paralysis, and disruption of the functioning of internal organs and the brain. When the ocular network is occluded, blindness develops.
- Dissection - with this pathology, blood flows between the layers of tissue of the vascular wall. Gradually the process worsens and ends with rupture and bleeding. Dissection of the aorta or other large arteries is very dangerous.
- Malformations are vascular tangles that interfere with normal blood circulation and compress neighboring tissues.
- The growth of tumors into the blood supply network, characteristic of cancer, causes bleeding of varying intensity. Vascular benign tumors are detected, which can compress tissue and disrupt the functioning of organs.
- Varicose veins occur due to insufficiency of the venous valves, leading to impaired blood flow. The lower extremities are most often affected, but other parts, such as the external genitalia and esophagus, are also affected.
If vascular pathologies are detected, you should consult a doctor with the diagnostic results. Depending on the location and characteristics of the identified problem, conservative or surgical treatment is prescribed.
Often, doctors refer the patient for a repeat tomography during the course of treatment. There is no need to worry about this - the examination is safe, harmless, is not accompanied by radiation, and therefore can be carried out any number of times.
Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck
Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck Synonyms for the name of the technique:
- duplex scanning
- triplex scanning
- ultrasound examination with color mapping of blood flow
- Doppler ultrasound
Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck includes 2 separate techniques:
- First of all, the patency of the vessels of the neck (brachiocephalic arteries, main arteries of the head in the neck) is assessed, since pathological changes that can lead to a stroke are most often detected in them.
- If indicated, the doctor may additionally prescribe a study of the cerebral vessels (intracranial arteries) - transcranial duplex (triplex) scanning. In 10-20% of people, especially the elderly, the study cannot be performed due to poor permeability of the skull bones for ultrasound, therefore, this study is performed first, and then payment is made.
Indications
- Prevention of stroke in people with risk factors (smoking, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, arterial hypertension, age over 40 years)
- Suspected stroke: weakness and numbness in an arm or leg
- "facial distortion"
- speech disorder
- Lost vision in one eye
- dizziness or unsteadiness when walking
What is being studied?
- In the neck are the carotid, vertebral and subclavian arteries.
- In the head - middle, anterior and posterior cerebral arteries, basilar artery, vertebral arteries (intracranial segment).
What is visible?
- Thickening of the vascular wall
- Atherosclerotic plaques
- Blood clots
- Dissection (separation) of the wall
- Tortuosity
- Aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations
Accurate assessment of the degree of carotid artery stenosis to determine indications for surgery. There are several ways to measure the degree of stenosis. Only one of them is the reference for determining indications for surgery. In our laboratory, the assessment of the degree of stenosis is performed in accordance with domestic and international recommendations. If there are indications for surgery, a consultation with a vascular surgeon is provided on the same day.
Preparation No special training is required.
Cost Duplex (triplex) scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries (main arteries of the head) - 3,000 rubles. Transcranial duplex (triplex) scanning - RUB 3,000.